Difference between revisions of "StorageWorks"
(→StorageWorks Building Blocks: "SBB Label" added) |
m (→SBB Identification Label: Numbering corrected) |
||
| Line 41: | Line 41: | ||
The following describes the SBB identification label nouns and symbols: | The following describes the SBB identification label nouns and symbols: | ||
| − | + | 1. '''Order Number''' is the type of SBB. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | 2. '''Capacity''' is the total amount of data the device stores. | ||
| + | |||
| + | 3. '''SCSI Logical Unit Number''' is assigned by the user. | ||
| + | |||
| + | 4. '''SCSI ID''' is assigned by the user. | ||
| + | |||
| + | 5. '''Controller Channel Number''' is assigned by the user. | ||
| + | |||
| + | 6. '''Device Bus Width''' is either narrow (N) or wide (W): | ||
:: '''N''' is a 8-bit device | :: '''N''' is a 8-bit device | ||
:: '''W''' is a 16-bit device | :: '''W''' is a 16-bit device | ||
| − | |||
| + | 7. '''Device Bus Compatibility''' is the type of shelf in which the device functions. | ||
:: '''N''' - the device is 8-bit shelf compatible. | :: '''N''' - the device is 8-bit shelf compatible. | ||
:: '''W''' - the device is 16-bit shelf compatible. | :: '''W''' - the device is 16-bit shelf compatible. | ||
:: '''N/W''' - the device is compatible with either shelf. | :: '''N/W''' - the device is compatible with either shelf. | ||
| − | |||
| + | 8. '''Bus Bit Rate in Mbits''' is the speed of the bus: | ||
:: '''S''' - Slow device (5 Mb/s) | :: '''S''' - Slow device (5 Mb/s) | ||
:: '''F''' - Fast device (10 Mb/s) | :: '''F''' - Fast device (10 Mb/s) | ||
:: '''10''' is Mbits per second. | :: '''10''' is Mbits per second. | ||
| − | + | ||
| + | 9. '''Transfer Rate in MB''' is the data transfer rate in MBytes per second. | ||
=== Third-party Storage Devices Compatibility === | === Third-party Storage Devices Compatibility === | ||
Latest revision as of 17:51, 22 August 2023
StorageWorks is a modular SCSI storage system manufactured and sold by DEC in the 1990s.
Contents
StorageWorks Building Blocks
The smallest configurable active unit is called StorageWorks Building Block or short SBB.
A system building block is primarily a device carrier that contains a storage device. There are also SBBs that contain storage accessories i.e. controllers, power supplies, battery backup units, etc.
An SBB carrier is the plastic case without a device installed.
SBBs come in several standardized sizes:
- 3.5" SBB (occupies 1 slot)
- 5.25" SBB (occupies 3 slots)
- Large controller SBB (two of which one above the other; occupies 6 slots)
Empty slots must be covered by a blank bezel to ensure proper cooling of installed SBBs.
3.5" SBBs typically contain disks or small tape drives (e.g. DAT), whereas the 5.25" SBBs are used for bigger devices, e.g. CDROM or tape drives.
Some common BBS devices:
- RZ25-VA 426 MB disk drive 3.5" SBB
- RZ26-VA 1.05 GB disk drive 3.5" SBB
- RZ28-VA 2.1 GB disk drive 3.5" SBB
- RRD42-VB 600 MB CDROM drive 5.25" SBB
- TLZ06-VA 4 GB DAT tape drive 3.5" SBB
- TZ86-VA 6 GB DLT tape drive 5.25" SBB
- TZ87-VA 20 GB DLT tape drive 5.25" SBB
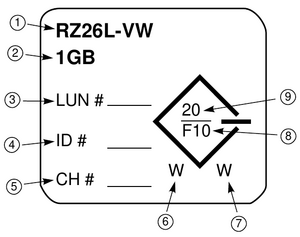
SBB Identification Label
The SBB identification label shows the SBB device, the shelf bus type (8- or 16-bit), and user specific information.
The following describes the SBB identification label nouns and symbols:
1. Order Number is the type of SBB.
2. Capacity is the total amount of data the device stores.
3. SCSI Logical Unit Number is assigned by the user.
4. SCSI ID is assigned by the user.
5. Controller Channel Number is assigned by the user.
6. Device Bus Width is either narrow (N) or wide (W):
- N is a 8-bit device
- W is a 16-bit device
7. Device Bus Compatibility is the type of shelf in which the device functions.
- N - the device is 8-bit shelf compatible.
- W - the device is 16-bit shelf compatible.
- N/W - the device is compatible with either shelf.
8. Bus Bit Rate in Mbits is the speed of the bus:
- S - Slow device (5 Mb/s)
- F - Fast device (10 Mb/s)
- 10 is Mbits per second.
9. Transfer Rate in MB is the data transfer rate in MBytes per second.
Third-party Storage Devices Compatibility
A lot of third-party storage devices work in DEC SBBs and together with DEC computer systems; example: IBM DPES-31080 1080 MB SCSI-2 disk drives.
StorageWorks Shelves
Building Blocks are mounted in StorageWorks Shelves.
A StorageWorks Shelf is made of:
- plastic housing
- backplane
and optional:
- two blowers (mounted at the back)
- mounting material
BA350
The first StorageWorks Shelf introduced was the BA350 for SCSI-1 and Narrow SCSI-2 devices.
A BA350 has got 8 slots for SBBs.
- Slots 1-5 are available for storage / controller SBBs.
- Slot 6 can be used for either a storage SBB or an optional redundant power supply SBB.
- Slot 7 is always used for the primary power supply SBB.
The BA350 can be configured for one single or two separate SCSI buses.
There are three sub-types of the BA350 shelf:
- BA350-SB SBB shelf, in which 3.5" and 5.25" form factor storage devices, controllers, and adapters are installed
- BA350-MA Controller Shelf, in which controllers and the associated cache memory is installed
- BA350-EA The Special Purpose Controller and SBB Shelf, in which controllers, the associated cache memory, and 3.5" and 5.25" form factor storage devices, controllers, and adapters are installed
StorageWorks Enclosures
StorageWorks shelves fit into any enclosure that can accommodate a 445 millimeter (17.5 inch) device in either the horizontal or vertical position. The mounting bracket kits permit installing a shelf in either a data center cabinet with a metric mounting hole pattern or an HSC controller cabinet with a Radio-Electronics-Television Manufacturer’s Association (RETMA) mounting hole pattern.
StorageWorks enclosures (SW500-series and SW800-series cabinets, and BA350-Kx deskside expansion units) are used for mounting shelves. Desktop expansion units (BA353-Ax) are used for mounting SBBs.
Each enclosure has a switch-controlled ac or dc power distribution unit.
External links
- StorageWorks Family User's Guide (EK-BA350-UG.C01)
- BA350-SA Modular Storage Shelf User's Guide (EK-350SA-UG-001)
- StorageWorks Solutions Configuration Guide (EK-BA350-CG.E01)