Difference between revisions of "Digital Storage Systems Interconnect"
(New section "Family of DSSI Products") |
(typo? DDSSI -> DSSI in 1 place) |
||
| (18 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | + | [[File:BC22Q-09 DSSI Cable.jpg|thumb|right|250px|DSSI cable]] | |
| − | DSSI | + | The '''Digital Storage Systems Interconnect''' (usually given as '''DSSI''') is a [[mass storage]] [[bus]] from [[Digital Equipment Corporation|DEC]]. The DSSI specification lists the main attributes of DSSI as: 8-bit wide [[parallel]]; multi-drop linear bus electrical topology; low-cost, [[single-ended signalling]] interface circuitry; [[direct current|DC]] coupling. The DSSI's [[analog]] characteristics mean that DSSI installations require [[terminator]]s. |
| − | [[ | + | The DSSI is an alternate physical layer in the [[Computer Interconnect]] system; the CI system had a 'native' physical layer before the creation of DSSI. (DSSI is also an alternative mass storage [[drive]] to [[device controller|controller]] interface bus, from the earlier [[Standard Disk Interconnect]].) The relationship between the DSSI and the CI's physical layer is shown in the following diagram: |
| + | <pre> | ||
| + | <-----+ | ||
| + | +---------------------+ | | ||
| + | | Port Driver | | | ||
| + | | Layer | | | ||
| + | | ( SCA Specification)| | | ||
| + | +---------------------+ | | ||
| + | | | | ||
| + | | | | ||
| + | ....................... | | ||
| + | . CI Port Adapter . | | ||
| + | . ( eg: VAX CI Port ) . | | ||
| + | ....................... | | ||
| + | | | P | ||
| + | +------> | | P | ||
| + | | +---------------------+ | D | ||
| + | | | CI Port | | | ||
| + | C | | Layer | | L | ||
| + | I | | ( DEC Std 161 ) | | A | ||
| + | | +---------------------+ | Y | ||
| + | A | | | | E | ||
| + | R | +------+ +------+ | R | ||
| + | C | | | | | ||
| + | H | +----------------------+ +---------------------+ | | ||
| + | I | | DSSI Datalink | | CI Datalink | | | ||
| + | T | | Layer | .... | Layer | | | ||
| + | E | | ( DSSI Spec. ) | | ( Dec Std 161 ) | | | ||
| + | C | +----------------------+ +---------------------+ | | ||
| + | T | | | <-----+ | ||
| + | U | | | <-----+ P L | ||
| + | R | +----------------------+ +---------------------+ | H A | ||
| + | E | | DSSI Physical | | CI Physical | | Y Y | ||
| + | | | Interconnect | | Interconnect | | S E | ||
| + | | | ( DSSI Spec. ) | | ( DEC Std 161 ) | | I R | ||
| + | | +----------------------+ +---------------------+ | C | ||
| + | +------> <-----+ A | ||
| + | L | ||
| − | + | Figure 1-2: CI PPD Architectural Layers | |
| + | </pre> | ||
| − | + | DSSI thus made it possible to build [[VAXcluster]]s from [[MicroVAX]] and smaller [[VAX]] computers, by adding CI-bus functionality to smaller VAX systems. It can also be used to create loosely-coupled [[multi-processor]]s, by sharing a number of [[disk drive]]s between two systems. Such shared drives are termed 'Integrated Storage Elements' (ISEs). | |
| − | + | A description of the DSSI from the 'Digital's Storage System Interconnect' protocol specification document: | |
| − | + | "The DSSI, supporting the needs of low-end and mid-range systems, is one in a family of high-performance computer-to-computer interconnects .. that combine a common host interface and port layer with an implementation-specific datalink and physical interconnect. | |
| + | CI-class interconnects provide the transmission services required by Digital's [[System Communication Architecture]] (SCA) - a four-tiered set of protocols and interfaces.." | ||
| − | === DSSI Controllers/Interfaces | + | == Advance in DSSI Interface Usage == |
| + | |||
| + | In the beginning there were DSSI interfaces and DSSI Integrated Storage Elements connected to them. Each individual ISE was a kind of [[Hierarchical Storage Controller]], i.e. a [[VAXcluster|cluster-capable]] controller, managing just a single storage device. This was a smart but expensive design and limited storage capacity to a maximum of 8 DSSI nodes (i.e. one or two DSSI controllers and seven resp. six DSSI devices) per DSSI bus. | ||
| + | |||
| + | In 1994 a new concept was introduced for DSSI devices: The '''[[HSD05 Array Controller]]''' as a first of three models of DSSI-to-[[SCSI]] bus adapters (HSD05/[[HSD10 DSSI-to-SCSI Bus Adapter|HSD10]]/[[HSD30]]). From now on an HSD05 could connect up to seven SCSI devices (disk and tape drives) to a DSSI bus as a single DSSI node, thus multiplying the available storage capacity. As an additional effect, the costs were reduced because cheaper SCSI disks (without a complex DSSI interface) could be used. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == DSSI Cabling == | ||
| + | |||
| + | The [http://bitsavers.org/pdf/dec/dsa/dssi/EK-RF72D-UG-008_RF_Series_Integrated_Storage_Element_Users_Guide_Apr93.pdf "RF Series Integrated Storage Element User Guide"] (EK-RF72D-UG-008) says "The DSSI bus is a 50-conductor cable. Inside an enclosure, the bus may be a flat ribbon cable or a round bundle of twisted pairs. Between enclosures, the bus is a shielded round cable approximately ½-inch in diameter." | ||
| + | |||
| + | The short cables run from the [[printed circuit board|PCBs]] that implement the interfaces to a standard [[connector]] on the back of the enclosure. (Different enclosures use different short cables with a given board; see the "KFQSA Module Installation and User Manual", Section 2.1 for a partial list.) | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Connectors === | ||
| + | |||
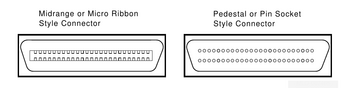
| + | [[Image:DSSI_Connectors.png|thumb|350px|left|DSSI MR & PS Connectors]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | The long inter-enclosure DSSI cables are found with two different types of connectors: | ||
| + | |||
| + | * '''MR''' (Micro Ribbon or midrange), with flat [[contact]]s = "50 Way High Density Micro Ribbon" | ||
| + | * '''PS''' (Pin Socket or pedestal style), with round [[pin]]s = "50 Way High Density Honda" | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:DSSI MR Connector female (Cable).jpg|thumb|right|80px|MR female connector]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | When found on cables, these exist in both 'straight' and 'right-angle' forms (to allow cables to be neatly dressed, in part so they are less likely to get damaged). | ||
| + | |||
| + | With these two different types of connectors, ''three'' different basic types of long DSSI cables are needed (cable names for types available from DEC included): | ||
| + | |||
| + | * MR-MR - BC21Q-xx (2x straight); BC29S-xx (right-angle to straight) | ||
| + | * PS-PS - BC21M-xx (2x right-angle) | ||
| + | * MR-PS - BC22Q-xx (right-angle PS to straight MR); BC29R-xx (right-angle PS to right-angle MR) | ||
| + | |||
| + | (As usual with DEC cables, the '-xx' gives the length, numerically.) The MR-PS cables can be reversed to provide PS-MR. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Two types of DSSI connectors are found on devices: | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Single DSSI '''Device Connector''' 50-pin ([[SCSI]]-like) | ||
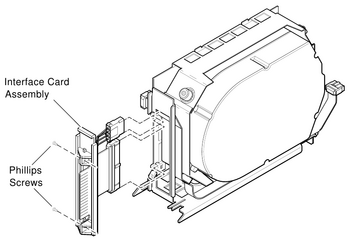
| + | * Dual 3.5" / Single 5.25" DSSI '''Disk Interface Card Assembly''' e.g. for [[VAX 4000]], BA430/BA440 | ||
| + | |||
| + | == DSSI Controllers/Interfaces == | ||
* [[KFQSA]] [[QBUS]] DSSI Adapter | * [[KFQSA]] [[QBUS]] DSSI Adapter | ||
| Line 25: | Line 102: | ||
* [[EDA640]] [[MicroVAX 3300/3400]] [[KA640]] embedded DSSI Adapter (EDA) | * [[EDA640]] [[MicroVAX 3300/3400]] [[KA640]] embedded DSSI Adapter (EDA) | ||
* [[KFA40]] [[DEC 4000]] I/O Module | * [[KFA40]] [[DEC 4000]] I/O Module | ||
| + | * [[SHAC]] [[VAX 4000 series]] embedded DSSI Adapter | ||
| + | * [[SWIFT]] [[VAXft series]] embedded DSSI Adapter | ||
| − | === | + | == DSSI Hierarchical Storage Controllers (HSDs) == |
| + | |||
| + | [[Hierarchical Storage Controller]]s: | ||
* [[HSD05]] | * [[HSD05]] | ||
| − | * [[HSD10]] | + | * [[HSD10 DSSI-to-SCSI Bus Adapter|HSD10]] |
* [[HSD30]] | * [[HSD30]] | ||
* [[HSD50]] | * [[HSD50]] | ||
| − | === DSSI Disk Drives == | + | == DSSI Storage Expanders == |
| + | |||
| + | * [[B213F]] | ||
| + | * [[B400X]] | ||
| + | * [[BA42A]] | ||
| + | * [[R215F]] | ||
| + | * [[R23RF]] | ||
| + | * [[R400X]] | ||
| + | * [[SF12]] | ||
| + | * [[SW301]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | == DSSI Disk Drives == | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Disk]]s: | ||
* [[RF30]] | * [[RF30]] | ||
* [[RF31]] | * [[RF31]] | ||
| + | * [[RF31F]] | ||
| + | * [[RF31T]] | ||
* [[RF32]] | * [[RF32]] | ||
* [[RF35]] | * [[RF35]] | ||
| Line 48: | Line 144: | ||
* [[RF75]] | * [[RF75]] | ||
| − | === DSSI Tape Drives | + | == DSSI Solid State Disk Drives == |
| + | |||
| + | [[Solid state disk]] drives: | ||
| + | |||
| + | * [[EF51R Solid State Disk Drive|EF51R]] | ||
| + | * [[EF52R Solid State Disk Drive|EF52R]] | ||
| + | * [[EF53 Solid State Disk Drive|EF53]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | == DSSI Tape Drives == | ||
* [[TF30]] | * [[TF30]] | ||
| Line 57: | Line 161: | ||
* [[TF88]] | * [[TF88]] | ||
* [[TF89]] | * [[TF89]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Images == | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:DSSI_PS_Connector_female_(Cable).jpg|thumb|left|300px|PS female connector]] | ||
| + | [[File:DSSI PS Connector female (Cable)-2.jpg|thumb|left|80px|PS female connector]] | ||
| + | [[File:DSSI_PS_Connector_male_(CPU).jpg|thumb|left|300px|PS male connector (CPU)]] | ||
| + | [[File:DSSI_PS_Terminator_female.jpg|thumb|left|300px|PS female terminator]] | ||
| + | [[File:BC22Q-09 Label.jpg|thumb|left|300px|BC22Q-09 label]] | ||
| + | [[File:DSSI_Interface_Card_Assembly.png|thumb|left|350px|Interface Card Assembly (5.25" FH disk)]] | ||
| + | [[File:DSSI_Interface_Card_Assembly_Dual_RF35_Connector.jpg|thumb|left|300px|Interface Card Assembly Dual RF35]] | ||
| + | [[File:DSSI_Device_Connector_RF30.jpg|thumb|left|300px| Device Connector RF30]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br clear=all> | ||
{{semi-stub}} | {{semi-stub}} | ||
| Line 65: | Line 182: | ||
** [http://www.bitsavers.org/pdf/dec/dsa/dssi/Digitals_Storage_System_Interconnect_Rev_1.0.0_199003.txt Digital's Storage System Interconnect] - protocol specification document | ** [http://www.bitsavers.org/pdf/dec/dsa/dssi/Digitals_Storage_System_Interconnect_Rev_1.0.0_199003.txt Digital's Storage System Interconnect] - protocol specification document | ||
* [http://www.bitsavers.org/pdf/dec/vax/3800/EK-338AC-DH-003_MicroVAX_Dual-Host_Systems_Dec90.pdf MicroVAX Dual-Host Systems] (EK-338AC-DH-003) - contains a clear description of how a DSSI can be used to create a loosely-couple multi-processor | * [http://www.bitsavers.org/pdf/dec/vax/3800/EK-338AC-DH-003_MicroVAX_Dual-Host_Systems_Dec90.pdf MicroVAX Dual-Host Systems] (EK-338AC-DH-003) - contains a clear description of how a DSSI can be used to create a loosely-couple multi-processor | ||
| + | * [https://manx-docs.org/collections/mds-199909/cd1/cluster/410abmgd.pdf DSSI VMScluster Installation and Troubleshooting Guide] (EK-410AB-MG.D01) | ||
| + | * [https://decdoc.itsx.net/dec94mds/rf72dug8.pdf RF Series Integrated Storage Element User Guide] (EK-RF72D-UG-008) | ||
| + | * [https://manx-docs.org/collections/mds-199909/cd2/cabinets/348abmg2.pdf BA430 BA440 Enclosure Maintenance.pdf] (EK-348AB-MG-002) | ||
[[Category: DEC Buses]] | [[Category: DEC Buses]] | ||
[[Category: DEC Mass Storage]] | [[Category: DEC Mass Storage]] | ||
[[Category: DSSI]] | [[Category: DSSI]] | ||
| + | [[Category: DEC Interface Standards]] | ||
Latest revision as of 02:29, 28 November 2025
The Digital Storage Systems Interconnect (usually given as DSSI) is a mass storage bus from DEC. The DSSI specification lists the main attributes of DSSI as: 8-bit wide parallel; multi-drop linear bus electrical topology; low-cost, single-ended signalling interface circuitry; DC coupling. The DSSI's analog characteristics mean that DSSI installations require terminators.
The DSSI is an alternate physical layer in the Computer Interconnect system; the CI system had a 'native' physical layer before the creation of DSSI. (DSSI is also an alternative mass storage drive to controller interface bus, from the earlier Standard Disk Interconnect.) The relationship between the DSSI and the CI's physical layer is shown in the following diagram:
<-----+
+---------------------+ |
| Port Driver | |
| Layer | |
| ( SCA Specification)| |
+---------------------+ |
| |
| |
....................... |
. CI Port Adapter . |
. ( eg: VAX CI Port ) . |
....................... |
| | P
+------> | | P
| +---------------------+ | D
| | CI Port | |
C | | Layer | | L
I | | ( DEC Std 161 ) | | A
| +---------------------+ | Y
A | | | | E
R | +------+ +------+ | R
C | | | |
H | +----------------------+ +---------------------+ |
I | | DSSI Datalink | | CI Datalink | |
T | | Layer | .... | Layer | |
E | | ( DSSI Spec. ) | | ( Dec Std 161 ) | |
C | +----------------------+ +---------------------+ |
T | | | <-----+
U | | | <-----+ P L
R | +----------------------+ +---------------------+ | H A
E | | DSSI Physical | | CI Physical | | Y Y
| | Interconnect | | Interconnect | | S E
| | ( DSSI Spec. ) | | ( DEC Std 161 ) | | I R
| +----------------------+ +---------------------+ | C
+------> <-----+ A
L
Figure 1-2: CI PPD Architectural Layers
DSSI thus made it possible to build VAXclusters from MicroVAX and smaller VAX computers, by adding CI-bus functionality to smaller VAX systems. It can also be used to create loosely-coupled multi-processors, by sharing a number of disk drives between two systems. Such shared drives are termed 'Integrated Storage Elements' (ISEs).
A description of the DSSI from the 'Digital's Storage System Interconnect' protocol specification document:
"The DSSI, supporting the needs of low-end and mid-range systems, is one in a family of high-performance computer-to-computer interconnects .. that combine a common host interface and port layer with an implementation-specific datalink and physical interconnect. CI-class interconnects provide the transmission services required by Digital's System Communication Architecture (SCA) - a four-tiered set of protocols and interfaces.."
Contents
Advance in DSSI Interface Usage
In the beginning there were DSSI interfaces and DSSI Integrated Storage Elements connected to them. Each individual ISE was a kind of Hierarchical Storage Controller, i.e. a cluster-capable controller, managing just a single storage device. This was a smart but expensive design and limited storage capacity to a maximum of 8 DSSI nodes (i.e. one or two DSSI controllers and seven resp. six DSSI devices) per DSSI bus.
In 1994 a new concept was introduced for DSSI devices: The HSD05 Array Controller as a first of three models of DSSI-to-SCSI bus adapters (HSD05/HSD10/HSD30). From now on an HSD05 could connect up to seven SCSI devices (disk and tape drives) to a DSSI bus as a single DSSI node, thus multiplying the available storage capacity. As an additional effect, the costs were reduced because cheaper SCSI disks (without a complex DSSI interface) could be used.
DSSI Cabling
The "RF Series Integrated Storage Element User Guide" (EK-RF72D-UG-008) says "The DSSI bus is a 50-conductor cable. Inside an enclosure, the bus may be a flat ribbon cable or a round bundle of twisted pairs. Between enclosures, the bus is a shielded round cable approximately ½-inch in diameter."
The short cables run from the PCBs that implement the interfaces to a standard connector on the back of the enclosure. (Different enclosures use different short cables with a given board; see the "KFQSA Module Installation and User Manual", Section 2.1 for a partial list.)
Connectors
The long inter-enclosure DSSI cables are found with two different types of connectors:
- MR (Micro Ribbon or midrange), with flat contacts = "50 Way High Density Micro Ribbon"
- PS (Pin Socket or pedestal style), with round pins = "50 Way High Density Honda"
When found on cables, these exist in both 'straight' and 'right-angle' forms (to allow cables to be neatly dressed, in part so they are less likely to get damaged).
With these two different types of connectors, three different basic types of long DSSI cables are needed (cable names for types available from DEC included):
- MR-MR - BC21Q-xx (2x straight); BC29S-xx (right-angle to straight)
- PS-PS - BC21M-xx (2x right-angle)
- MR-PS - BC22Q-xx (right-angle PS to straight MR); BC29R-xx (right-angle PS to right-angle MR)
(As usual with DEC cables, the '-xx' gives the length, numerically.) The MR-PS cables can be reversed to provide PS-MR.
Two types of DSSI connectors are found on devices:
- Single DSSI Device Connector 50-pin (SCSI-like)
- Dual 3.5" / Single 5.25" DSSI Disk Interface Card Assembly e.g. for VAX 4000, BA430/BA440
DSSI Controllers/Interfaces
- KFQSA QBUS DSSI Adapter
- KFMSA XMI Dual DSSI Adapter
- KFMSB XMI DSSI adapter
- KFESA EISA DSSI Adapter
- KFESB EISA DSSI Adapter
- KFPSA PCI DSSI Adapter
- KFE52 VAXft Multi-Function Interface
- KDXDA VAXft 810 DSSI Interface
- EDA640 MicroVAX 3300/3400 KA640 embedded DSSI Adapter (EDA)
- KFA40 DEC 4000 I/O Module
- SHAC VAX 4000 series embedded DSSI Adapter
- SWIFT VAXft series embedded DSSI Adapter
DSSI Hierarchical Storage Controllers (HSDs)
Hierarchical Storage Controllers:
DSSI Storage Expanders
DSSI Disk Drives
DSSI Solid State Disk Drives
Solid state disk drives:
DSSI Tape Drives
Images
External Links
- DSSI - DSSI and related documents at Bitsavers
- Digital's Storage System Interconnect - protocol specification document
- MicroVAX Dual-Host Systems (EK-338AC-DH-003) - contains a clear description of how a DSSI can be used to create a loosely-couple multi-processor
- DSSI VMScluster Installation and Troubleshooting Guide (EK-410AB-MG.D01)
- RF Series Integrated Storage Element User Guide (EK-RF72D-UG-008)
- BA430 BA440 Enclosure Maintenance.pdf (EK-348AB-MG-002)