Difference between revisions of "CPU/Memory Interconnect"
m (Add new cat) |
(Original name was 'Comet Memory Interconnect') |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
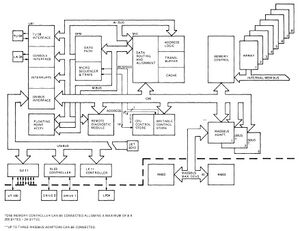
[[Image:VAX750block.jpg|right|thumb|300px|VAX-11/750 system block diagram, showing how the CMI ties together the major /750 functional units]] | [[Image:VAX750block.jpg|right|thumb|300px|VAX-11/750 system block diagram, showing how the CMI ties together the major /750 functional units]] | ||
| − | The '''CPU/Memory Interconnect''' (often given as '''CMI''') is the main [[bus]] which connects the main sub-systems (such as the [[Central Processing Unit|CPU]] and [[main memory]], as well as [[input/output|I/O]] adapters) in the [[VAX-11/750]] | + | The '''CPU/Memory Interconnect''' (often given as '''CMI'''; the original name was '''Comet Memory Interconnect''' - 'Comet' was the code-name of the /750)) is the main [[bus]] which connects the main sub-systems (such as the [[Central Processing Unit|CPU]] and [[main memory]], as well as [[input/output|I/O]] adapters) in the [[VAX-11/750]]. A sub-system connected to the CMI is referred to as a 'nexus'. |
The primary functions of the CMI are to do priority arbitration for use of the bus, and carry data between the sub-systems, as well as carrying [[interrupt]]s. It is also used for a variety of lesser functions, such as [[diagnostic]]s, loading writeable [[microcode]], etc. | The primary functions of the CMI are to do priority arbitration for use of the bus, and carry data between the sub-systems, as well as carrying [[interrupt]]s. It is also used for a variety of lesser functions, such as [[diagnostic]]s, loading writeable [[microcode]], etc. | ||
| Line 57: | Line 57: | ||
[[Category: VAX Buses]] | [[Category: VAX Buses]] | ||
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category: CMI]] |
Latest revision as of 18:36, 18 May 2024
The CPU/Memory Interconnect (often given as CMI; the original name was Comet Memory Interconnect - 'Comet' was the code-name of the /750)) is the main bus which connects the main sub-systems (such as the CPU and main memory, as well as I/O adapters) in the VAX-11/750. A sub-system connected to the CMI is referred to as a 'nexus'.
The primary functions of the CMI are to do priority arbitration for use of the bus, and carry data between the sub-systems, as well as carrying interrupts. It is also used for a variety of lesser functions, such as diagnostics, loading writeable microcode, etc.
The CMI is carried over the main /750 backplane, into which the various sub-systems plug. It is synchronous and interlocked (like the SBI of the VAX-11/780); at the analog level, it is tri-state.
Details
The CMI consists of 45 bi-directional lines: priority arbitration, address, data, control, and status. A uni-directional clock signal line is used to synchronize the operations on the CMI. At any given point in time, one nexus is the 'master', and another (selected by it) is the 'slave' in each CMI interaction.
Arbitration is fully distributed; each nexus has a priority arbitration line which it can assert, and on each cycle, each requesting nexus looks to see if it is the highest-priority nexus for that cycle.
CMI units
The CMI units present in every /750 are:
- KA750 CPU - L0002-L0003-L0004-L0005/L0008
- MS750 Memory System - L0011/L0016/L0022
Optional units include:
- RH750 Massbus Adapter - L0007
- DW750 Second Unibus Interface - L0010
- CI750 Computer Interconnect Interface - L0009
- DR750 Parallel Interface - L0014
CMI Option Slot Configuration Rules
Allowable Configurations of CMI Slots 7, 8, & 9:
| Slot 7 | Slot 8 | Slot 9 |
|---|---|---|
| RH750 | RH750 | RH750 |
| DW750 | RH750 | RH750 |
| DR750 | RH750 | RH750 |
| DW750 | DR750 | RH750 |
| DW750 | CI750 | RH750 |
| CI750 | RH750 | RH750 |
NOTES:
- Combination of DR750 and CI750 is not allowed
- Only one DR750 per system is allowed
- Only one DW750 per system is allowed
- Only one CI750 per system is allowed
External links
- VAX Hardware Handbook Volume 1 - the CMI is covered in Chapter 9 (pp. 316-321 of the PDF)