Difference between revisions of "Digital Storage Systems Interconnect"
(→DSSI Cabling: Add description of cabling) |
(Section "DSSI Storage Expanders" added) |
||
| Line 71: | Line 71: | ||
* [[HSD30]] | * [[HSD30]] | ||
* [[HSD50]] | * [[HSD50]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | == DSSI Storage Expanders == | ||
| + | |||
| + | * [[B213F]] | ||
| + | * [[B400X]] | ||
| + | * [[BA42A]] | ||
| + | * [[R215F]] | ||
| + | * [[R23RF]] | ||
| + | * [[R400X]] | ||
| + | * [[SF12]] | ||
| + | * [[SW301]] | ||
== DSSI Disk Drives == | == DSSI Disk Drives == | ||
Revision as of 12:33, 6 September 2023
The Digital Storage Systems Interconnect (usually given as DSSI) is a mass storage bus from DEC. The DSSI specification lists the main attributes of DSSI as: 8-bit wide parallel; multi-drop linear bus electrical topology; low-cost, single-ended signalling interface circuitry; DC coupling.
It is an alternate physical layer in the Computer Interconnect system; the CI system had a 'native' physical layer before the creation of DSSI. The relationship between the DSSI and the CI's physical layer is shown in the following diagram:
<-----+
+---------------------+ |
| Port Driver | |
| Layer | |
| ( SCA Specification)| |
+---------------------+ |
| |
| |
....................... |
. CI Port Adapter . |
. ( eg: VAX CI Port ) . |
....................... |
| | P
+------> | | P
| +---------------------+ | D
| | CI Port | |
C | | Layer | | L
I | | ( DEC Std 161 ) | | A
| +---------------------+ | Y
A | | | | E
R | +------+ +------+ | R
C | | | |
H | +----------------------+ +---------------------+ |
I | | DSSI Datalink | | CI Datalink | |
T | | Layer | .... | Layer | |
E | | ( DSSI Spec. ) | | ( Dec Std 161 ) | |
C | +----------------------+ +---------------------+ |
T | | | <-----+
U | | | <-----+ P L
R | +----------------------+ +---------------------+ | H A
E | | DSSI Physical | | CI Physical | | Y Y
| | Interconnect | | Interconnect | | S E
| | ( DSSI Spec. ) | | ( DEC Std 161 ) | | I R
| +----------------------+ +---------------------+ | C
+------> <-----+ A
L
Figure 1-2: CI PPD Architectural Layers
DSSI thus made it possible to build VAXclusters from MicroVAX and smaller VAX computers, by adding CI-bus functionality to smaller VAX systems. It can also be used to create loosely-coupled multi-processors, by sharing a number of disk drives between two systems. Such shared drives are termed 'Integrated Storage Elements' (ISEs).
A description of the DSSI from the 'Digital's Storage System Interconnect' protocol specification document:
"The DSSI, supporting the needs of low-end and mid-range systems, is one in a family of high-performance computer-to-computer interconnects .. that combine a common host interface and port layer with an implementation-specific datalink and physical interconnect. CI-class interconnects provide the transmission services required by Digital's System Communication Architecture (SCA) - a four-tiered set of protocols and interfaces.."
Contents
DSSI Controllers/Interfaces
- KFQSA QBUS DSSI Adapter
- KFMSA XMI Dual DSSI Adapter
- KFMSB XMI DSSI adapter
- KFESA EISA DSSI Adapter
- KFESB EISA DSSI Adapter
- KFPSA PCI DSSI Adapter
- KFE52 VAXft Multi-Function Interface
- KDXDA VAXft 810 DSSI Interface
- EDA640 MicroVAX 3300/3400 KA640 embedded DSSI Adapter (EDA)
- KFA40 DEC 4000 I/O Module
DSSI Hierarchical Storage Controllers (HSDs)
Hierarchical Storage Controllers:
DSSI Storage Expanders
DSSI Disk Drives
DSSI Tape Drives
DSSI Cabling
The "RF Series Integrated Storage Element User Guide" (EK-RF72D-UG-008) says "The DSSI bus is a 50-conductor cable. Inside an enclosure, the bus may be a flat ribbon cable or a round bundle of twisted pairs. Between enclosures, the bus is a shielded round cable approximately ½-inch in diameter."
The short cables run from the PCBs that implement the interfaces to a standard connector on the back of the enclosure. (Different enclosures use different short cables with a given board; see the "KFQSA Module Installation and User Manual", Section 2.1 for a partial list.)
Connectors
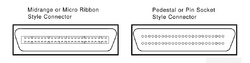
There are (at least) four types of DSSI connectors:
Two DSSI cable connectors:
- MR (midrange or micro ribbon) connector = "50 Way High Density Micro Ribbon"
- PS (pedestal style or pin socket) connector = "50 Way High Density Honda"
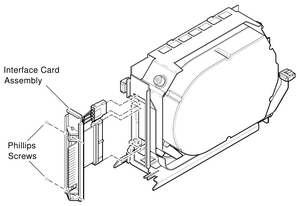
Two DSSI device connectors:
- Single DSSI Device Connector 50-pin (SCSI-like)
- Dual 3.5" / Single 5.25" DSSI Disk Interface Card Assembly e.g. for VAX 4000, BA430/BA440
- BA430 BA440 Enclosure Maintenance.pdf (EK-348AB-MG-002)
- DSSI VMScluster Installation and Troubleshooting Guide (EK-410AB-MG.D01)
External Links
- DSSI - DSSI and related documents at Bitsavers
- Digital's Storage System Interconnect - protocol specification document
- MicroVAX Dual-Host Systems (EK-338AC-DH-003) - contains a clear description of how a DSSI can be used to create a loosely-couple multi-processor
- RF Series Integrated Storage Element User Guide (EK-RF72D-UG-008)