Difference between revisions of "Windows 2.0"
(→Windows/386) |
m (Push it down a level) |
||
| (16 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[Image:Windows 386 2.11 boot logo.jpg|150px|thumb|right|The Windows/386 splash screen]] | [[Image:Windows 386 2.11 boot logo.jpg|150px|thumb|right|The Windows/386 splash screen]] | ||
| − | Windows 2.0 was the second release of the Microsoft Windows environment for [[MS-DOS]]. It was not a commercial success, | + | '''Windows 2.0''' was the second release of the [[Microsoft Windows]] [[operating environment]] for [[MS-DOS]]. It was not a commercial success - however, it furthered the development of the kernel so that it could use XMS memory, and it later introduced a 286-specific version that could do some limited multi-tasking with MS-DOS - and a 386-specific version that could spawn multiple [[VDM]]'s. |
An interesting thing about version 2.0 of Microsoft Windows, is the reference to [[Presentation Manager]] and the future of [[OS/2]] in the literature. Even the appearance of the GUI between OS/2 1.1 & 1.2 and Windows 2.0 is consistent. | An interesting thing about version 2.0 of Microsoft Windows, is the reference to [[Presentation Manager]] and the future of [[OS/2]] in the literature. Even the appearance of the GUI between OS/2 1.1 & 1.2 and Windows 2.0 is consistent. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Also to appease Compaq, Microsoft actually finished and shipped Windows/386 in September of 1987, with the 'regular' version to follow in November of 1987. | ||
It was superseded by [[Windows 3.0]]. | It was superseded by [[Windows 3.0]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Versions == | ||
| + | Windows 2.0 came in 3 'waves': first the 2.0x wave - in 1987, 2.1 - in 1988 - and finally 2.11, in 1989. | ||
== Windows/286 == | == Windows/286 == | ||
[[Image:Windows 286 box front.jpg|150px|A Windows/286 retail box.]] | [[Image:Windows 286 box front.jpg|150px|A Windows/286 retail box.]] | ||
| + | [[Image:Windows 286 running.png|200px|thumb|right|Windows 286 running a command window]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
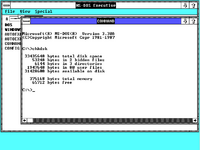
| + | This version had some specific code to the 80286 CPU allowing limited MS-DOS multitasking. However since each instance of MS-DOS consumed the same limited 640kb memory pool, it was largely ineffective. This version was 286-specific, in that it used the a20 gate to give Windows/286 an extra 64kb of RAM. Windows/286 was expected to run with MS-DOS 3.3, so the high memory area was not in use, nor was there a himem.sys at the time. DOS extenders pretty much all did their own thing at this time, and they were mostly incompatible with both Windows/286 & Windows/386. | ||
| − | + | Windows/286 could run MS-DOS sessions in a window, although memory was so constrained it was mostly useless. Honestly, I wonder if this was the outgrowth of the "European" MS-DOS 4... | |
== Windows/386 == | == Windows/386 == | ||
| Line 15: | Line 24: | ||
[[Image:Windows 386 2.1 back.jpg|150px]] | [[Image:Windows 386 2.1 back.jpg|150px]] | ||
| − | [[Image:Windows 386 running.jpg|200px|thumb|right|Windows/386 running multiple | + | [[Image:Windows 386 running.jpg|200px|thumb|right|Windows/386 running multiple VDMs]] |
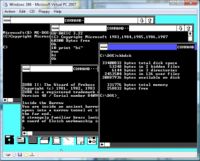
| − | Windows/386 was Microsoft's first product to allow people to directly use the V86 mode of the 80386 CPU. With enough extended memory you could run several virtual MS-DOS machines. What was 'cool' is that each VDM was copied from the primary memory map, so that way each VM had the same operating features, and each had the same amount of free memory. The selling point at the time, was that each VDM could run | + | Windows/386 was Microsoft's first product to allow people to directly use the V86 mode of the [[I386|80386]] CPU. With enough extended memory you could run several virtual MS-DOS machines. What was 'cool' is that each VDM was copied from the primary memory map, so that way each VM had the same operating features, and each had the same amount of free memory. The selling point at the time, was that each VDM could run its own programs in its own memory space. From the sample picture, a VM is running [[GW-Basic]], another is running [[Zork II]], and another is running chkdsk. Each one started up with the same amount of free memory. Windows/386 also facilitated basic clipboard operations between VMs so you could copy data between MS-DOS applications, and of course Windows applications. |
| − | It's worth noting that this version of | + | It's worth noting that this version of Windows still ran in the limited space of the MS-DOS 640kb area, but it went to protected mode to run the v86 machines - with expanded memory - while itself was limited to the real memory space. Needless to say IBM should have taken note, as this quasi-32bit shell suddenly could do something that the 16bit version of [[OS/2#16_bit_versions|OS/2]] could never do, and years before the release of OS/2 2.0 - which could run multiple MS-DOS VMs. |
Windows/386 shipped with a 'working model' of Excel, that was limited to 16 columns and 64 rows. | Windows/386 shipped with a 'working model' of Excel, that was limited to 16 columns and 64 rows. | ||
| − | Naturally since | + | Naturally, since [[Compaq]] was the first to release a 386 based computer, they were bundling Windows/386 with it. There is a press release available here [[Microsoft Windows-386 Being Delivered With Compaq 80386-Based PCs Through Dec. 31, 1987]]. NEC also released a 1987 version of Windows/386 in December: it was tagged as version 2.03. |
| − | + | [[Image:Battletech under Windows 386 2.11.jpg|thumb|right|200px|Battletech CGA under Windows/386 VGA]] | |
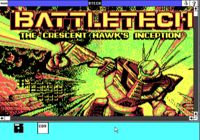
| + | Windows/386 is interesting in that you can run 'lesser' graphical programs inside of Windows, meaning that a VGA-equipped machine could play CGA games in a window. OS/2 2.0 could run lesser programs as well in a box, and some of the same level. Windows/386 could also run itself within itself. The actual GUI portion was "win86.com", targeted for the 8086. If you re-installed Windows/386 into a different directory with a 'lesser' video card you could even run Windows/86 in a window. | ||
| − | + | Windows/386 is also known for the laughable promotion video: | |
| − | Windows/386 is | + | [https://youtu.be/noEHHB6rnMI?t=7m12s Youtube video of Windows/386]. See how long you can stand it! |
| − | Windows | + | {{nav Microsoft Windows}} |
| − | |||
| − | + | [[Category: Microsoft Operating Environments]] | |
| − | [[Category:Operating Environments]] | ||
Latest revision as of 18:11, 13 January 2024
Windows 2.0 was the second release of the Microsoft Windows operating environment for MS-DOS. It was not a commercial success - however, it furthered the development of the kernel so that it could use XMS memory, and it later introduced a 286-specific version that could do some limited multi-tasking with MS-DOS - and a 386-specific version that could spawn multiple VDM's.
An interesting thing about version 2.0 of Microsoft Windows, is the reference to Presentation Manager and the future of OS/2 in the literature. Even the appearance of the GUI between OS/2 1.1 & 1.2 and Windows 2.0 is consistent.
Also to appease Compaq, Microsoft actually finished and shipped Windows/386 in September of 1987, with the 'regular' version to follow in November of 1987.
It was superseded by Windows 3.0.
Versions
Windows 2.0 came in 3 'waves': first the 2.0x wave - in 1987, 2.1 - in 1988 - and finally 2.11, in 1989.
Windows/286
This version had some specific code to the 80286 CPU allowing limited MS-DOS multitasking. However since each instance of MS-DOS consumed the same limited 640kb memory pool, it was largely ineffective. This version was 286-specific, in that it used the a20 gate to give Windows/286 an extra 64kb of RAM. Windows/286 was expected to run with MS-DOS 3.3, so the high memory area was not in use, nor was there a himem.sys at the time. DOS extenders pretty much all did their own thing at this time, and they were mostly incompatible with both Windows/286 & Windows/386.
Windows/286 could run MS-DOS sessions in a window, although memory was so constrained it was mostly useless. Honestly, I wonder if this was the outgrowth of the "European" MS-DOS 4...
Windows/386
Windows/386 was Microsoft's first product to allow people to directly use the V86 mode of the 80386 CPU. With enough extended memory you could run several virtual MS-DOS machines. What was 'cool' is that each VDM was copied from the primary memory map, so that way each VM had the same operating features, and each had the same amount of free memory. The selling point at the time, was that each VDM could run its own programs in its own memory space. From the sample picture, a VM is running GW-Basic, another is running Zork II, and another is running chkdsk. Each one started up with the same amount of free memory. Windows/386 also facilitated basic clipboard operations between VMs so you could copy data between MS-DOS applications, and of course Windows applications.
It's worth noting that this version of Windows still ran in the limited space of the MS-DOS 640kb area, but it went to protected mode to run the v86 machines - with expanded memory - while itself was limited to the real memory space. Needless to say IBM should have taken note, as this quasi-32bit shell suddenly could do something that the 16bit version of OS/2 could never do, and years before the release of OS/2 2.0 - which could run multiple MS-DOS VMs.
Windows/386 shipped with a 'working model' of Excel, that was limited to 16 columns and 64 rows.
Naturally, since Compaq was the first to release a 386 based computer, they were bundling Windows/386 with it. There is a press release available here Microsoft Windows-386 Being Delivered With Compaq 80386-Based PCs Through Dec. 31, 1987. NEC also released a 1987 version of Windows/386 in December: it was tagged as version 2.03.
Windows/386 is interesting in that you can run 'lesser' graphical programs inside of Windows, meaning that a VGA-equipped machine could play CGA games in a window. OS/2 2.0 could run lesser programs as well in a box, and some of the same level. Windows/386 could also run itself within itself. The actual GUI portion was "win86.com", targeted for the 8086. If you re-installed Windows/386 into a different directory with a 'lesser' video card you could even run Windows/86 in a window.
Windows/386 is also known for the laughable promotion video: Youtube video of Windows/386. See how long you can stand it!
| v • d • e Microsoft Windows Versions, Vendors and Related |
|---|
| 16 bit - Windows 1.0 • Windows 2.0 • Windows 3.0 • Windows 3.1 • Windows 3.2
Hybrid 32/16 bit - win32s • Windows 95 • Windows 98 • Windows ME 32 bit - Windows NT 3.1 • Windows NT 3.5 • Windows NT 3.51• Windows NT 4.0 |