Difference between revisions of "IBM 5150"
m (Avoid dab page) |
ForOldHack (talk | contribs) (→Added memory capacaties, as well as information on the ROM chips.) |
||
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
The '''IBM 5150''' was [[International Business Machines|IBM]]'s entry into the [[personal computer]] marketplace; the '''IBM PC'''. It was introduced in stores on 1981-08-12. | The '''IBM 5150''' was [[International Business Machines|IBM]]'s entry into the [[personal computer]] marketplace; the '''IBM PC'''. It was introduced in stores on 1981-08-12. | ||
| − | The original configuration had a [[motherboard]] designed for up to 64KB of [[Dynamic RAM|RAM]], and a cassette [[tape drive]], but could be expanded to include a [[Disk#Low-cost disks|diskette drive]], and a [[Disk#Recent developments|hard disk]]. | + | The original configuration had a [[motherboard]] with 16K built in, designed for up to 64KB of [[Dynamic RAM|RAM]], and a cassette [[tape drive]], but could be expanded to include a [[Disk#Low-cost disks|diskette drive]], and a [[Disk#Recent developments|hard disk]]. |
At the beginning they were advertised for around $1,600 for a unit with just 16KB of RAM and a keyboard[http://www.vintage-computer.com/ibm_pc.shtml]. Retail would be around $1,000 though[http://classiccmp.org/pipermail/cctech/2013-July/106735.html], or maybe more likely in the $1,300 - $1,400 range[http://classiccmp.org/pipermail/cctech/2013-July/106743.html]). | At the beginning they were advertised for around $1,600 for a unit with just 16KB of RAM and a keyboard[http://www.vintage-computer.com/ibm_pc.shtml]. Retail would be around $1,000 though[http://classiccmp.org/pipermail/cctech/2013-July/106735.html], or maybe more likely in the $1,300 - $1,400 range[http://classiccmp.org/pipermail/cctech/2013-July/106743.html]). | ||
| − | In practice you would add a at least a video adapter, probably some RAM, and a floppy disk drive. Then the price would be quite different. Back then, both types of disk drives were of the 5 1/4" full height form factor. | + | In practice you would add a at least a video adapter, probably some RAM, and a floppy disk drive. Then the price would be quite different. Back then, both types of disk drives were of the 5 1/4" full height form factor, single sided or double sided. |
IBM made the PC an open standard, publishing not only schematics, but also including a [[BIOS]] [[listing]] in the technical reference. When people wished to build clones of the IBM PC, IBM would license them for a 5% royalty fee, which not only made the PC a popular platform to clone, but also with the available schematics, allowed for everyone to be pin compatible with the ISA slots, creating a thriving hardware expansion business. | IBM made the PC an open standard, publishing not only schematics, but also including a [[BIOS]] [[listing]] in the technical reference. When people wished to build clones of the IBM PC, IBM would license them for a 5% royalty fee, which not only made the PC a popular platform to clone, but also with the available schematics, allowed for everyone to be pin compatible with the ISA slots, creating a thriving hardware expansion business. | ||
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
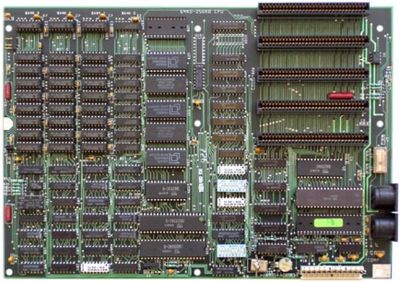
[[Image:IBM 5150 motherboard.jpg|thumb|left|400px|IBM PC Motherboard]] | [[Image:IBM 5150 motherboard.jpg|thumb|left|400px|IBM PC Motherboard]] | ||
| − | The IBM PC included [[Microsoft BASIC]] in [[ROM]], which allowed the PC to function like many of the computers of the time with a simple ROM BASIC. With the addition of a disk drive, OS options included [[CP/M]] and [[MS-DOS]] at the time of sale. | + | The IBM PC included [[Microsoft BASIC]] in [[ROM]], called Cassette Basic, which allowed the PC to function like many of the computers of the time with a simple ROM BASIC. With the addition of a disk drive, OS options included [[CP/M-86]] and [[MS-DOS 1.0, and later MS-DOS 1.1]] at the time of sale. DOS included a simple version of BASIC, known as disk BASIC, and a graphics version known as Advanced BASIC (BASICA.COM) |
The IBM PC, also established the 8 bit expansion slot, or [[Industry Standard Architecture|ISA]] bus standard as it was later called. | The IBM PC, also established the 8 bit expansion slot, or [[Industry Standard Architecture|ISA]] bus standard as it was later called. | ||
| − | The PC started the [[IBM PC]] line; it was replaced by the wildly popular [[IBM XT]]. | + | The PC started the [[IBM PC]] line; it was replaced by the wildly popular [[IBM XT]], adding 3 more slots, and support for more memory on the motherboard ( 64k, expandable to 256k ). |
| + | |||
| + | The picture shows 5 ROMS, one was the ROM BIOS, and the other 4 were cassette BASIC. | ||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
Revision as of 05:50, 14 March 2019
| IBM 5150/IBM PC | |
 The IBM PC | |
| Manufacturer: | International Business Machines |
|---|---|
| Year Introduced: | 1981 |
| Word Size: | 16 bit |
The IBM 5150 was IBM's entry into the personal computer marketplace; the IBM PC. It was introduced in stores on 1981-08-12.
The original configuration had a motherboard with 16K built in, designed for up to 64KB of RAM, and a cassette tape drive, but could be expanded to include a diskette drive, and a hard disk.
At the beginning they were advertised for around $1,600 for a unit with just 16KB of RAM and a keyboard[1]. Retail would be around $1,000 though[2], or maybe more likely in the $1,300 - $1,400 range[3]).
In practice you would add a at least a video adapter, probably some RAM, and a floppy disk drive. Then the price would be quite different. Back then, both types of disk drives were of the 5 1/4" full height form factor, single sided or double sided.
IBM made the PC an open standard, publishing not only schematics, but also including a BIOS listing in the technical reference. When people wished to build clones of the IBM PC, IBM would license them for a 5% royalty fee, which not only made the PC a popular platform to clone, but also with the available schematics, allowed for everyone to be pin compatible with the ISA slots, creating a thriving hardware expansion business.
The IBM PC included Microsoft BASIC in ROM, called Cassette Basic, which allowed the PC to function like many of the computers of the time with a simple ROM BASIC. With the addition of a disk drive, OS options included CP/M-86 and MS-DOS 1.0, and later MS-DOS 1.1 at the time of sale. DOS included a simple version of BASIC, known as disk BASIC, and a graphics version known as Advanced BASIC (BASICA.COM)
The IBM PC, also established the 8 bit expansion slot, or ISA bus standard as it was later called.
The PC started the IBM PC line; it was replaced by the wildly popular IBM XT, adding 3 more slots, and support for more memory on the motherboard ( 64k, expandable to 256k ).
The picture shows 5 ROMS, one was the ROM BIOS, and the other 4 were cassette BASIC.