Difference between revisions of "Ethernet transceiver"
m (→H4000 with Removable Tap: Fixed typo) |
m (→H4000 Ethernet Transceiver (Thickwire)) |
||
| Line 35: | Line 35: | ||
Year of introduction: 1982 | Year of introduction: 1982 | ||
| − | You cannot disabled the '''[ | + | You cannot disabled the '''[http://www.ethermanage.com/ethernet/sqe/sqe.html|Heartbeat]''' feature of the standard H4000 Ethernet Transceiver, there was a special version (H4000-BA) without Heartbeat available in case you need that. |
====H4000 with Inclusive Tap==== | ====H4000 with Inclusive Tap==== | ||
Revision as of 10:44, 10 June 2022
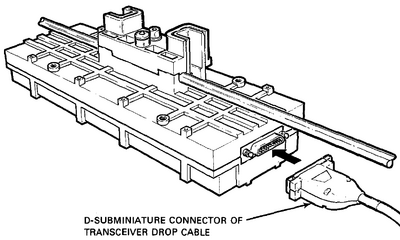
An Ethernet Transceiver connects one of the following Ethernet cable types:
- Thickwire Coaxial
- Thinwire Coaxial
- Twisted Pair
- Fibre Optic (different types)
to an Ethernet interface using a Tranceicver cable.
Most modern standard Ethernet interfaces have got the Transceiver included in the network interface module (resp. interface chip), so that neither separate Tranceiver nor Transceiver cable are needed.
A lot of recent high-speed Ethernet interfaces (1 GB/s and above) and Switches have Transceivers again. They enable to flexibly adapt to different network media, e.g. different types of Fibre Optic cables.
<Picture of a recent Transceiver module>
Contents
- 1 Transceiver Cables
- 2 Ethernet Transceiver Functions
- 3 DEC Ethernet Transceiver Models
Transceiver Cables
Ethernet Transceiver Functions
From "EK-H4000-TM-PRE H4000 Ethernet Transceiver Technical Manual", chapter 1.2.2 "Transceiver Functional Description":
The transceiver performs the following functions:
- Transmit: Responds to the signals input from the transceiver cable and transmits the signals on the coaxial cable.
- Receive: Responds to signals transmitted on the coaxial cable and couples the received signals to the transceiver cable.
- Collision Detect: Monitors the signals transmitted on the coaxial cable and, if a collision occurs, signals appropriately on the transceiver cable.
Additionally, the transceiver does the following:
- Maintains electrical isolation between the coaxial cable and the transceiver cable,
- Maintains low loading/high impedance on the coaxial cable,
- Provides continuous data loopback (i.e., the receiver portion of the transceiver is always active; thus, the message being transmitted is coupled back on the transceiver cable),
- Provides self test of the collision detection circuitry at the end of each transmission,
- Contains protective circuitry which ensures that network integrity will be maintained in the event of a faulty transceiver, controller, or repeater.
DEC Ethernet Transceiver Models
H4000 Ethernet Transceiver (Thickwire)
Year of introduction: 1982
You cannot disabled the [1] feature of the standard H4000 Ethernet Transceiver, there was a special version (H4000-BA) without Heartbeat available in case you need that.
H4000 with Inclusive Tap
The H4000 Ethernet Transceiver with Inclusive Tap was the very first Ethernet Transceiver from DEC.
It has got two drawbacks:
- If the tap gets damaged, the whole unit is inoperable and cannot be repaired.
- It is very inconvenient to mount the unit to a Thickwire segment difficult to access, e.g. located in a ceiling plenum.
H4000 with Removable Tap
The H4000 Ethernet Transceiver with Removable Tap is an improved version of the model with a fixed tap.
You can tap the cable using the removable tapping unit (which is much smaller and lighter than the complete unit) and attach the rest of the unit when the tapping is done.
If the tap gets damaged, you can use a replacement one.
<Picture of an H4000 with Removable Tap>
H4005 Ethernet Transceiver (Thickwire)
Year of introduction: 1988?
<Picture of an H4005>
DESTA Thinwire Ethernet Station Adapter
Year of introduction: 1986
Early DESTA
The early DESTA (REV A) is a H4005 with a modified top assembly carrying a female BNC socket.
You can replace the BNC top assembly with that of an H4005 and thus use the early DESTA with Thickwire Ethernet.
On the other hand you can use the top assembly of an early DESTA to use an H4005 for Thinwire Ethernet.
<Picture of an early DESTA>
Late DESTA
The late DESTA (REV B) is housed in a slightly smaller box and the BNC socket is fixed.
<Picture of a late DESTA>
H3350 Twisted Pair Transceiver
Year of introduction: ?
<Picture of an H3350 Twisted Pair Transceiver>
DECXM Thinwire Transceiver
Year of introduction: ?
<Picture of a DECXM Thinwire Transceiver>
DETPM 10BaseT Transceiver
Year of introduction: ?
<Picture of a DETPM 10BaseT Transceiver>