Difference between revisions of "Turing machine"
Jonathanjo (talk | contribs) (From wanted pages) |
(No difference)
|
Revision as of 12:45, 7 April 2024
A Turing Machine is a kind of abstract computer, devised by mathematician Alan Turing in 1936, to develop theories of computability -- that which can, and which cannot, be computed.
The classic introduction to this kind of machine is MIT professor Marvin Minksy's Computation: Finite and Infinite Machines (Prentice-Hall 1967):
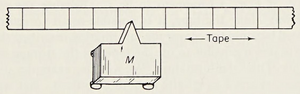
A Turing machine is a finite-state machine associated with an external storage or memory medium. This medium has the form of a sequence of squares, marked of on a linear tape. The machine is couple to the tape through a head, which is situated, at each moment, on some square of the tape (see fig). The head has three functions, all of which are exercised in each operation cycle of the finite-state machine. The functions are: reading the square of the tape beeing "scanned," writing on the scanned square, and moving the machine to an adjacent square (which becomes the scanned square in the next operation cycle).
The basic operation is that each square can have a single symbol from a finite set of symbols; each step possibly changes the symbol and moves the tape to the left or the right.
They are comprehensively covered in computing literature, with endless variations, including a large number of physical implementations.
A number of very important theoretical results came from study of these machines:
- A Turing machine is adequate to simulate any other kind of automata, ignoring specified size and speed constraints.
- A machine which can simulate a Turing machine can therefore simulate any machine and is said to be Turing complete.