Difference between revisions of "Digital Storage Systems Interconnect"
(New section "Family of DSSI Products") |
m (→DSSI Disk Drives: RF31F and RF31T added) |
||
| Line 37: | Line 37: | ||
* [[RF30]] | * [[RF30]] | ||
* [[RF31]] | * [[RF31]] | ||
| + | * [[RF31F]] | ||
| + | * [[RF31T]] | ||
* [[RF32]] | * [[RF32]] | ||
* [[RF35]] | * [[RF35]] | ||
Revision as of 08:44, 18 August 2023
The Digital Storage Systems Interconnect (usually given as DSSI) is a mass storage bus from DEC. It can also be used to create loosely-coupled multi-processors by sharing a number of disk drives between two systems. Such shared drives are termed 'Integrated Storage Elements' (ISEs).
DSSI made it possible to build VAXclusters from MicroVAX and smaller VAX computers by adding CI-bus functionality to smaller VAX systems.
Description from the 'Digital's Storage System Interconnect' protocol specification document:
"The DSSI, supporting the needs of low-end and mid-range systems, is one in a family of high-performance computer-to-computer interconnects (CI's) that combine a common host interface and port layer with an implementation-specific datalink and physical interconnect.
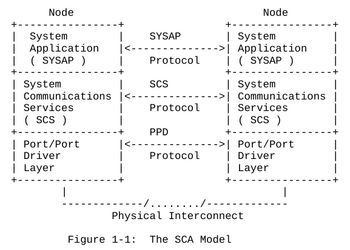
CI-class interconnects provide the transmission services required by Digital's Systems Communication Architecture (SCA) - a four-tiered set of protocols and interfaces as shown [to the right]."
Contents
Family of DSSI Products
DSSI Controllers/Interfaces
- KFQSA QBUS DSSI Adapter
- KFMSA XMI Dual DSSI Adapter
- KFMSB XMI DSSI adapter
- KFESA EISA DSSI Adapter
- KFESB EISA DSSI Adapter
- KFPSA PCI DSSI Adapter
- KFE52 VAXft Multi-Function Interface
- KDXDA VAXft 810 DSSI Interface
- EDA640 MicroVAX 3300/3400 KA640 embedded DSSI Adapter (EDA)
- KFA40 DEC 4000 I/O Module
DSSI Hierarchical Storage Controllers (HSDs)
DSSI Disk Drives
DSSI Tape Drives
External Links
- DSSI - DSSI and related documents at Bitsavers
- Digital's Storage System Interconnect - protocol specification document
- MicroVAX Dual-Host Systems (EK-338AC-DH-003) - contains a clear description of how a DSSI can be used to create a loosely-couple multi-processor