Difference between revisions of "BM792 ROM"
m (→Reference: +cat) |
m (+img, links, ext links) |
||
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
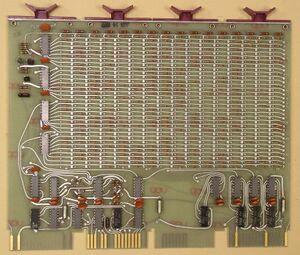
| − | + | [[Image:BM792-YA.jpg|300px|thumb|right|M792-YA card]] | |
| − | + | The '''BM792 ROM''' card was the first [[UNIBUS]] [[Read-only memory|ROM]] card for the [[PDP-11]] series of computers; it contained only 32 [[word]]s of memory. It was a [[DEC card form factor|quad]] format card, and used an [[Small Peripheral Controller|SPC]] slot. Most versions were used for [[bootstrap]]ping the machine, from [[disk]], [[paper tape|paper]] and [[magnetic tape]], etc, but it could be used for any purpose | |
| − | The board came in two main variants: the | + | It used individual [[diode]]s in an array to represent individual [[bit]]s; if the diode was present, the bit contained a '1'; if the diode was not present, a '0'. [[Jumper]]s allowed the board to occupy any 32-word block from 0773000 to 0773700, so longer programs could be accomodated with multiple cards. |
| + | |||
| + | The board came in two main variants: the M792 came fully populated with diodes, and the user removed diodes (either by de-soldering them, or clipping their leads) to produce the desired [[program]]; other variants, designated M792-Yx (where 'x' is a capital letter, starting with 'A') came pre-programmed from DEC to perform various functions. | ||
==Variants== | ==Variants== | ||
| − | * BM792-YA - Serial line, high-speed paper tape reader | + | * BM792-YA - [[Asynchronous serial line|Serial line]] ([[KL11 asynchronous serial line interface|KL11]]/[[DL11 asynchronous serial line interface|DL11]]), high-speed [[paper tape]] reader ([[PC11 High-Speed Paper-Tape Reader/Punch Control|PC11]]) |
| − | * BM792-YB - [[TC11]] [[DECtape]] and disks ([[RC11]], [[RF11]], [[RK11]], [[RP11]]) | + | * BM792-YB - [[TC11 DECtape controller|TC11]] [[DECtape]] and disks ([[RC11 disk controller|RC11]], [[RF11 disk controller|RF11]], [[RK11 disk controller|RK11]], [[RP11 disk controller|RP11]]) |
| − | * BM792-YC - Card reader | + | * BM792-YC - [[CR11 Card Readers|CR11]] [[punched card]] reader |
| − | * MR11-DB - A two board set, consisting of the BM792-YD and -YE, it supported the same devices as the -YB, with the addition of the [[TM11]] magnetic tape | + | * MR11-DB - A two board set, consisting of the BM792-YD and -YE, it supported the same devices as the -YB, with the addition of the [[TM11 magtape controller|TM11]] [[magnetic tape]] |
* BM792-YF - DECtape and RF11 and RK11 disks | * BM792-YF - DECtape and RF11 and RK11 disks | ||
| − | * BM792-YH - [[TA11]] casette magnetic tape | + | * BM792-YH - [[TA11 Magnetic Tape Cassette controller|TA11]] casette magnetic tape |
| + | * BM792-YJ - Special TM11 loader | ||
| + | * BM792-YK - Special version for the [[VT20]], using its second serial line | ||
| + | * BM792-YL - [[RX11 floppy disk controller|RX11]] [[floppy disk]] controller | ||
| + | |||
| + | Note that there are two variants of the -YA (see the link below). | ||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
| Line 18: | Line 25: | ||
* [[UNIBUS boot ROMs]] | * [[UNIBUS boot ROMs]] | ||
| − | == | + | ==External links== |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | * [http://www.bitsavers.org/pdf/dec/unibus/DEC-11-HBMAA-E-D_BM792_Read-only-memory_and_MR11-DB_Bootstrap_Loader_Jan75.pdf BM792 read-only-memory and MR11-DB bootstrap loader] (DEC-11-HBMAA-E-D) | |
| + | * [http://www.bitsavers.org/pdf/dec/unibus/MR11-DB_64_Word_Bootstrap_M792_May72.pdf MR11-DB bulk storage bootstrap loader engineering drawings] | ||
| + | * [http://ana-3.lcs.mit.edu/~jnc/tech/pdp11/ROMs/M792-YA.mac Dis-assembled and commented dump of M792-YA boot ROMs] | ||
| + | * [http://ana-3.lcs.mit.edu/~jnc/tech/pdp11/ROMs/M792-YK.mac Dis-assembled and commented dump of M792-YK boot ROMs] | ||
[[Category: UNIBUS ROMs]] | [[Category: UNIBUS ROMs]] | ||
Latest revision as of 18:05, 4 December 2021
The BM792 ROM card was the first UNIBUS ROM card for the PDP-11 series of computers; it contained only 32 words of memory. It was a quad format card, and used an SPC slot. Most versions were used for bootstrapping the machine, from disk, paper and magnetic tape, etc, but it could be used for any purpose
It used individual diodes in an array to represent individual bits; if the diode was present, the bit contained a '1'; if the diode was not present, a '0'. Jumpers allowed the board to occupy any 32-word block from 0773000 to 0773700, so longer programs could be accomodated with multiple cards.
The board came in two main variants: the M792 came fully populated with diodes, and the user removed diodes (either by de-soldering them, or clipping their leads) to produce the desired program; other variants, designated M792-Yx (where 'x' is a capital letter, starting with 'A') came pre-programmed from DEC to perform various functions.
Variants
- BM792-YA - Serial line (KL11/DL11), high-speed paper tape reader (PC11)
- BM792-YB - TC11 DECtape and disks (RC11, RF11, RK11, RP11)
- BM792-YC - CR11 punched card reader
- MR11-DB - A two board set, consisting of the BM792-YD and -YE, it supported the same devices as the -YB, with the addition of the TM11 magnetic tape
- BM792-YF - DECtape and RF11 and RK11 disks
- BM792-YH - TA11 casette magnetic tape
- BM792-YJ - Special TM11 loader
- BM792-YK - Special version for the VT20, using its second serial line
- BM792-YL - RX11 floppy disk controller
Note that there are two variants of the -YA (see the link below).