Difference between revisions of "Qemu"
From Computer History Wiki
m (Proper cat) |
m (Add some links, etc) |
||
| (2 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | Qemu is a machine emulator & system virtualizer. | + | '''Qemu''' is a machine emulator & system virtualizer. |
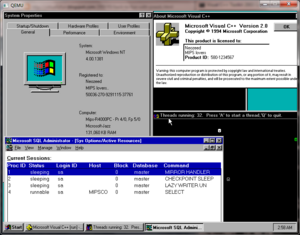
[[Image:Windows nt 4 0 MIPS.png|300px|thumb|right|Windows NT 4.0 MIPS under Qemu]] | [[Image:Windows nt 4 0 MIPS.png|300px|thumb|right|Windows NT 4.0 MIPS under Qemu]] | ||
| − | Qemu can emulate numerious CPUs and machine types. Most are geared towards running Linux, the x86/x64 emulators are the most flexible, and most well used. The | + | Qemu can emulate numerious CPUs and machine types. Most are geared towards running [[Linux]], the x86/x64 emulators are the most flexible, and most well used. The latest version, released in January 2024, is 8.2.1. |
As of 0.15.0 the following machine emulators are available: | As of 0.15.0 the following machine emulators are available: | ||
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
While not active, there is also the following in the tree: | While not active, there is also the following in the tree: | ||
| − | * | + | *[[DEC Alpha]] (really incomplete) |
| − | |||
== Running Qemu == | == Running Qemu == | ||
| Line 340: | Line 339: | ||
*[[Installing NetBSD 6.1.5 Sparc64 on Qemu]] | *[[Installing NetBSD 6.1.5 Sparc64 on Qemu]] | ||
| − | == | + | {{semi-stub}} |
| + | |||
| + | == External links == | ||
* Qemu's main site - http://wiki.qemu.org/Index.html | * Qemu's main site - http://wiki.qemu.org/Index.html | ||
* Win32 builds of Qemu including ready to run images http://www.h7.dion.ne.jp/~qemu-win/ | * Win32 builds of Qemu including ready to run images http://www.h7.dion.ne.jp/~qemu-win/ | ||
* Automated builds of Qemu are available [http://qemu.weilnetz.de/w64/ here for Win64], and [http://qemu.weilnetz.de/w32/ here for Win32]. | * Automated builds of Qemu are available [http://qemu.weilnetz.de/w64/ here for Win64], and [http://qemu.weilnetz.de/w32/ here for Win32]. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
[[Category: Emulators]] | [[Category: Emulators]] | ||
Latest revision as of 10:58, 27 February 2024
Qemu is a machine emulator & system virtualizer.
Qemu can emulate numerious CPUs and machine types. Most are geared towards running Linux, the x86/x64 emulators are the most flexible, and most well used. The latest version, released in January 2024, is 8.2.1.
As of 0.15.0 the following machine emulators are available:
- i386-softmmu IBM PC emulator
- x86_64-softmmu x64 IBM PC emulator
- arm-softmmu
- cris-softmmu
- m68k-softmmu
- microblaze-softmmu
- mips-softmmu
- mips64-softmmu
- mipsel-softmmu
- mips64el-softmmu
- ppc-softmmu
- ppcemb-softmmu
- ppc64-softmmu
- sh4-softmmu
- sh4eb-softmmu
- sparc-softmmu
- sparc64-softmmu
- s390x-softmmu
While not active, there is also the following in the tree:
- DEC Alpha (really incomplete)
Running Qemu
Qemu is driven by command line arguments... The first thing that you typically do is setup a virtual hard disk with qemu-img. Once your disk is ready then you can configure each system emulator with various flags.
qemu-img
qemu-img version 0.14.92, Copyright (c) 2004-2008 Fabrice Bellard
usage: qemu-img command [command options]
QEMU disk image utility
Command syntax:
check [-f fmt] filename
create [-f fmt] [-o options] filename [size]
commit [-f fmt] [-t cache] filename
convert [-c] [-p] [-f fmt] [-t cache] [-O output_fmt] [-o options] [-s snapshot_name] filename [filename2 [...]] output_filename
info [-f fmt] filename
snapshot [-l | -a snapshot | -c snapshot | -d snapshot] filename
rebase [-f fmt] [-t cache] [-p] [-u] -b backing_file [-F backing_fmt] filename
resize filename [+ | -]size
Command parameters:
'filename' is a disk image filename
'fmt' is the disk image format. It is guessed automatically in most cases
'cache' is the cache mode used to write the output disk image, the valid
options are: 'none', 'writeback' (default), 'writethrough' and 'unsafe'
'size' is the disk image size in bytes. Optional suffixes
'k' or 'K' (kilobyte, 1024), 'M' (megabyte, 1024k), 'G' (gigabyte, 1024M)
and T (terabyte, 1024G) are supported. 'b' is ignored.
'output_filename' is the destination disk image filename
'output_fmt' is the destination format
'options' is a comma separated list of format specific options in a
name=value format. Use -o ? for an overview of the options supported by the
used format
'-c' indicates that target image must be compressed (qcow format only)
'-u' enables unsafe rebasing. It is assumed that old and new backing file
match exactly. The image doesn't need a working backing file before
rebasing in this case (useful for renaming the backing file)
'-h' with or without a command shows this help and lists the supported formats
'-p' show progress of command (only certain commands)
Parameters to snapshot subcommand:
'snapshot' is the name of the snapshot to create, apply or delete
'-a' applies a snapshot (revert disk to saved state)
'-c' creates a snapshot
'-d' deletes a snapshot
'-l' lists all snapshots in the given image
Supported formats: raw cow qcow vdi vmdk cloop dmg bochs vpc vvfat qcow2 qed parallels nbd blkdebug sheepdog blkverify host_device file
Qemu
Please note that some of these flags change between versions
Qemu 0.15.0 rc2
QEMU emulator version 0.14.92, Copyright (c) 2003-2008 Fabrice Bellard
usage: qemu [options] [disk_image]
'disk_image' is a raw hard disk image for IDE hard disk 0
Standard options:
-h or -help display this help and exit
-version display version information and exit
-machine [type=]name[,prop[=value][,...]]
selects emulated machine (-machine ? for list)
property accel=accel1[:accel2[:...]] selects accelerator
supported accelerators are kvm, xen, tcg (default: tcg)
-cpu cpu select CPU (-cpu ? for list)
-smp n[,maxcpus=cpus][,cores=cores][,threads=threads][,sockets=sockets]
set the number of CPUs to 'n' [default=1]
maxcpus= maximum number of total cpus, including
offline CPUs for hotplug, etc
cores= number of CPU cores on one socket
threads= number of threads on one CPU core
sockets= number of discrete sockets in the system
-numa node[,mem=size][,cpus=cpu[-cpu]][,nodeid=node]
-fda/-fdb file use 'file' as floppy disk 0/1 image
-hda/-hdb file use 'file' as IDE hard disk 0/1 image
-hdc/-hdd file use 'file' as IDE hard disk 2/3 image
-cdrom file use 'file' as IDE cdrom image (cdrom is ide1 master)
-drive [file=file][,if=type][,bus=n][,unit=m][,media=d][,index=i]
[,cyls=c,heads=h,secs=s[,trans=t]][,snapshot=on|off]
[,cache=writethrough|writeback|none|unsafe][,format=f]
[,serial=s][,addr=A][,id=name][,aio=threads|native]
[,readonly=on|off]
use 'file' as a drive image
-set group.id.arg=value
set <arg> parameter for item <id> of type <group>
i.e. -set drive.$id.file=/path/to/image
-global driver.property=value
set a global default for a driver property
-mtdblock file use 'file' as on-board Flash memory image
-sd file use 'file' as SecureDigital card image
-pflash file use 'file' as a parallel flash image
-boot [order=drives][,once=drives][,menu=on|off]
'drives': floppy (a), hard disk (c), CD-ROM (d), network (n)
-snapshot write to temporary files instead of disk image files
-m megs set virtual RAM size to megs MB [default=128]
-mem-path FILE provide backing storage for guest RAM
-k language use keyboard layout (for example 'fr' for French)
-audio-help print list of audio drivers and their options
-soundhw c1,... enable audio support
and only specified sound cards (comma separated list)
use -soundhw ? to get the list of supported cards
use -soundhw all to enable all of them
-usb enable the USB driver (will be the default soon)
-usbdevice name add the host or guest USB device 'name'
-device driver[,prop[=value][,...]]
add device (based on driver)
prop=value,... sets driver properties
use -device ? to print all possible drivers
use -device driver,? to print all possible properties
File system options:
-fsdev local,id=id,path=path,security_model=[mapped|passthrough|none]
Virtual File system pass-through options:
-virtfs local,path=path,mount_tag=tag,security_model=[mapped|passthrough|none]
-name string1[,process=string2]
set the name of the guest
string1 sets the window title and string2 the process name (on Linux)
-uuid %08x-%04x-%04x-%04x-%012x
specify machine UUID
Display options:
-display sdl[,frame=on|off][,alt_grab=on|off][,ctrl_grab=on|off]
[,window_close=on|off]|curses|none|
vnc=<display>[,<optargs>]
select display type
-nographic disable graphical output and redirect serial I/Os to console
-curses use a curses/ncurses interface instead of SDL
-no-frame open SDL window without a frame and window decorations
-alt-grab use Ctrl-Alt-Shift to grab mouse (instead of Ctrl-Alt)
-ctrl-grab use Right-Ctrl to grab mouse (instead of Ctrl-Alt)
-no-quit disable SDL window close capability
-sdl enable SDL
-spice <args> enable spice
-portrait rotate graphical output 90 deg left (only PXA LCD)
-rotate <deg> rotate graphical output some deg left (only PXA LCD)
-vga [std|cirrus|vmware|qxl|xenfb|none]
select video card type
-full-screen start in full screen
-g WxH[xDEPTH] Set the initial graphical resolution and depth
-vnc display start a VNC server on display
1 target only:
-win2k-hack use it when installing Windows 2000 to avoid a disk full bug
-no-fd-bootchk disable boot signature checking for floppy disks
-no-acpi disable ACPI
-no-hpet disable HPET
-balloon none disable balloon device
-balloon virtio[,addr=str]
enable virtio balloon device (default)
-acpitable [sig=str][,rev=n][,oem_id=str][,oem_table_id=str][,oem_rev=n][,asl_compiler_id=str][,asl_compiler_rev=n][,data=file1[:file2]...]
ACPI table description
-smbios file=binary
load SMBIOS entry from binary file
-smbios type=0[,vendor=str][,version=str][,date=str][,release=%d.%d]
specify SMBIOS type 0 fields
-smbios type=1[,manufacturer=str][,product=str][,version=str][,serial=str]
[,uuid=uuid][,sku=str][,family=str]
specify SMBIOS type 1 fields
Network options:
-net nic[,vlan=n][,macaddr=mac][,model=type][,name=str][,addr=str][,vectors=v]
create a new Network Interface Card and connect it to VLAN 'n'
-net user[,vlan=n][,name=str][,net=addr[/mask]][,host=addr][,restrict=on|off]
[,hostname=host][,dhcpstart=addr][,dns=addr][,tftp=dir][,bootfile=f]
[,hostfwd=rule][,guestfwd=rule] connect the user mode network stack to VLAN 'n', configure its
DHCP server and enabled optional services
-net tap[,vlan=n][,name=str],ifname=name
connect the host TAP network interface to VLAN 'n'
-net socket[,vlan=n][,name=str][,fd=h][,listen=[host]:port][,connect=host:port]
connect the vlan 'n' to another VLAN using a socket connection
-net socket[,vlan=n][,name=str][,fd=h][,mcast=maddr:port[,localaddr=addr]]
connect the vlan 'n' to multicast maddr and port
use 'localaddr=addr' to specify the host address to send packets from
-net dump[,vlan=n][,file=f][,len=n]
dump traffic on vlan 'n' to file 'f' (max n bytes per packet)
-net none use it alone to have zero network devices. If no -net option
is provided, the default is '-net nic -net user'
-netdev [user|tap|socket],id=str[,option][,option][,...]
Character device options:
-chardev null,id=id[,mux=on|off]
-chardev socket,id=id[,host=host],port=host[,to=to][,ipv4][,ipv6][,nodelay]
[,server][,nowait][,telnet][,mux=on|off] (tcp)
-chardev socket,id=id,path=path[,server][,nowait][,telnet],[mux=on|off] (unix)
-chardev udp,id=id[,host=host],port=port[,localaddr=localaddr]
[,localport=localport][,ipv4][,ipv6][,mux=on|off]
-chardev msmouse,id=id[,mux=on|off]
-chardev vc,id=id[[,width=width][,height=height]][[,cols=cols][,rows=rows]]
[,mux=on|off]
-chardev file,id=id,path=path[,mux=on|off]
-chardev pipe,id=id,path=path[,mux=on|off]
-chardev console,id=id[,mux=on|off]
-chardev serial,id=id,path=path[,mux=on|off]
Bluetooth(R) options:
-bt hci,null dumb bluetooth HCI - doesn't respond to commands
-bt hci,host[:id]
use host's HCI with the given name
-bt hci[,vlan=n]
emulate a standard HCI in virtual scatternet 'n'
-bt vhci[,vlan=n]
add host computer to virtual scatternet 'n' using VHCI
-bt device:dev[,vlan=n]
emulate a bluetooth device 'dev' in scatternet 'n'
Linux/Multiboot boot specific:
-kernel bzImage use 'bzImage' as kernel image
-append cmdline use 'cmdline' as kernel command line
-initrd file use 'file' as initial ram disk
Debug/Expert options:
-serial dev redirect the serial port to char device 'dev'
-parallel dev redirect the parallel port to char device 'dev'
-monitor dev redirect the monitor to char device 'dev'
-qmp dev like -monitor but opens in 'control' mode
-mon chardev=[name][,mode=readline|control][,default]
-debugcon dev redirect the debug console to char device 'dev'
-pidfile file write PID to 'file'
-singlestep always run in singlestep mode
-S freeze CPU at startup (use 'c' to start execution)
-gdb dev wait for gdb connection on 'dev'
-s shorthand for -gdb tcp::1234
-d item1,... output log to /tmp/qemu.log (use -d ? for a list of log items)
-D logfile output log to logfile (instead of the default /tmp/qemu.log)
-hdachs c,h,s[,t]
force hard disk 0 physical geometry and the optional BIOS
translation (t=none or lba) (usually qemu can guess them)
-L path set the directory for the BIOS, VGA BIOS and keymaps
-bios file set the filename for the BIOS
-enable-kvm enable KVM full virtualization support
-xen-domid id specify xen guest domain id
-xen-create create domain using xen hypercalls, bypassing xend
warning: should not be used when xend is in use
-xen-attach attach to existing xen domain
xend will use this when starting qemu
-no-reboot exit instead of rebooting
-no-shutdown stop before shutdown
-loadvm [tag|id]
start right away with a saved state (loadvm in monitor)
-option-rom rom load a file, rom, into the option ROM space
-clock force the use of the given methods for timer alarm.
To see what timers are available use -clock ?
-rtc [base=utc|localtime|date][,clock=host|vm][,driftfix=none|slew]
set the RTC base and clock, enable drift fix for clock ticks (x86 only)
-icount [N|auto]
enable virtual instruction counter with 2^N clock ticks per
instruction
-watchdog i6300esb|ib700
enable virtual hardware watchdog [default=none]
-watchdog-action reset|shutdown|poweroff|pause|debug|none
action when watchdog fires [default=reset]
-echr chr set terminal escape character instead of ctrl-a
-virtioconsole c
set virtio console
-show-cursor show cursor
-tb-size n set TB size
-incoming p prepare for incoming migration, listen on port p
-nodefaults don't create default devices
-prom-env variable=value
set OpenBIOS nvram variables
-semihosting semihosting mode
-old-param old param mode
-readconfig <file>
-writeconfig <file>
read/write config file
-nodefconfig
do not load default config files at startup
During emulation, the following keys are useful:
ctrl-alt-f toggle full screen
ctrl-alt-n switch to virtual console 'n'
ctrl-alt toggle mouse and keyboard grab
When using -nographic, press 'ctrl-a h' to get some help.
Qemu tutorials
So far we've setup the following tutorials suitable for Qemu:
- Installing Windows NT 3.1 on Qemu
- Installing Windows NT 3.5 on Qemu
- Installing Windows NT 3.51 on Qemu
- Installing Windows NT 4.0 on Qemu
- Installing Windows NT 4.0 on Qemu(MIPS)
- Installing NeXTSTEP on Qemu This also gives a guide on compiling Qemu, prior to the 0.15 release.
External links
- Qemu's main site - http://wiki.qemu.org/Index.html
- Win32 builds of Qemu including ready to run images http://www.h7.dion.ne.jp/~qemu-win/
- Automated builds of Qemu are available here for Win64, and here for Win32.