|
|
| (6 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) |
| Line 6: |
Line 6: |
| | | current version = 4.9.0 (Dec 2008) | | | current version = 4.9.0 (Dec 2008) |
| | | year introduced = 1985 | | | year introduced = 1985 |
| − | | type = Multitasking, multiuser | + | | type = [[Multi-tasking]], [[multi-user]] |
| | | architecture = [[68010]], [[IBMPC]] | | | architecture = [[68010]], [[IBMPC]] |
| | }} | | }} |
| | | | |
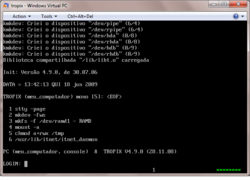
| − | [http://allegro.nce.ufrj.br/tropix/index.html TROPIX] got it's start after UFRJ could not secure a source license to AT&T UNIX. So they decided to write their own. Using a Version 7 68000 machine, they were able to clone out their own system. For a while the project seemed dead with the mainstream arrival of Linux, however there has been some new activity on the TROPIX front. | + | The '''TROPIX''' [[operating system]] got its start after UFRJ could not secure a source license to AT&T [[UNIX]]. So they decided to write their own. Using a [[Version 7]] [[Motorola 68000]] machine, they were able to clone out their own system. For a while the project seemed dead with the mainstream arrival of Linux, however there has been some new activity on the TROPIX front. |
| | | | |
| | == System requirements == | | == System requirements == |
| Line 32: |
Line 32: |
| | | | |
| | First you'll need some instructions. This is the google translated instructions: | | First you'll need some instructions. This is the google translated instructions: |
| − | <pre>
| |
| | | | |
| | + | [[TROPIX Manual]] |
| | | | |
| | + | === Step by Step guide === |
| | + | <pre> |
| | + | TROPIX CD boot |
| | | | |
| | + | > |
| | | | |
| | + | enter |
| | | | |
| | + | boot> |
| | | | |
| | + | -f |
| | | | |
| | + | n |
| | | | |
| | + | r |
| | | | |
| | + | s |
| | | | |
| | + | s |
| | | | |
| | + | s |
| | | | |
| | + | s |
| | | | |
| − | ******* ******* ******* ******* * * *
| + | fdisk> |
| − | * * * *
| |
| − | * * * *
| |
| − | ******* ******* * * * * *
| |
| − | * * * * * *
| |
| − | * * * * * *
| |
| − | * * * ******* * * * *
| |
| | | | |
| | + | w |
| | | | |
| | + | s |
| | | | |
| | + | q |
| | | | |
| | + | boot> |
| | | | |
| | + | -i |
| | | | |
| | | | |
| | + | login root |
| | + | password tropix |
| | | | |
| | + | mkfs /dev/rhda1 |
| | + | mount /dev/hda1 /aroot |
| | + | cd /usr/etc/install |
| | + | install |
| | | | |
| | + | s |
| | + | hda1 |
| | + | s |
| | + | n (it'll copy files) |
| | + | s |
| | | | |
| | | | |
| | + | reboot |
| | + | </pre> |
| | | | |
| | + | I'm still working out the networking... |
| | | | |
| − | | + | <pre> |
| − | | + | /dev/ed0 dhcp |
| − | TROPIX - Installation Guide
| + | netmask=0.0.0.0, default |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | Version 4.9.0
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | Guide
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | December 2008
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | INSTALL (ref) TROPIX: Installation Guide Pag. 2
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | CONTENT
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | Chapter 1 - Introduction ........................... 4
| |
| − | | |
| − | Chapter 2 - New versions of ................ 6
| |
| − | | |
| − | Chapter 3 - Characteristics ...................... 11
| |
| − | | |
| − | Chapter 4 - PC Configuration ................... 12
| |
| − | | |
| − | Chapter 5 - Establishment of CDROM ..................... 13
| |
| − | | |
| − | Chapter 6 - Creation of the boot disk .......... 14
| |
| − | | |
| − | Chapter 7 - Some conventions / features
| |
| − | TROPIX ............................... 16
| |
| − | | |
| − | Chapter 8 - Running TROPIX directly from
| |
| − | CDROM or floppy .................... 18
| |
| − | | |
| − | Chapter 9 - Preparation of disks / files
| |
| − | other ............................ 22
| |
| − | | |
| − | Chapter 10 - Modes of TROPIX installation disk
| |
| − | Hard ............................... 23
| |
| − | | |
| − | Chapter 11 - Installation of files in TROPIX
| |
| − | MS-DOS/Windows ....................... 24
| |
| − | | |
| − | Chapter 12 - Disk and partition ................... 26
| |
| − | | |
| − | Chapter 13 - The editor of partitions "fdisk" ........ 28
| |
| − | | |
| − | Chapter 14 - Reducing the size of a partition
| |
| − | MS-DOS/Windows ....................... 32
| |
| − | | |
| − | Chapter 15 - Installation of partitions in TROPIX
| |
| − | own ............................. 35
| |
| − | | |
| − | Chapter 16 - Setting up the USB drivers .... 37
| |
| − | | |
| − | Chapter 17 - What now? ............................. 38
| |
| − | | |
| − | Chapter 18 - Utilities and features original
| |
| − | the TROPIX ............................ 40
| |
| − | | |
| − | Chapter 19 - Introduction to the Graphical Interface
| |
| − | X-Window ............................. 41
| |
| − | | |
| − | Chapter 20 - Creation and installation of the floppy /
| |
| − | archives of the Graphical Interface ........ 42
| |
| − | | |
| − | Chapter 21 - Setting the graphical interface .... 43
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | Version 4.9.0 Updated 10:12:08
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | INSTALL (ref) TROPIX: Installation Guide Pag. 3
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | Chapter 22 - Use of the basic graphical interface 45
| |
| − | | |
| − | Chapter 23 - Obtaining and installing the source code
| |
| − | the TROPIX ............................ 46
| |
| − | | |
| − | Chapter 24 - Compilation of the kernel, libraries and
| |
| − | utilities of TROPIX ................ 47
| |
| − | | |
| − | Chapter 25 - Use the text editor "vi" ....... 48
| |
| − | | |
| − | Chapter 26 - A list of key commands
| |
| − | TROPIX ............................... 49
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | Version 4.9.0 Updated 10:12:08
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | INSTALL (ref) TROPIX: Installation Guide Pag. 4
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | ************************************************** *******
| |
| − | * *
| |
| − | * Chapter 1 *
| |
| − | * *
| |
| − | * INTRODUCTION *
| |
| − | * *
| |
| − | ************************************************** *******
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | The TROPIX (pronounced "trópix") is an Operating System of 32
| |
| − | bit, multiuser and multitasking, philosophy of UNIX ®, developed
| |
| − | the Center for Computer Electronics, Federal University of Rio
| |
| − | January (NCE / UFRJ).
| |
| − | | |
| − | The TROPIX was originally conceived during the years 1982 to 1986
| |
| − | (at the time with the name PLURIX) to the computer PEGASUS. This
| |
| − | computer was built in the NCE, and was based on
| |
| − | MOTOROLA 68010/20 processor. Since its beginning, the system was
| |
| − | designed for symmetric multiprocessing, operating in a
| |
| − | PEGASUS 2 CPUs which had 68,020.
| |
| − | | |
| − | The system was shipped in 1987 to the computer ICARUS,
| |
| − | based on these same processor, and added the
| |
| − | support for real time. Was initiated in 1994 for the transport
| |
| − | Intel line of processors (386, 486, Pentium), and since 1996 the
| |
| − | TROPIX is already operating on PCs and is used in several
| |
| − | computers.
| |
| − | | |
| − | In this version for PCs, is not yet completed the detection of
| |
| − | motherboard with more than one CPU, which is necessary for the
| |
| − | multiprocessing.
| |
| − | | |
| − | In relation to real time, has recently completed a thesis of
| |
| − | Masters was developed in which a version of the core TROPIX
| |
| − | in real time.
| |
| − | | |
| − | The TROPIX has several utilities, such as
| |
| − | study / learning / use of an operating system
| |
| − | UNIX philosophy, the development of programs (software) and
| |
| − | implementation of servers to the Internet. Furthermore, it is ideal
| |
| − | for use in courses on operating systems, it contains
| |
| − | primitive to the "light" ( "threads"), memory
| |
| − | shared, the level of user traffic lights, among others.
| |
| − | | |
| − | This text (which you're reading) contains introductory information
| |
| − | on the distribution and installation of the system TROPIX. During the
| |
| − | installation, it can be viewed / printed on your PC (see
| |
| − | end of Chapter 8). In addition, it contains the information for
| |
| − | Installation of X-Window Graphical Interface (Chapters 19 to 22), and
| |
| − | information for installing / compiling the source code TROPIX
| |
| − | (Chapters 23 and 24).
| |
| − | | |
| − | The operating system is a TROPIX software free, and you are
| |
| − | welcome to redistribute it under certain conditions, for details,
| |
| − | type "man" license (after installation).
| |
| − | | |
| − | Currently, the development and maintenance of TROPIX are
| |
| − | made by Peter and Salenbauch Oswaldo Vernet. For more
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | Version 4.9.0 Updated 10:12:08
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | INSTALL (ref) TROPIX: Installation Guide Pag. 5
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | information, suggestions, reporting errors, or in case of
| |
| − | no doubt about its installation and use, use the
| |
| − | address "tropix@tropix.nce.ufrj.br.
| |
| − | | |
| − | Visit regularly the homepage of TROPIX, at
| |
| − | "http://www.tropix.nce.ufrj.br" to learn about new
| |
| − | system versions.
| |
| − | | |
| − | The continuation of this work is a posthumous tribute to Newton
| |
| − | Faller, the great creator of the projects PEGASUS, PLURIX, and TROPIX
| |
| − | so many others.
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | Version 4.9.0 Updated 10:12:08
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | INSTALL (ref) TROPIX: Installation Guide Pag. 6
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | ************************************************** *******
| |
| − | * *
| |
| − | * Chapter 2 *
| |
| − | * *
| |
| − | * NEW * VERSION OF
| |
| − | * *
| |
| − | ************************************************** *******
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | What's new in this version "4.9.0"
| |
| − | | |
| − | 1: Implement the USB 2.0 protocol.
| |
| − | | |
| − | 2: Supports SATA disks.
| |
| − | | |
| − | 3: New version of the graphical interface (based on version 4.7.0
| |
| − | distributed by Consortium XFree86).
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | To monitor the TROPIX, included the news of
| |
| − | previous versions.
| |
| − | | |
| − | News of version "4.8.0"
| |
| − | | |
| − | 1: File System NFS (Network File System, Version 2),
| |
| − | for the mounting of remote file systems.
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | News of version "4.7.0"
| |
| − | | |
| − | 1: Distribution of object code in ROM.
| |
| − | | |
| − | 2: New graphic utility "xcpu" which draws the graph of Use
| |
| − | CPU.
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | News of version "4.6.0"
| |
| − | | |
| − | 1: Support for USB disks (simulations in memory, "pen drive"),
| |
| − | with annexation / desanexação dynamics.
| |
| − | | |
| − | 2: Mount (read only) file system
| |
| − | NTFS.
| |
| − | | |
| − | 3: Mounting images of file systems (in files
| |
| − | regular).
| |
| − | | |
| − | 4: New version of the graphical interface (based on version 4.4.0
| |
| − | distributed by Consortium XFree86).
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | News of version "4.5.0"
| |
| − | | |
| − | 1: Recognition of "mouse" USB.
| |
| − | | |
| − | 2: New graphic tools: the file manager "xfm",
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | Version 4.9.0 Updated 10:12:08
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | INSTALL (ref) TROPIX: Installation Guide Pag. 7
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | the program to access remote mailboxes "xpop3" and
| |
| − | generate fractal images of Mandelbrot "xmandel.
| |
| − | | |
| − | 3: Extension of the core to enable the sharing of
| |
| − | interrupts (IRQ) between devices.
| |
| − | | |
| − | 4: Access to file systems FAT-32 for more than 4 GB.
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | News of version "4.4.0"
| |
| − | | |
| − | 1: Mounting the File System of Linux EXT2.
| |
| − | | |
| − | 2: Support to the mouse PS / 2.
| |
| − | | |
| − | 3: New version (XFree86 Version 4.3.0) System Chart
| |
| − | X-Window, supporting the most recent of the plates
| |
| − | ATI graphics, and TRIDENT S3.
| |
| − | | |
| − | 4: New features of the library "stdio" with areas of 4 KB for
| |
| − | it compatible with the new file system T1.
| |
| − | | |
| − | 5: Role of 64-bit arithmetic for the values "long long"
| |
| − | the language "C". This is important for access to files
| |
| − | with more than 4 GB.
| |
| − | | |
| − | 6: Access to the history of the "sh" through the keys of arrows
| |
| − | also in text mode.
| |
| − | | |
| − | 7: New commands: The defragmenter "xdefrag" (program
| |
| − | chart) can improve the allocation of blocks of systems
| |
| − | T1 files, the converter program "a2ps" converts a
| |
| − | ISO text to PostScript to be printed on printers
| |
| − | who accept this language.
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | News of version "4.3.0"
| |
| − | | |
| − | 1: The new file system T1, in blocks of 4 KB and
| |
| − | identifiers of up to 255 characters, which has a performance
| |
| − | much higher than the previous file system (S7) of
| |
| − | blocks of 512 bytes. This version continues supporting the
| |
| − | V7 file system.
| |
| − | | |
| − | 2: Create the file "/ etc / fstab" for better control of
| |
| − | assembly of devices.
| |
| − | | |
| − | 3: New interface for recognition devices
| |
| − | IDE / ATA / ATAPI.
| |
| − | | |
| − | 4: Floppy BOOT distribution of the image containing a
| |
| − | file system that is unpacked in a Ramdas (the
| |
| − | simulation of a disk in main memory). This facilitates
| |
| − | installation of TROPIX.
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | News of version "4.2.0"
| |
| − | | |
| − | 1: Increase the size of the areas of entry / exit of the "cache" of
| |
| − | structured devices from 512 to 4096 bytes. With this,
| |
| − | allows the read / write devices that have
| |
| − | larger than 512 bytes (eg CDROM, whose
| |
| − | block is 2 KB) in addition to increasing the speed of
| |
| − | processing of devices already supported.
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | Version 4.9.0 Updated 10:12:08
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | INSTALL (ref) TROPIX: Installation Guide Pag. 8
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | 2: Establishment of the abstract layer of "we-index" to enable
| |
| − | the assembly of several file systems.
| |
| − | | |
| − | 3: Mount the file systems FAT12/16/32.
| |
| − | | |
| − | 4: Mounting the file systems from original CDROM, beyond
| |
| − | extensions "Rock Ridge" and "Joliet".
| |
| − | | |
| − | 5: Implementation of symbolic links.
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | News of version "4.1.0"
| |
| − | | |
| − | 1: New "driver" for the Adaptec SCSI controller: Now
| |
| − | supporting the 29,160 new drivers for 160 MB / s.
| |
| − | | |
| − | 2: Add the "chip" s of the VIA and Intel for the use of DMA
| |
| − | access to IDE.
| |
| − | | |
| − | 3: Extended the build system of language "C" for
| |
| − | accept identifiers without size limitation.
| |
| − | | |
| − | 4: Enter the functions of the library "C" for reading
| |
| − | directories in a system independent of
| |
| − | files: "opendir", "readdir", ...
| |
| − | | |
| − | 5: The "boot" of TROPIX was extended, and now accepts the discs
| |
| − | Iomega ZIP (100 MB) to load the system at all
| |
| − | their steps.
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | News of version "4.0.0"
| |
| − | | |
| − | 1: Improved recognition and assessment of the speed of
| |
| − | processor of the computer during stage 2 of the load
| |
| − | system ( "boot2).
| |
| − | | |
| − | 2: Support for IDE disks over 8 GB.
| |
| − | | |
| − | 3: Recognition Device PnP (Plug and Play ").
| |
| − | | |
| − | 4: Use of DMA to access the IDE (at
| |
| − | only for the "chip" Acer Aladdin ").
| |
| − | | |
| − | 5: Command "mail" completely rewritten, now can receive
| |
| − | and send attachments.
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | News of version "3.2.3"
| |
| − | | |
| − | This version "contained as the main novelty library
| |
| − | shared (similar to Windows DLLs). All
| |
| − | older versions of libraries ( "libc", "libm", "libcurses" and
| |
| − | "libxti") are now grouped in a single library
| |
| − | shared "/ lib / libt.o.
| |
| − | | |
| − | The same occurs also with the libraries of graphical interface
| |
| − | X-Window: all are now integrated in the two
| |
| − | shared library "/ usr / xwin / lib / libx.o" and
| |
| − | "/ usr / xwin / lib / liby.o.
| |
| − | | |
| − | With the use of shared libraries, the size of
| |
| − | executable modules decreased drastically. This
| |
| − | reduced in both the time and amount of cargo
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | Version 4.9.0 Updated 10:12:08
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | INSTALL (ref) TROPIX: Installation Guide Pag. 9
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | occupied space (both on disk and in main memory).
| |
| − | As an example, a typical utility, the "cp" which occupied 13,704
| |
| − | bytes, went to occupy only 4,032, ie, fell short of
| |
| − | third the size. In the case of graphic tools, this
| |
| − | reduction is much greater, mentioned as an example the program
| |
| − | "xedit" which went from 612 KB to less than 4KB!
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | This version also includes some new programs, among
| |
| − | which:
| |
| − | | |
| − | 1: "cdplay: plays audio CDs in units IDE / ATAPI and
| |
| − | SCSI.
| |
| − | | |
| − | 2: "cdtowave": Extract audio tracks from CDs into units
| |
| − | IDE / ATAPI and SCSI.
| |
| − | | |
| − | 3: sbvol "controls the volume (master) of SB-16 boards.
| |
| − | | |
| − | 4: "mkshlib" and "ldshlib" creates and loads the libraries
| |
| − | shared.
| |
| − | | |
| − | 5: "nohup: run command immune to SIGHUP signal.
| |
| − | | |
| − | 6: "paste" lines of a multiple.
| |
| − | | |
| − | 7: "FDC": computer desk for small numbers of point
| |
| − | floating.
| |
| − | | |
| − | 8: "xcoremap" graphics program to draw a map of
| |
| − | allocation of the computer's main memory.
| |
| − | | |
| − | 9: "xedit" graphics program to edit texts (like
| |
| − | the "notepad" in Windows).
| |
| − | | |
| − | 10: "xpaint" now accepts the JPEG format.
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | Other changes / enhancements:
| |
| − | | |
| − | 1: "Drivers for IDE-ATAPI devices: These" drivers "
| |
| − | will allow access to TROPIX-IDE ATAPI devices,
| |
| − | such as CD-ROMs and ZIP drives the internal disk.
| |
| − | However, the file systems on CD-ROMs also
| |
| − | are not being recognized.
| |
| − | | |
| − | 2 "Driver" for driver "Realtek RTL 8129/8139 Fast
| |
| − | Ethernet (10/100 Mbs).
| |
| − | | |
| − | 3: The swap partition is no longer necessary to
| |
| − | installation, both in its own partition, as in
| |
| − | MS-DOS/Windows files.
| |
| − | | |
| − | 4: It is recognized Fax-Modem U.S. Robotics 56K PCI.
| |
| − | | |
| − | 5: Inauguration of distribution of the source code of
| |
| − | TROPIX of libraries and utilities.
| |
| − | | |
| − | 6: The WWW server of TROPIX already allows the resumption of
| |
| − | transfers from the point they were
| |
| − | interrupted.
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | News of version "3.2.1"
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | Version 4.9.0 Updated 10:12:08
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | INSTALL (ref) TROPIX: Installation Guide Pag. 10
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | Includes the first distribution of the source code of the core of
| |
| − | system, recommending him for a further course in systems
| |
| − | operational.
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | News of version "3.2.0"
| |
| − | | |
| − | Contained as the main news media (in part) to
| |
| − | sound card "Sound Blaster".
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | News of version "3.1.8"
| |
| − | | |
| − | Contained as the new X-Window Graphical Interface and
| |
| − | support for file systems MS-DOS/Windows with FAT32.
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | Version 4.9.0 Updated 10:12:08
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | INSTALL (ref) TROPIX: Installation Guide Pag. 11
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | ************************************************** *******
| |
| − | * *
| |
| − | * Chapter 3 *
| |
| − | * *
| |
| − | * FEATURES *
| |
| − | * *
| |
| − | ************************************************** *******
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | The distribution of TROPIX is free, and it can be installed
| |
| − | via a CDROM or floppy.
| |
| − | | |
| − | 1. The CDROM is distributed through an image, and contains the
| |
| − | TROPIX complete object (including the System Chart
| |
| − | X-Window). This image should be used to burn a CDROM
| |
| − | through an appropriate program: see chapter 5.
| |
| − | | |
| − | 2. The distribution by floppy disk is part of the basic
| |
| − | with 2 disks, 3 ½ "and X-Window System in Figure 2
| |
| − | Additional disks: see the chapters 19 to 22.
| |
| − | | |
| − | The installation on PCs can be done in two ways: on partitions
| |
| − | own or in files from one partition to FAT16 or FAT32
| |
| − | MS-DOS/Windows (in this case without the need for change
| |
| − | partitions of disks). It included a manager of cargo
| |
| − | operating systems ( "boot0"), to amicable coexistence with
| |
| − | other operating systems.
| |
| − | | |
| − | Currently the TROPIX has the basic commands of UNIX (in addition to
| |
| − | some more commands themselves), a development system for
| |
| − | the language ANSI "C", support for the network of computers
| |
| − | Internet with TCP / IP, SLIP, PPP (for dial-line) and
| |
| − | Client / Server "telnet", "rlogin", "ftp", "mail", "pop3" and
| |
| − | others.
| |
| − | | |
| − | Whole TROPIX is based on the code character ISO-8859-1
| |
| − | (Latin-1, the same Windows 95/98/NT/2000/XP), taking all the
| |
| − | stress available in all modes (text, graphic) and
| |
| − | commands. Moreover, all the manuals can be found in
| |
| − | screen (on-line), and are in Portuguese.
| |
| − | | |
| − | The file systems MS-DOS/Windows FAT-12/16/32/NTFS (both in
| |
| − | partitions on the disks as hard drives) can be mounted
| |
| − | (the latter only for reading).
| |
| − | | |
| − | For mounting remote file systems we have available the
| |
| − | NFS protocol, version 2.
| |
| − | | |
| − | CD-ROMs can also be fitted to all variants
| |
| − | (ISO-9660, Joliet and Rock-Ridge).
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | Version 4.9.0 Updated 10:12:08
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | INSTALL (ref) TROPIX: Installation Guide Pag. 12
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | ************************************************** *******
| |
| − | * *
| |
| − | * Chapter 4 *
| |
| − | * *
| |
| − | * PC * SETUP
| |
| − | * *
| |
| − | ************************************************** *******
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | The PC must have an Intel processor or equivalent 486/PENTIUM.
| |
| − | The minimum reasonable main memory is 8 MB. With 4 MB can be
| |
| − | use the system, but there may be difficulties in both
| |
| − | use the Internet and compile programs. For the Graphical Interface
| |
| − | X-Window is required at least 16 MB.
| |
| − | | |
| − | The USB drivers are accepted, but the patterns and UHCI
| |
| − | OHCI.
| |
| − | | |
| − | Disks are supported for 3 ½ "and 5 ¼" disk drives and IDE / EIDE.
| |
| − | Also supported SCSI disk drives connected through the
| |
| − | Adaptec 1542 SCSI controller (ISA) and 2940/29160 (PCI).
| |
| − | | |
| − | From version 4.9.0 USB devices are supported with
| |
| − | Protocol 1.1 and 2.0 with annexation / desanexação dynamics.
| |
| − | | |
| − | The Iomega ZIP disks (100 MB) are also supported in versions
| |
| − | the parallel port, IDE / ATAPI and SCSI (where connected to one of
| |
| − | SCSI controllers listed above).
| |
| − | | |
| − | For the Internet, are supported controllers "ethernet"
| |
| − | Novell (NE1000, NE2000 ISA / PCI), 3Com 3c503 and Realtek RTL 8129/8139
| |
| − | Fast Ethernet (10/100 Mbs), and lines with serial protocols
| |
| − | SLIP or PPP.
| |
| − | | |
| − | Are supported also the parallel ports for use of
| |
| − | printers.
| |
| − | | |
| − | Are accepted Fax-modems and ISA Fax-Modem U.S. Robotics 56K PCI.
| |
| − | | |
| − | From version 3.2.0 is also supported the output of digital sound
| |
| − | PCM sound cards through the "Sound Blaster 16 (or successor).
| |
| − | With this, you can play sound files from "*. wav" in TROPIX.
| |
| − | | |
| − | Are already supported "mouse" s USB.
| |
| − | | |
| − | As already mentioned, there are two ways of installing the TROPIX
| |
| − | disks of the PC (see chapter 10). In any of these
| |
| − | modes must be allocated a certain area of the hard disks
| |
| − | (typically 128 MB).
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | Version 4.9.0 Updated 10:12:08
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | INSTALL (ref) TROPIX: Installation Guide Pag. 13
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | ************************************************** *******
| |
| − | * *
| |
| − | * Chapter 5 *
| |
| − | * *
| |
| − | * * CREATING THE CDROM
| |
| − | * *
| |
| − | ************************************************** *******
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | Having obtained the collection "cdrom.tgz" distribution of the CDROM
| |
| − | TROPIX, you must save it.
| |
| − | | |
| − | 1. If you use a UNIX system, must decompress
| |
| − | "cdrom.tgz" via "gunzip" (generating a collection "tar")
| |
| − | and then use the command "tar" to get the files:
| |
| − | | |
| − | install.txt
| |
| − | tropix.iso
| |
| − | | |
| − | The file "install.txt" is the guide to installation (you are
| |
| − | reading) and the file "tropix.iso" is the image of the CDROM.
| |
| − | | |
| − | The CDROM should be recorded through an appropriate utility
| |
| − | (such as "cdrecord").
| |
| − | | |
| − | 2. If you use WinXP/Win2000/WinNT/Win98/Win95/Win3.x should
| |
| − | decompress the collection "cdrom.tgz" through "Winzip",
| |
| − | getting the files:
| |
| − | | |
| − | install.txt
| |
| − | tropix.iso
| |
| − | | |
| − | The file "install.txt" is the guide to installation (you are
| |
| − | reading) and the file "tropix.iso" is the image of the CDROM.
| |
| − | | |
| − | The CDROM should be recorded through an appropriate utility
| |
| − | (such as "Easy CD Creator" or "Nero").
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | Version 4.9.0 Updated 10:12:08
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | INSTALL (ref) TROPIX: Installation Guide Pag. 14
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | ************************************************** *******
| |
| − | * *
| |
| − | * Chapter 6 *
| |
| − | * *
| |
| − | * ESTABLISHMENT OF Floppy Disk "BOOT" *
| |
| − | * *
| |
| − | ************************************************** *******
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | Having obtained the collection "tropix.tgz" distribution of TROPIX
| |
| − | base is necessary (at least) create the disk, 3 ½ "called
| |
| − | of BOOT.
| |
| − | | |
| − | 1. If you use a UNIX system, must decompress
| |
| − | "tropix.tgz" via "gunzip" (generating a collection "tar")
| |
| − | and then use the command "tar" to get the files:
| |
| − | | |
| − | install.txt
| |
| − | fdimage.exe
| |
| − | boot.dsk
| |
| − | gar1.dsk
| |
| − | | |
| − | The file "install.txt" is the guide to installation (you are
| |
| − | reading), the file "fdimage.exe" is a utility to copy
| |
| − | the MS-DOS/Windows (in this case will not be used), and
| |
| − | remaining files are the contents of 2 disks called
| |
| − | the BOOT and GAR1.
| |
| − | | |
| − | The BOOT disk, can be created through a command of
| |
| − | type:
| |
| − | | |
| − | boot.dsk cat> / dev/fd0
| |
| − | | |
| − | (the exact name of the device depends on the system disk
| |
| − | being used).
| |
| − | | |
| − | You can also use the command "dd" in the form:
| |
| − | | |
| − | boot.dsk dd if = of = / dev/fd0
| |
| − | | |
| − | 2. If you use WinXP/Win2000/WinNT/Win98/Win95/Win3.x should
| |
| − | decompress the collection "tropix.tgz" through "Winzip",
| |
| − | getting the files:
| |
| − | | |
| − | install.txt
| |
| − | fdimage.exe
| |
| − | boot.dsk
| |
| − | gar1.dsk
| |
| − | | |
| − | The file "install.txt" is the guide to installation (you are
| |
| − | reading), the "fdimage.exe" is a tool for copying and
| |
| − | remaining files are the contents of 2 disks. The
| |
| − | BOOT floppy disk must be created through a command of
| |
| − | type
| |
| − | | |
| − | fdimage.exe-v boot.dsk A:
| |
| − | | |
| − | For WinXP/Win2000/WinNT, use the window of commands;
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | Version 4.9.0 Updated 10:12:08
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | INSTALL (ref) TROPIX: Installation Guide Pag. 15
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | Win98/Win95/Win3.x to use the DOS mode, in this case not
| |
| − | recommend using the DOS command window, because sometimes the
| |
| − | writing is performed incorrectly.
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | Use a new disk, of good quality. Many of the errors
| |
| − | reported are caused by defective disks.
| |
| − | | |
| − | After the generation of the disk, we protect it against
| |
| − | written.
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | Version 4.9.0 Updated 10:12:08
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | INSTALL (ref) TROPIX: Installation Guide Pag. 16
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | ************************************************** *******
| |
| − | * *
| |
| − | * Chapter 7 *
| |
| − | * *
| |
| − | * SOME CONVENTIONS / FEATURES OF TROPIX *
| |
| − | * *
| |
| − | ************************************************** *******
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | Conceptually, the operating system is similar to TROPIX
| |
| − | UNIX type systems, although there are some differences. To
| |
| − | unambiguous way of describing the installation procedure and use
| |
| − | TROPIX of the PCs, use the conventions described below. Note
| |
| − | and these conventions because they are used in TROPIX as a
| |
| − | whole, including the system after installation.
| |
| − | | |
| − | Keystrokes <enter> means to press the key that has this name;
| |
| − | typing <sp> (blank) means hit the space bar.
| |
| − | | |
| − | Keystrokes <^ D> means press both keys "ctl" and
| |
| − | "D". By doing this, we first compress the key "ctl"
| |
| − | (holding it compressed) and then press the key "D".
| |
| − | Similarly, typing <^ A>, <^ B>, ... means to compress the keys
| |
| − | "ctl" with "A", "B", ... On some keyboards, we have
| |
| − | "ctrl" instead of "ctl".
| |
| − | | |
| − | Keystrokes <ctl-alt-del> means compressing both the three
| |
| − | keys displayed; hit <reset> means of compressing the button
| |
| − | "reset" the PC that, in general, is in the office of the PC (and not in
| |
| − | keyboard).
| |
| − | | |
| − | Keystrokes "-fd0 tropix means hit the keys in sequence" - ",
| |
| − | "f", "d", "0", <sp>, "t", "r", "the", "p", "i", "x" and <enter>. When
| |
| − | specify a string for keyboard (such as
| |
| − | given above) implicitly assume that a keyboard to <enter>
| |
| − | end of the chain (unless it is explicitly stated the
| |
| − | otherwise).
| |
| − | | |
| − | We must remember that in TROPIX, as in all systems
| |
| − | Operating similar to UNIX, uppercase characters are
| |
| − | Different lowercase letters. In the above example, therefore, not
| |
| − | must compress the key <Shift> because the letters to be generated
| |
| − | are all lowercase.
| |
| − | | |
| − | Some of the commands may request a TROPIX
| |
| − | information / confirmation of action. This request is identified by a
| |
| − | "prompt" that can be a character or a string that
| |
| − | system writes to the screen.
| |
| − | | |
| − | In TROPIX, some of the "prompt" s contain a string
| |
| − | brackets before a "." This means that typing
| |
| − | chain or simply typing <enter> have the same effect. This
| |
| − | string of characters is called the "default", ie what
| |
| − | will be interpreted by the lack of a string
| |
| − | explicitly keyboard.
| |
| − | | |
| − | For the question
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | Version 4.9.0 Updated 10:12:08
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | INSTALL (ref) TROPIX: Installation Guide Pag. 17
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | Loads (fd0, tropix)? (s):
| |
| − | | |
| − | is equivalent typing "s" followed by <enter> or simply
| |
| − | <enter>, which means "yes." If you want to answer "no",
| |
| − | we have to hit "n" followed by <enter>.
| |
| − | | |
| − | In some commands, an answer with a capital letter ( "S" or "N")
| |
| − | means that this and all subsequent questions are
| |
| − | answered automatically (yes to "S" and
| |
| − | negatively to "N"). The manual for each command (see below)
| |
| − | information if it follows this convention.
| |
| − | | |
| − | In TROPIX, usually, the system stops writing to the screen
| |
| − | complete a screen (24 lines). This is convenient because the user
| |
| − | have time to read the text without a new text replaces the text
| |
| − | current that (maybe) has not yet been read. To continue
| |
| − | writing the text simply typing <^ Q>. Besides, an output on the screen
| |
| − | can be stopped at any time by typing <^ S>. This can be
| |
| − | changed by the command "stty" (see below).
| |
| − | | |
| − | When entering the "multiplayer" (see below) the TROPIX offers 8
| |
| − | independent virtual screens. The switching between the virtual screens
| |
| − | is done by typing <^ S> (to stop the output in the virtual screen
| |
| − | current), followed by the number of the virtual screen to which want
| |
| − | ir (1 to 8), and finally, <^ Q> (to activate the new screen output
| |
| − | virtual). Note that the number of the current virtual screen is displayed
| |
| − | in the center of the last line.
| |
| − | | |
| − | With certain combinations of keys, used sequentially, we can
| |
| − | generate special characters. Thus, typing up ", to" get "a" and
| |
| − | with "c" get "C". With this method we can get almost all
| |
| − | vowels of strong Western languages. If you do not want this
| |
| − | composition, just typing "\" between the characters. Thus,
| |
| − | example, if keyboard "~ \ the" get "-a".
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | Version 4.9.0 Updated 10:12:08
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | INSTALL (ref) TROPIX: Installation Guide Pag. 18
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | ************************************************** *******
| |
| − | * *
| |
| − | * Chapter 8 *
| |
| − | * *
| |
| − | * RUNNING TROPIX DIRECTLY TO CDROM or Floppy *
| |
| − | * *
| |
| − | ************************************************** *******
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | Both of the CDROM TROPIX (obtained in Chapter 5), such as floppy disk
| |
| − | BOOT (obtained in Chapter 6), contains a compressed image of a
| |
| − | TROPIX file system independent. Both can be implemented
| |
| − | inserting them into the corresponding drive and typing or <ctl-alt-del>
| |
| − | <reset> (this operation, loading the operating system, called
| |
| − | the "boot").
| |
| − | | |
| − | Do not forget to check if the order of several devices in
| |
| − | sequence of "boot" your computer's BIOS is desired.
| |
| − | | |
| − | This is useful for:
| |
| − | | |
| − | 1. TROPIX test the compatibility of your computer. If
| |
| − | have any conflict, notify us (via the
| |
| − | address in Chapter 1).
| |
| − | | |
| − | 2. Run TROPIX experimentally, to know the
| |
| − | system without changing the hard drive of your computer.
| |
| − | | |
| − | 3. Read this guide to install on the computer screen and / or
| |
| − | print it on your printer (see the end of this chapter).
| |
| − | | |
| − | 4. TROPIX install in your computer's hard drive. There
| |
| − | two modes of installation: see Chapter 10.
| |
| − | | |
| − | 5. Fix the TROPIX resident on the hard disk, if
| |
| − | present problems.
| |
| − | | |
| − | After the "reset", the "boot1" (the first stage of operation
| |
| − | "boot") will be read from the CDROM or floppy. It is written the message:
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | TROPIX CD boot1, Version: 4.9.0, from 17:06:06
| |
| − | | |
| − | >
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | <Enter> Key will read the "boot2" (the second stage) of the CDROM
| |
| − | or floppy; after reading, we have the message
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | TROPIX boot2, Version: 4.9.0, from 17:11:08
| |
| − | | |
| − | Copyright © 1988-2008 NCE / UFRJ
| |
| − | | |
| − | Pentium ................................
| |
| − | .................................................. ..
| |
| − | ........ (and other data from computer) ............
| |
| − | .................................................. ..
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | Version 4.9.0 Updated 10:12:08
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | INSTALL (ref) TROPIX: Installation Guide Pag. 19
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | boot>
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | At this point, the "boot2" is awaiting a command. He is a
| |
| − | versatile program, which can (among others) load and run a
| |
| − | program, edit / print the partition table and list the contents
| |
| − | or the memory device. If keyboard "", it prints its
| |
| − | list of commands.
| |
| − | | |
| − | In our case, we hit "-i" to decompress the image of
| |
| − | ROOT file system from the CDROM or floppy disk to an area in
| |
| − | end of main memory. This area will then be used as a
| |
| − | Ramdas, ie the simulation of a disk into memory.
| |
| − | | |
| − | After decompression, the message is written
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | TROPIX Intel x86 - Version 4.9.0 of 28.11.08 ...
| |
| − | | |
| − | Copyright © 1988-2008 NCE / UFRJ
| |
| − | | |
| − | The operating system is distributed TROPIX ABSOLUTELY
| |
| − | NO WARRANTY. This is a "software" free, and you are welcome
| |
| − | to redistribute it under certain conditions, for details,
| |
| − | type "man leave."
| |
| − | | |
| − | Want to change parameters? (n):
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | <Enter> Key again, the message appears
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | TROPIX (Mycomputer) mono [5]:
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | Once reached this point, the operating system already TROPIX
| |
| − | took control in the way "single", with only a
| |
| − | active virtual screen (the one you're using).
| |
| − | | |
| − | Press <^ D>, to come in "multiplayer" in which several
| |
| − | Virtual screens are available. Number will be written
| |
| − | information on the screen, until a line containing:
| |
| − | | |
| − | LOGIN:
| |
| − | | |
| − | Enter "root" and will print the line:
| |
| − | | |
| − | Password:
| |
| − | | |
| − | Then press "tropix" (which will not be ecoado on screen) and finally
| |
| − | will print the line:
| |
| − | | |
| − | root @ Mycomputer: [/ home / root] #
| |
| − | | |
| − | Ready! A critical part was unsuccessful. The TROPIX is already running on
| |
| − | multiuser mode on your computer.
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | During loading, the core of the message write TROPIX
| |
| − | | |
| − | Want to change parameters? (n):
| |
| − | | |
| − | after which normally <Enter> key. With this, we accept the
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | Version 4.9.0 Updated 10:12:08
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | INSTALL (ref) TROPIX: Installation Guide Pag. 20
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | values "default" of parameters, which generally are desired.
| |
| − | We can however modify various parameters, the most common
| |
| − | the rootdev ", ie the device's root system. This parameter
| |
| − | contains the value nodev (ie undefined), and the initialization of
| |
| − | core, it seeks a suitable root. The order of search is:
| |
| − | | |
| − | 1. TROPIX partitions of hard drives (eg "hda2a");
| |
| − | | |
| − | 2. devices simulating disks from files
| |
| − | MS-DOS/Windows (eg "MD1");
| |
| − | | |
| − | 3. CDROMs (eg "hdb" or "sdb").
| |
| − | | |
| − | 4. disks (eg "fd0").
| |
| − | | |
| − | We can change the value "default", with a <raiz desejada>
| |
| − | through
| |
| − | | |
| − | rootdev = <raiz desejada>
| |
| − | | |
| − | and then typing <^ D>. This is useful, for example, when it
| |
| − | we have a root partition on a hard disk or file
| |
| − | MS-DOS/Windows and want to start a new installation from the
| |
| − | CDROM or floppy.
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | Note that the keyboard was that after "LOGIN" is the name of the account ( "root"
| |
| − | in the case) and that the keyboard was after "Password" is that their
| |
| − | password ( "tropix" in case). This means that we are using
| |
| − | the "root", which is the superuser account with credentials (almost)
| |
| − | unlimited. This is necessary during installation, but is not
| |
| − | recommended for normal use.
| |
| − | | |
| − | To see this guide for distribution / installation of the screen
| |
| − | computer, type "man install. To move forward / backward by
| |
| − | several pages of the guide, use the command <^ D>, <^ U>. To view the
| |
| − | content, use "2p" to go directly to the page <n> (obtained
| |
| − | through the content), use "<n> p". To terminate the execution of
| |
| − | "man", enter "q".
| |
| − | | |
| − | To print this guide, use the command
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | cat / usr / man / ref / install> / dev / lp
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | (this is only possible if your PC has the printer on port / IRQ
| |
| − | default). Remember that the guide uses the ISO-8859-1
| |
| − | (Latin-1) character, if your printer does not accept this code
| |
| − | character, use the command
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | stty ascii 2> / dev / lp
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | before the "cat" to remove the accents of the characters.
| |
| − | | |
| − | If your printer is a HP, accepting the PCL language, you
| |
| − | can use the command "hpprint.
| |
| − | | |
| − | Another possibility is to print this guide through
| |
| − | MS-DOS/Windows using the sequence of commands:
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | Version 4.9.0 Updated 10:12:08
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | INSTALL (ref) TROPIX: Installation Guide Pag. 21
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | mount / dev/hda1 / mnt
| |
| − | cp / usr / man / ref / install / mnt
| |
| − | umount / dev/hda1
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | where "/ dev/hda1" should be replaced by a partition DOS / Windows
| |
| − | FAT 16/32 right (in general you can use your own "/ dev/hda1",
| |
| − | it probably is the drive "C"). To obtain the names
| |
| − | the partitions corresponding to MS-DOS/Windows partitions, use the
| |
| − | command "prdisktb.
| |
| − | | |
| − | After these commands, print the file "install" by
| |
| − | MS-DOS/Windows, it is better to use Windows, because the code
| |
| − | of characters used (ISO-8859-1 (Latin-1)).
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | Version 4.9.0 Updated 10:12:08
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | INSTALL (ref) TROPIX: Installation Guide Pag. 22
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | ************************************************** *******
| |
| − | * *
| |
| − | * Chapter 9 *
| |
| − | * *
| |
| − | * PREPARATION OF floppy / * OTHER ARCHIVES
| |
| − | * *
| |
| − | ************************************************** *******
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | This chapter contains information only for installation by
| |
| − | floppy disks. If you are installing from a CDROM, you can
| |
| − | skip it.
| |
| − | | |
| − | Note that the collection "tropix.tgz" contains the image of 2 disks,
| |
| − | BOOT and GAR1. The BOOT disk, has been created in Chapter 6.
| |
| − | | |
| − | If you have a partition DOS / Windows or NTFS on your FAT16/32
| |
| − | computer, creating a floppy GAR1 may be waived. The idea
| |
| − | is to copy the image to a directory "\ TROPIX" partition
| |
| − | DOS / Windows.
| |
| − | | |
| − | 1. If you use a UNIX system, you must use the commands
| |
| − | type:
| |
| − | mount / dev/hda1 / mnt
| |
| − | mkdir / mnt / TROPIX
| |
| − | gar1.dsk cp / mnt / TROPIX
| |
| − | umount / dev/hda1
| |
| − | | |
| − | where "/ dev/hda1" may be replaced by another partition
| |
| − | DOS / Windows you want.
| |
| − | | |
| − | If your partition is NTFS, find out if your UNIX system
| |
| − | supports the writing in these file systems, many
| |
| − | UNIX systems (including Linux) support in general only
| |
| − | reading).
| |
| − | | |
| − | 2. If you use WinXP/Win2000/WinNT/Win98/Win95/Win3.x should
| |
| − | use the "Windows Explorer" to create the directory
| |
| − | "C: \ TROPIX" and then copy the file "gar1.dsk" for the
| |
| − | directory created. Instead of "C", can be used another
| |
| − | desired partition.
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | If you do not have a partition DOS / Windows or NTFS on your FAT16/32
| |
| − | computer, or is wanting to install on another computer TROPIX,
| |
| − | GAR1 the disk must be created.
| |
| − | | |
| − | This should be done the way already seen in Chapter 6 of course
| |
| − | susbtituindo to "boot.dsk" by "gar1.dsk.
| |
| − | | |
| − | Use diskettes new, of good quality. Many of the errors
| |
| − | reported are caused by defective disks.
| |
| − | | |
| − | After creation, we protect the disk against written.
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | Version 4.9.0 Updated 10:12:08
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | INSTALL (ref) TROPIX: Installation Guide Pag. 23
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | ************************************************** *******
| |
| − | * *
| |
| − | * Chapter 10 *
| |
| − | * *
| |
| − | * METHODS OF INSTALLING TROPIX disk *
| |
| − | * *
| |
| − | ************************************************** *******
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | There are two ways to install the disk TROPIX:
| |
| − | | |
| − | 1. In the TROPIX own partitions. This mode offers the best
| |
| − | performance, but the installation requires a certain care.
| |
| − | Can be optionally installed a manager "boot",
| |
| − | to allow the choice of operating system to load.
| |
| − | Follow the sequence of chapters 12, 13, 14, 15, 16 and 17.
| |
| − | | |
| − | 2. In MS-DOS/Windows files. This mode does not offer a
| |
| − | performance as good and "boot" of TROPIX will always be
| |
| − | via CDROM or floppy, but the installation is more
| |
| − | simple. See the chapters 11, 16 and 17.
| |
| − | | |
| − | We suggest you read this guide to the end, before starting the
| |
| − | installation, so you'll have a better overview and can evaluate
| |
| − | the various options appropriately.
| |
| − | | |
| − | The procedures for the installation of TROPIX described here were
| |
| − | made for the installation takes place without setbacks. In
| |
| − | However, it is possible that (by neglect of the user) is the loss of
| |
| − | existing files on your computer and / or the operating system
| |
| − | original (eg MS-DOS/Windows) can not run more.
| |
| − | This may occur mainly due to the misuse of
| |
| − | editor of partitions "fdisk" (Chapter 13).
| |
| − | | |
| − | Even during normal use of the system (after installation
| |
| − | correct), it is possible to accidentally remove files
| |
| − | MS-DOS/Windows for use with mounted FAT partition, or using
| |
| − | the "dosmp.
| |
| − | | |
| − | Although we have tested the operation of the system, believing that
| |
| − | it does not contain any serious error, where there is theoretically a
| |
| − | possibility that, through some error still unknown,
| |
| − | is affected some other operating system.
| |
| − | | |
| − | WE DO NOT LIABLE FOR THESE POSSIBLE ACCIDENTS! YOU
| |
| − | IS INSTALLING / USING TROPIX UNDER ITS OWN
| |
| − | LIABILITY AND RISK!
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | Version 4.9.0 Updated 10:12:08
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | INSTALL (ref) TROPIX: Installation Guide Pag. 24
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | ************************************************** *******
| |
| − | * *
| |
| − | * Chapter 11 *
| |
| − | * *
| |
| − | * INSTALLATION TROPIX IN THE ARCHIVES MS-DOS/Windows *
| |
| − | * *
| |
| − | ************************************************** *******
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | This mode offers a performance not as good as the installation of
| |
| − | Partitions in TROPIX own, in contrast, the installation is more
| |
| − | simply because it is not necessary to rearrange the partitions of the disk.
| |
| − | This method is only possible with file systems FAT-16 or
| |
| − | FAT-32, is still not possible with NTFS.
| |
| − | | |
| − | The idea is to use an existing partition of
| |
| − | MS-DOS/Windows it and create the directory "\ TROPIX" containing 2
| |
| − | files: "ROOT" and "HOME". These files will contain the systems
| |
| − | TROPIX files and load the system will be done through CDROM
| |
| − | or floppy disk.
| |
| − | | |
| − | The steps of the installation are:
| |
| − | | |
| − | 1. Initially it is interesting to verify the integrity of
| |
| − | MS-DOS/Windows partition chosen. For this use the
| |
| − | CHKDSK utility or SCANDISK (MS-DOS or Windows).
| |
| − | | |
| − | Another option is to use NDD (Norton Disk Doctor) of "NORTON
| |
| − | Utilities. "Note the size of available free space of
| |
| − | partition chosen: for a normal installation are
| |
| − | required 128 MB.
| |
| − | | |
| − | 2. As a second step, we defragment the partition
| |
| − | chosen. This means compress all files
| |
| − | MS-DOS/Windows the beginning of the partition, so it is
| |
| − | only a free area at the end, which will create the 2
| |
| − | files in the directory "\ TROPIX. This can be done by
| |
| − | Defrag utility (MS-DOS or Windows) or the DISK SPEED
| |
| − | the "Norton Utilities".
| |
| − | | |
| − | 3. Enter the BOOT ROM or floppy disk and load the TROPIX
| |
| − | system (as in chapter 8). Log in multiuser mode.
| |
| − | | |
| − | 4. Go to the directory "/ usr / etc / install" (use the command "cd
| |
| − | / usr / etc / install "). The normal installation will occupy 128 MB of
| |
| − | MS-DOS/Windows your partition (64 MB for the ROOT, 64 MB for
| |
| − | HOME), which is sufficient for the graphical interface
| |
| − | X-Window. If you have this space available and is
| |
| − | happy with it, go to step 5.
| |
| − | | |
| − | To change the size of the installation, just edit the file
| |
| − | "install.dos" (see chapter 25, for an introduction to the use
| |
| − | the text editor "vi"). To change the size of a
| |
| − | file, simply change the number after the line that
| |
| − | starting with "mkfile.
| |
| − | | |
| − | 5. Start the installation, typing the command "install.dos.
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | Version 4.9.0 Updated 10:12:08
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | INSTALL (ref) TROPIX: Installation Guide Pag. 25
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | Note that with "C:" we are referring to the first partition
| |
| − | regular first disc, ditto with "D" for the second
| |
| − | disc.
| |
| − | | |
| − | This step creates the 2 files in the partition MS-DOS/Windows
| |
| − | chosen, creates file systems and copies the TROPIX
| |
| − | TROPIX files to the hard disk. During installation
| |
| − | (if you're installing from floppy disks) will be
| |
| − | need an additional disk (whose content will be lost)
| |
| − | to be used for the loading of TROPIX. Follow the instructions.
| |
| − | | |
| − | If you want to keep an older version of system
| |
| − | HOME files, DO NOT delete the file MS-DOS/Windows HOME
| |
| − | (disregard the message "The file" home "already exists") and
| |
| − | respond affirmatively to the question "Want to keep the
| |
| − | older version of HOME ".
| |
| − | | |
| − | 6. Congratulations! The TROPIX is already installed and operational in its
| |
| − | hard disk.
| |
| − | | |
| − | If you want to run TROPIX, simply reload the
| |
| − | system (<ctl-alt-del> typing or <reset>) with the CDROM or the
| |
| − | DOS floppy disk inserted. In the case of the CDROM, it is necessary
| |
| − | modify the system root for "MD1" during loading of
| |
| − | nucleus (ie, type 'MD1 = rootdev).
| |
| − | | |
| − | If the CDROM and floppy are not entered, will
| |
| − | loading the operating system standard (eg
| |
| − | MS-DOS/Windows). To exit the TROPIX, use the command
| |
| − | "shutdown".
| |
| − | | |
| − | 7. To uninstall TROPIX its MS-DOS/Windows partition,
| |
| − | simply remove the directory "\ TROPIX" (along with their 2
| |
| − | files).
| |
| − | | |
| − | To facilitate the future installation of a new version of TROPIX,
| |
| − | recommend placing your files only on your private
| |
| − | the "home" (the file name starting with "/ home /...").
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | Version 4.9.0 Updated 10:12:08
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | INSTALL (ref) TROPIX: Installation Guide Pag. 26
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | ************************************************** *******
| |
| − | * *
| |
| − | * Chapter 12 *
| |
| − | * *
| |
| − | Disks and partition * *
| |
| − | * *
| |
| − | ************************************************** *******
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | To install the partitions in TROPIX own (which enables the
| |
| − | best performance) to have a basic concept of how
| |
| − | are organized on PC hard drives.
| |
| − | | |
| − | Each disc is divided into one or more sections called
| |
| − | "partitions". Each of these partitions is designed to be used by
| |
| − | an operating system (in some cases some of the partitions can
| |
| − | be shared by two or more operating systems).
| |
| − | | |
| − | We can have up to 4 partitions "regular" (or "primary") in each
| |
| − | disc. If this number is not enough, we can define one of
| |
| − | partitions as the type "extended", which may contain several
| |
| − | other (sub-) partitions partitions called "logical".
| |
| − | | |
| − | Users of MS-DOS/Windows certainly have had contact with
| |
| − | partitions, since these systems each partition receives a letter,
| |
| − | starting from "C". Thus, we have partitions "C", "D", "E", ...
| |
| − | | |
| − | The nomenclature used in TROPIX is quite different set of letters
| |
| − | above. Let's consider a computer with one IDE disk. The
| |
| − | four partitions are called "hda1", "hda2", "hda3" and
| |
| − | "hda4. If one is "extended" for example "hda3" she
| |
| − | contain the (sub-) partitions "logical" hda3a "," hda3b, "... Besides
| |
| − | this, we have "hda" to represent the disc as a whole.
| |
| − | | |
| − | If your computer has more of an IDE disk, the second is the
| |
| − | "hdb ..." instead of "hda ..." (simply replace the "at" with "b" in
| |
| − | example above). If your computer has SCSI disks, the names will be
| |
| − | "sda ..."," sdb ...", ... (simply replace the "h" in "s" in the example
| |
| − | above).
| |
| − | | |
| − | As already mentioned, we have only one extended partition. By
| |
| − | this, in TROPIX was a new type of partition
| |
| − | extended (the extended partition type TROPIX), structurally
| |
| − | identical to the original, but with a different identification code. The
| |
| − | objective is to enable the grouping of all (sub-) partitions
| |
| − | TROPIX desired in only one partition (extended) alone, even
| |
| − | which is already an extended partition traditional (we call
| |
| − | kind of).
| |
| − | | |
| − | Choosing the distribution of its multiple partitions (one or
| |
| − | mais) disks, must be taken into account how many disks are
| |
| − | present, how many partitions are needed / already allocated, ...
| |
| − | | |
| − | In the example of the next chapter, we create a (new) partition
| |
| − | Extended (Type TROPIX) to include all partitions TROPIX.
| |
| − | This is a simple and elegant, it only need
| |
| − | particiju vague.
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | Version 4.9.0 Updated 10:12:08
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | INSTALL (ref) TROPIX: Installation Guide Pag. 27
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | Naturally, we can also create a partition for each regular
| |
| − | TROPIX desired partition, or adding new partitions
| |
| − | logical TROPIX a DOS extended partition already exists.
| |
| − | | |
| − | For the purpose of "boot", the file system of ROOT can TROPIX
| |
| − | be allocated to any partition of any disk.
| |
| − | | |
| − | If space is available in more than one hard disk,
| |
| − | strongly advised to distribute the partitions between the various
| |
| − | discs.
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | Version 4.9.0 Updated 10:12:08
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | INSTALL (ref) TROPIX: Installation Guide Pag. 28
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | ************************************************** *******
| |
| − | * *
| |
| − | * Chapter 13 *
| |
| − | * *
| |
| − | * The EDITOR of partitions "fdisk" *
| |
| − | * *
| |
| − | ************************************************** *******
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | As with other operating systems also have the TROPIX
| |
| − | your partition editor, who (as usual) is also called
| |
| − | "fdisk". However, TROPIX the "fdisk" is incorporated into
| |
| − | "boot2," and can only be performed during loading of the system (and not
| |
| − | with the system already running). The idea is to emphasize the impossibility
| |
| − | to change the partitions to the system in operation.
| |
| − | | |
| − | To run "fdisk", insert the CDROM or floppy disk of the BOOT
| |
| − | TROPIX, and recharge the system (as in chapter 8). When
| |
| − | arise the "prompt" boot> "the" boot2, "type"-f ":
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | boot>-f
| |
| − | | |
| − | Entering the editor, tables, partitions "fdisk"
| |
| − | | |
| − | Enter "?" for a list of commands
| |
| − | | |
| − | Disk "hda": 6149.88 MB (12594960 blocks) geo = (784, 255, 63, L)
| |
| − | | |
| − | IND. -DEV-AD-START-- END-BLOCK-TAM (MB) TYPE
| |
| − | | |
| − | 1 hda1 * 63 4209029 4208967 2055.16 0C DOS FAT32 (L)
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | The geometry of the disc ( "geo") is given by the number of cylinders
| |
| − | (784), number of heads (255) and the number of sectors per track
| |
| − | (63). The letter "L" indicates that the end to this disc, the extensions
| |
| − | the INT 13 BIOS are active (otherwise, the letter indicated
| |
| − | would be "G").
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | As with the "prompt" the "fdisk", typing "?" get a list
| |
| − | commands available:
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | fdisk>?
| |
| − | | |
| − | Editor of the partition table
| |
| − | | |
| − | commands:
| |
| − | -: Print the partition table
| |
| − | p: Idem with vacancies areas
| |
| − | c: Exchange the device (disk)
| |
| − | n: Creates a new partition
| |
| − | d: Delete a partition
| |
| − | m: Changes the size of a partition
| |
| − | a: Exchange the state (active / not active) partition
| |
| − | l: Prints the types of partitions
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | Version 4.9.0 Updated 10:12:08
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | INSTALL (ref) TROPIX: Installation Guide Pag. 29
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | t: Exchange type of partition
| |
| − | s: Print the vague areas of the disc
| |
| − | u: On / off alignment (starts on)
| |
| − | w: Rewrite (updates) the partition table on disk
| |
| − | q: Terminates the execution of the editor of partitions
| |
| − | | |
| − | Note: For any given application, "n" command cancels the
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | Initially we will create an extended partition to contain the 2
| |
| − | file systems (traditional) of TROPIX. Press "n" and follow the
| |
| − | following dialog (note the choice of the extended partition type):
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | fdisk> n
| |
| − | | |
| − | Give the desired type: regular (r), extended (e) or logical (l): e
| |
| − | | |
| − | Number of partition = 2? (s):
| |
| − | | |
| − | Give the type of extended partition: DOS (d) or TROPIX (x): x
| |
| − | | |
| − | Initial block = 4209030? (s):
| |
| − | | |
| − | End block = 12402179 (4000.56 MB)? (s): n
| |
| − | | |
| − | Take the desired size (MB): 128
| |
| − | | |
| − | Disk "hda": 6149.88 MB (12594960 blocks) geo = (784, 255, 63, L)
| |
| − | | |
| − | IND. -DEV-AD-START-- END-BLOCK-TAM (MB) TYPE
| |
| − | | |
| − | 1 hda1 * 63 4209029 4208967 2055.16 0C DOS FAT32 (L)
| |
| − | 2 hda2 4209030 4482134 273105 133.35 AE TROPIX Extended
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | At this point we can (optionally) use the "u" for not
| |
| − | align the following partitions (see below). The example continues
| |
| − | assuming that we have not the command "u".
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | Then we create a logical partition to the root. Press "n" and
| |
| − | follow the following dialogue:
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | fdisk> n
| |
| − | | |
| − | Give the desired type: regular (r), extended (e) or logical (l): l
| |
| − | | |
| − | Extended partition "hda2":
| |
| − | | |
| − | Initial block = 4209093? (s):
| |
| − | | |
| − | End block = 4482134 (133.32 MB)? (s): n
| |
| − | | |
| − | Take the desired size (MB): 64
| |
| − | | |
| − | Disk "hda": 6149.88 MB (12594960 blocks) geo = (784, 255, 63, L)
| |
| − | | |
| − | IND. -DEV-AD-START-- END-BLOCK-TAM (MB) TYPE
| |
| − | | |
| − | 1 hda1 * 63 4209029 4208967 2055.16 0C DOS FAT32 (L)
| |
| − | 2 hda2 4209030 4482134 273105 133.35 AE TROPIX Extended
| |
| − | 3 hda2a 4209093 4353614 144522 70.57 A9 TROPIX T1
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | Version 4.9.0 Updated 10:12:08
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | INSTALL (ref) TROPIX: Installation Guide Pag. 30
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | Then we create a logical partition to HOME. Press "n" and
| |
| − | follow the following dialogue:
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | fdisk> n
| |
| − | | |
| − | Give the desired type: regular (r), extended (e) or logical (l): l
| |
| − | | |
| − | Extended partition "hda2":
| |
| − | | |
| − | Initial block = 4353678? (s):
| |
| − | | |
| − | End block = 4482134 (62.72 MB)? (s):
| |
| − | | |
| − | Disk "hda": 6149.88 MB (12594960 blocks) geo = (784, 255, 63, L)
| |
| − | | |
| − | IND. -DEV-AD-START-- END-BLOCK-TAM (MB) TYPE
| |
| − | | |
| − | 1 hda1 * 63 4209029 4208967 2055.16 0C DOS FAT32 (L)
| |
| − | 2 hda2 4209030 4482134 273105 133.35 AE TROPIX Extended
| |
| − | 3 hda2a 4209093 4353614 144522 70.57 A9 TROPIX T1
| |
| − | 4 hda2b 4353678 4482134 128457 62.72 A9 TROPIX T1
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | Finally, we will enable the root partition, to allow the load
| |
| − | system ( "boot") by the load manager (the "boot0).
| |
| − | Press "a" and follow the following dialogue:
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | fdisk> to
| |
| − | | |
| − | Index of the partition: 3
| |
| − | | |
| − | Disk "hda": 6149.88 MB (12594960 blocks) geo = (784, 255, 63, L)
| |
| − | | |
| − | IND. -DEV-AD-START-- END-BLOCK-TAM (MB) TYPE
| |
| − | | |
| − | 1 hda1 * 63 4209029 4208967 2055.16 0C DOS FAT32 (L)
| |
| − | 2 hda2 4209030 4482134 273105 133.35 AE TROPIX Extended
| |
| − | 3 hda2a * 4209093 4353614 144522 70.57 A9 TROPIX T1
| |
| − | 4 hda2b 4353678 4482134 128457 62.72 A9 TROPIX T1
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | Once attached to the partition table, we can write it in
| |
| − | disk through the following commands:
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | fdisk> w
| |
| − | | |
| − | Rewrites the partition table? (n): s
| |
| − | | |
| − | fdisk> q
| |
| − | | |
| − | Leaving the editor, tables, partitions
| |
| − | | |
| − | boot>
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | The only command "dangerous" is the "w" (with the confirmation),
| |
| − | as all other commands only modify the table of
| |
| − | partitions in main memory, not update it on your hard disk.
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | Version 4.9.0 Updated 10:12:08
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | INSTALL (ref) TROPIX: Installation Guide Pag. 31
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | So you can "play" at will, creating and removing
| |
| − | partitions, until you are satisfied with your configuration, giving
| |
| − | then the "w" final.
| |
| − | | |
| − | Note that the data sizes (128 MB, 64 MB and 64 MB) were
| |
| − | followed exactly, in fact they were rounded to
| |
| − | multiples of the size of the cylinder of the disk. As this disc has a
| |
| − | reasonably large cylinder (255 * 63 = 16065 blocks = ~ 7.8 MB)
| |
| − | differences are significant. One way to avoid this is to use
| |
| − | command "u", which prevents the rounding.
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | Version 4.9.0 Updated 10:12:08
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | INSTALL (ref) TROPIX: Installation Guide Pag. 32
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | ************************************************** *******
| |
| − | * *
| |
| − | * Chapter 14 *
| |
| − | * *
| |
| − | * Reduce the size of a partition MS-DOS/Windows *
| |
| − | * *
| |
| − | ************************************************** *******
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | One of the most frequent is to PCs that have only one disk
| |
| − | Rigid fully occupied with only one partition MS-DOS/Windows,
| |
| − | corresponding to "C:".
| |
| − | | |
| − | In this case, at first sight, there are only 2 possibilities for
| |
| − | more space for partitions TROPIX: install a new hard disk,
| |
| − | or save your files and reinstall MS-DOS/Windows
| |
| − | MS-DOS/Windows in a partition of smaller size.
| |
| − | | |
| − | A third possibility is to reduce the partition
| |
| − | MS-DOS/Windows in their location (ie, without destroying the
| |
| − | its contents). This can be done by the command "chsize" of
| |
| − | utility "dosmp. You can also use the "fips" of
| |
| − | LINUX, or the program Partition Magic, Powerquest's name, if
| |
| − | you by chance have the.
| |
| − | | |
| − | Before using the command "chsize", to reduce the size of
| |
| − | MS-DOS/Windows partition, it is essential to verify its integrity and
| |
| − | defragmenting it. The verification of integrity can be made by
| |
| − | CHKDSK utility or SCANDISK (the MS-DOS/Windows) or NDD
| |
| − | (Norton Disk Doctor) of "Norton Utilities". The defragmentação can
| |
| − | be made by the defrag utility (the MS-DOS/Windows), or the SPEED
| |
| − | DISK of "Norton Utilities".
| |
| − | | |
| − | Remember that the programs of defragmentation may NOT
| |
| − | move the file to swap the MS-DOS/Windows. You must remove it
| |
| − | (using the "Control Panel") and then reinstall it.
| |
| − | | |
| − | If you or MIRROR IMAGE USA, the last sector of the partition contains a
| |
| − | file "hidden" name of "\ image.idx" or "\ mirorsav.fil. You must
| |
| − | remove this file (using "attrib" and "del"). It will be recreated
| |
| − | the next time you run or MIRROR IMAGE (we hope,
| |
| − | not tested).
| |
| − | | |
| − | Another source of problems are the files named "* \ desktop .*", the
| |
| − | which Windows does not move: they must be saved and later
| |
| − | restored.
| |
| − | | |
| − | If you a USA system compressed files with "Stacker,"
| |
| − | "SuperStor", "Doublespace," ... possibly (?) "Chsize" will not
| |
| − | work. Not tested "chsize" in these cases (even if we know
| |
| − | PARTITION MAGIC the support).
| |
| − | | |
| − | After defragmentation, insert the CDROM or floppy disk of the BOOT
| |
| − | TROPIX and push the system (as in chapter 8), entering the
| |
| − | multiuser mode.
| |
| − | | |
| − | Remove the boot floppy (if you are installing from
| |
| − | floppy disk) and insert a floppy disk (for example MS-DOS/Windows) and
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | Version 4.9.0 Updated 10:12:08
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | INSTALL (ref) TROPIX: Installation Guide Pag. 33
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | mount it by
| |
| − | | |
| − | mount / dev/fd0 / fd0
| |
| − | | |
| − | This disk is intended to store the original superbloco
| |
| − | MS-DOS/Windows file system in case of any
| |
| − | problems.
| |
| − | | |
| − | Then press
| |
| − | | |
| − | cd / fd0
| |
| − | dosmp / dev/hda1
| |
| − | | |
| − | where "/ dev/hda1" should be replaced by the corresponding partition
| |
| − | MS-DOS/Windows the file system in question (in general will be
| |
| − | the "/ dev/hda1" which is the drive "C").
| |
| − | | |
| − | Typing
| |
| − | | |
| − | chsize
| |
| − | | |
| − | get (eg):
| |
| − | | |
| − | Size of the existing DOS partition = 511.84 MB
| |
| − | Current size of the file system DOS = 511.84 MB
| |
| − | Space available at the end = 427.26 MB
| |
| − | | |
| − | Make sure the free space available is sufficient for the new
| |
| − | desired partition. In our example, we have enough space for the
| |
| − | typical case of 128 MB (427.26> 128). Remember of course
| |
| − | leave some room for future (new) files DOS.
| |
| − | | |
| − | To free up 128 MB (which will be used for the new partition to be
| |
| − | created for the TROPIX), we hit
| |
| − | | |
| − | rw
| |
| − | chsize-s 128
| |
| − | | |
| − | and get (for example):
| |
| − | | |
| − | Size of the existing DOS partition = 511.84 MB
| |
| − | Current size of the file system DOS = 511.84 MB
| |
| − | Space available at the end = 427.26 MB
| |
| − | | |
| − | The new DOS partition size = 382.03 MB
| |
| − | (782401 blocks)
| |
| − | Size of new file system DOS = 382.03 MB
| |
| − | Size of the new partition (to be created) = 129.81 MB
| |
| − | (265856 blocks)
| |
| − | | |
| − | Continue? (n):
| |
| − | | |
| − | Note that the values are not exactly the requests due to
| |
| − | rounding to whole cylinders.
| |
| − | | |
| − | If we agree with the values given, we hit "s" and note
| |
| − | the values given: the new DOS partition size = 382.03 MB, 782,401
| |
| − | blocks and size of new partition (to be created) = 129.81 MB,
| |
| − | 265856 blocks.
| |
| − | | |
| − | The command "dosmp" superbloco saves the original system
| |
| − | DOS files in the file "dos_sb" the current directory (if in
| |
| − | mounted disk) to the case of any problems.
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | Version 4.9.0 Updated 10:12:08
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | INSTALL (ref) TROPIX: Installation Guide Pag. 34
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | Then we do "dosmp" (with "q") and TROPIX (with "reboot").
| |
| − | | |
| − | MS-DOS/Windows again between the system and make sure he
| |
| − | still functioning properly. Check the integrity of
| |
| − | file system (usually "C:") and if all your files
| |
| − | remain accessible.
| |
| − | | |
| − | If there is a problem with the system MS-DOS/Windows, restore the
| |
| − | original file system, reload the TROPIX and running
| |
| − | commands
| |
| − | | |
| − | mount / dev/fd0 / fd0
| |
| − | cd / fd0
| |
| − | dos_sb dd if = of = / dev/hda1
| |
| − | | |
| − | with the disk on which was stored in the original superbloco
| |
| − | DOS system. In this case, notify us (using the address
| |
| − | e of Chapter 1) the failure of "chsize.
| |
| − | | |
| − | Once established that the system is working MS-DOS/Windows
| |
| − | correctly, use the "fdisk" the TROPIX (as
| |
| − | Chapter 13) to change the partition table.
| |
| − | | |
| − | Initially, change the size of the DOS partition (using
| |
| − | command "m"). The new size (value in blocks) should be
| |
| − | exactly the size noted above (in this case, 382.03 MB, 782,401
| |
| − | blocks).
| |
| − | | |
| − | Finally, create a partition in space TROPIX released as
| |
| − | example in Chapter 13 (in this case, 129.81 MB, 265856 blocks).
| |
| − | | |
| − | Ready! It is time to install the new partition TROPIX,
| |
| − | as Chapter 15.
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | Version 4.9.0 Updated 10:12:08
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | INSTALL (ref) TROPIX: Installation Guide Pag. 35
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | ************************************************** *******
| |
| − | * *
| |
| − | * Chapter 15 *
| |
| − | * *
| |
| − | * INSTALLATION TROPIX on partitions OWN *
| |
| − | * *
| |
| − | ************************************************** *******
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | This is the best way, it offers the best performance and
| |
| − | allows the installation of "boot0," a manager "boot". This
| |
| − | manager allows the choice of operating system to load (from
| |
| − | TROPIX way that can be loaded without the use of CDROM or
| |
| − | diskette). He has been tested with Linux, FreeBSD and
| |
| − | DOS/WinXP/Win2000/WinNT/Win98/Win95/Win3.x.
| |
| − | | |
| − | If you're reading this chapter, we assume that you already have space in
| |
| − | TROPIX disk partitions and have to learn how to use the editor,
| |
| − | partitions "fdisk".
| |
| − | | |
| − | The idea is to create two or more partitions for TROPIX. The
| |
| − | minimum is to create a root partition. We recommend, however,
| |
| − | create at least one more, HOME, to contain the files
| |
| − | private users.
| |
| − | | |
| − | If you have 128 MB available, we suggest 64 MB and 64 MB for ROOT
| |
| − | for HOME, these sizes will be sufficient even for
| |
| − | X-Window graphical interface. If you have more space available, you can
| |
| − | increase the sizes of partitions, or to create partitions
| |
| − | additional.
| |
| − | | |
| − | The steps of the installation are:
| |
| − | | |
| − | 1. Create partitions for TROPIX by the editor of
| |
| − | partitions "fdisk" (see chapter 13). DO NOT forget to
| |
| − | "enable" the root partition. It is not necessary that the partition
| |
| − | ROOT (which will be given the "boot") is the first disc.
| |
| − | | |
| − | We suggest creating an extended partition type to TROPIX
| |
| − | contain the various partitions needed / desired, that the
| |
| − | But it is not necessary: it is more convenient for your
| |
| − | case, the partitions TROPIX may also be of the "regular"
| |
| − | ( "primary"), or logical partitions within a
| |
| − | DOS extended partition type. If you have more than one
| |
| − | disk, it is interesting to distribute the various partitions by
| |
| − | disks.
| |
| − | | |
| − | 2. Enter the BOOT ROM or floppy disk and load the TROPIX
| |
| − | system (as in chapter 8). Log in multiuser mode.
| |
| − | | |
| − | 3. Go to the directory "/ usr / etc / install" (use the command "cd
| |
| − | / usr / etc / install "). Start the installation via the command
| |
| − | "install". This step creates file systems in TROPIX
| |
| − | selected partition and copies the files of the fundamental
| |
| − | TROPIX to the hard disk. Follow the instructions.
| |
| − | | |
| − | If you want to keep an older version of system
| |
| − | HOME files, answer yes to question "Would
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | Version 4.9.0 Updated 10:12:08
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | INSTALL (ref) TROPIX: Installation Guide Pag. 36
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | keep the old version of HOME ", and for a copy of
| |
| − | files does not permit the rewriting of the files. "profile."
| |
| − | | |
| − | Congratulations! The TROPIX is already installed and operational on your disk
| |
| − | rigid.
| |
| − | | |
| − | If you installed the manager, "boot" to run
| |
| − | TROPIX, recharge the system with the CDROM or floppy inserted BOOT,
| |
| − | and "prompt"
| |
| − | | |
| − | boot>
| |
| − | | |
| − | <enter> hit. If the system is recharged without CDROM or
| |
| − | will load the disk operating system "normal" (eg
| |
| − | Windows 95/98).
| |
| − | | |
| − | If you install the manager, after the recharge of the system
| |
| − | manager prints a list of partition "active" of its
| |
| − | several disks, and hopes you hit the index of the partition
| |
| − | desired. The partition "default" can be modified through
| |
| − | command "edboot.
| |
| − | | |
| − | To exit the system TROPIX, use "shutdown".
| |
| − | | |
| − | If the manager of "boot" does not work, reload the TROPIX
| |
| − | via CDROM or floppy BOOT (enter in multiuser mode) and
| |
| − | restore the original manager, running the command-type
| |
| − | | |
| − | cat / etc / boot / mbr> / dev / hda
| |
| − | | |
| − | and notify us (via e-mail address in Chapter 1) to
| |
| − | failure of "boot0.
| |
| − | | |
| − | To facilitate the future installation of a new version of TROPIX,
| |
| − | recommend placing your files only on your private
| |
| − | the "home" (the file name starting with "/ home /...").
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | Version 4.9.0 Updated 10:12:08
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | INSTALL (ref) TROPIX: Installation Guide Pag. 37
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | ************************************************** *******
| |
| − | * *
| |
| − | * Chapter 16 *
| |
| − | * *
| |
| − | * SET OF USB DRIVERS *
| |
| − | * *
| |
| − | ************************************************** *******
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | O TROPIX (na versão atual) suporta controladores USB dos padrões
| |
| − | UHCI, OHCI e EHCI.
| |
| − | | |
| − | Há previsão de até 8 controladores ("usb0" a "usb7"); o sistema vem
| |
| − | configurado com os controladores "usb0" a "usb3" habilitados e os
| |
| − | demais desabilitados.
| |
| − | | |
| − | Isto pode ser alterado (somente para esta execução do sistema)
| |
| − | através da modificação de parâmetros durante a carga do sistema;
| |
| − | responda afirmativamente à pergunta
| |
| − | | |
| − | Deseja modificar parâmetros? (n):
| |
| − | | |
| − | tal como mencionado no capítulo 8, e altere os valores de "usb0" a
| |
| − | "usb7" para 0 ou 1.
| |
| − | | |
| − | Para a habilitação/desabilitação dos controladores (de modo
| |
| − | permamente) use o comando "edscb" (Use "man scb" e "man edscb").
| |
| − | | |
| − | Para verificar se o controlador USB está sendo reconhecido
| |
| − | corretamente, acompanhe as mensagens durante a carga do sistema (ou
| |
| − | então use o comando "dmesg" posteriormente).
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | Version 4.9.0 Updated 10:12:08
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | INSTALL (ref) TROPIX: Installation Guide Pag. 38
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | ************************************************** *******
| |
| − | * *
| |
| − | * Capítulo 17 *
| |
| − | * *
| |
| − | * E AGORA ...? *
| |
| − | * *
| |
| − | ************************************************** *******
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | Uma vez com o sistema implantado e em funcionamento, temos todos os
| |
| − | manuais do TROPIX (em português) à disposição através do utilitário
| |
| − | "man". Além disto, todos os comandos fornecem um pequeno resumo de
| |
| − | sua utilização através da opção "-H" (por exemplo "passwd -H").
| |
| − | | |
| − | Para consultar o manual do utilitário "passwd" (por exemplo), tecle
| |
| − | "man passwd". Para avançar/retroceder pelas várias páginas dos
| |
| − | manuais, temos os comandos <^D>, <^U>. Para encerrar a execução de
| |
| − | "man", use "q". Experimente "man man".
| |
| − | | |
| − | Recomendamos inicialmente a modificação da senha da conta "root" e
| |
| − | a criação de contas regulares (isto é, NÃO superusuários). Para a
| |
| − | modificação de senhas, utilize o comando "passwd"; para a
| |
| − | criação/gerência de contas, use o comando "edusr".
| |
| − | | |
| − | Também uma tarefa importante é a atualização do arquivo
| |
| − | "/etc/fstab", que contém informações dos sistemas de arquivos a
| |
| − | montar. Leia o manual de "fstab" (fmt), "getmntent" (libc) e
| |
| − | "mount" (cmd). Em particular, se você não tiver a partição HOME,
| |
| − | remova a linha correspondente de "/etc/fstab".
| |
| − | | |
| − | De vez em quando (digamos, uma vez por semana) é interessante
| |
| − | verificar a integridade dos sistemas de arquivos. Para tanto, após
| |
| − | a carga do sistema (ainda em modo "monousuário"), utilize o comando
| |
| − | "fsck". Repare que o arquivo "/etc/fstab" também controla os
| |
| − | sistemas de arquivos examinados por "fsck" (convém colocar o
| |
| − | "/dev/root" como o último da lista). Para obter uma lista de todas
| |
| − | as partições presentes nos diversos discos do seu computador, use
| |
| − | "prdisktb".
| |
| − | | |
| − | Através do comando "edscb" você pode alterar o nome do computador
| |
| − | ("nodename") e acertar as portas/IRQs dos seus dispositivos (portas
| |
| − | seriais, paralelas, "ethernet", ...). Use "man scb" e "man edscb".
| |
| − | | |
| − | O TROPIX é distribuído com o DMA dos controladores IDE desligados,
| |
| − | pois com certos controladores podem surgir problemas. Experimente
| |
| − | ligá-lo através de "dmaenable=1", inicialmente durante o "boot"
| |
| − | para testar, e se funcionar adequadamente, no arquivo "/tropix"
| |
| − | através do utilitário "edscb". Com isto, você aumentará a
| |
| − | performance dos seus discos rígidos IDE.
| |
| − | | |
| − | Leia o capítulo 26, onde é dada uma lista dos principais comandos
| |
| − | do TROPIX.
| |
| − | | |
| − | Aprenda a usar o "histórico" do "sh". Ele permite reexecutar
| |
| − | comandos, inclusive com modificações (cada linha do histórico pode
| |
| − | ser editada com os mesmos comandos do "vi", antes de ser
| |
| − | reexecutada).
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | Version 4.9.0 Updated 10:12:08
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | INSTALL (ref) TROPIX: Installation Guide Pag. 39
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | Esta versão do TROPIX já possui o utilitário "sbwave" para tocar
| |
| − | músicas PCM através de placas "Sound Blaster" ISA, veja o manual.
| |
| − | | |
| − | Durante a instalação, a INTERNET já é configurada para funcionar no
| |
| − | modo interno ("loopback"), o que é necessário pela Interface
| |
| − | Gráfica X-Window. Para configurar a INTERNET para o uso com outros
| |
| − | dispositivos, use "man internet".
| |
| − | | |
| − | Para a montagem de sistemas de arquivos remotos através do Sistema
| |
| − | de Arquivos NFS (Network File System), use "man nfs".
| |
| − | | |
| − | Leia o capítulo 18: ele menciona características não convencionais
| |
| − | do TROPIX, as quais incluímos no sistema por considerá-las úteis.
| |
| − | | |
| − | Para instalar a Interface Gráfica X-Window, consulte os capítulos
| |
| − | 19 a 22.
| |
| − | | |
| − | Para obter/compilar o código fonte do TROPIX, consulte os capítulos
| |
| − | 23 e 24.
| |
| − | | |
| − | Naturalmente, este capítulo dá apenas o resumo de uma direção geral
| |
| − | a tomar. O ideal é consultar um livro de introdução ao UNIX.
| |
| − | | |
| − | Esperamos que o TROPIX lhe seja útil, tanto no aprendizado de
| |
| − | sistemas de filosofia UNIX, como na utilização de mais um sistema
| |
| − | operacional. Em caso de dúvidas ou relatos de erros, utilize o
| |
| − | endereço eletrônico do capítulo 1.
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | Version 4.9.0 Updated 10:12:08
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | INSTALL (ref) TROPIX: Installation Guide Pag. 40
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | ************************************************** *******
| |
| − | * *
| |
| − | * Capítulo 18 *
| |
| − | * *
| |
| − | * CARACTERÍSTICAS E UTILITÁRIOS ORIGINAIS DO TROPIX *
| |
| − | * *
| |
| − | ************************************************** *******
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | Embora o TROPIX seja um sistema de filosofia UNIX, há algumas
| |
| − | características originais que não são encontradas em outros
| |
| − | sistemas deste tipo. A seguir são dadas algumas destas
| |
| − | originalidades:
| |
| − | | |
| − | 1. Na maioria dos sistemas UNIX, quando listamos um arquivo de
| |
| − | várias páginas no vídeo, ele "rola" fora da tela antes que
| |
| − | possamos le-lo. Temos então de usar o comando "more" na forma
| |
| − | | |
| − | cat texto.txt | more
| |
| − | | |
| − | ou então,
| |
| − | | |
| − | more texto.txt
| |
| − | | |
| − | Isto é o caso, também, se usamos o comando "ls -l" com
| |
| − | diretórios contendo muitos arquivos.
| |
| − | | |
| − | No TROPIX, isto não é necessário; a saída do vídeo é pausada
| |
| − | quando ela completa o número de linhas visíveis. To
| |
| − | continuar a saída no vídeo, basta teclar <^Q>.
| |
| − | | |
| − | Isto pode ser alterado através do comando "stty" (veja o
| |
| − | respectivo manual).
| |
| − | | |
| − | 2. O utilitário "show": permite visualizar um arquivo de texto
| |
| − | de forma conveniente no vídeo, podendo avançar/retroceder
| |
| − | sobre o texto com comandos semelhantes ao do editor de textos
| |
| − | "vi". É especialmente útil para examinar a saída de um
| |
| − | programa, usando um "pipe" (veja o manual).
| |
| − | | |
| − | 3. O comando "gar": este utilitário é uma extensão do "tar",
| |
| − | padrão do mundo UNIX. O "gar", além de criar/extrair coleções
| |
| − | do formato "tar", extrair coleções do formato "cpio", ele
| |
| − | cria/extrai/compara/adiciona coleções do formato próprio
| |
| − | ("gar") com/sem compactação. Você certamente já utilizou o
| |
| − | "gar" ao instalar o TROPIX (veja o manual).
| |
| − | | |
| − | 4. Os utilitários "cmptree/cptree"; permitem
| |
| − | copiar/comparar/atualizar árvores do sistema de arquivos
| |
| − | locais ao próprio computadores (veja o manual).
| |
| − | | |
| − | 5. A família de utilitários "tcmpto": permite
| |
| − | copiar/comparar/atualizar árvores do sistema de arquivos
| |
| − | de/entre o computador local e um computador remoto, através
| |
| − | de protocolo próprio TCP/IP (veja o manual).
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | Version 4.9.0 Updated 10:12:08
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | INSTALL (ref) TROPIX: Installation Guide Pag. 41
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | ************************************************** *******
| |
| − | * *
| |
| − | * Capítulo 19 *
| |
| − | * *
| |
| − | * INTRODUÇÃO À INTERFACE GRÁFICA X-WINDOW *
| |
| − | * *
| |
| − | ************************************************** *******
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | O sistema X-Window para o TROPIX é uma interface gráfica baseada na
| |
| − | versão 4.7.0 distribuída pelo Consórcio XFree86.
| |
| − | | |
| − | A presente versão inclui servidores específicos para algumas das
| |
| − | placas gráficas mais usuais. Além disto, são distribuídos os
| |
| − | clientes indispensáveis para o funcionamento mínimo do sistema.
| |
| − | | |
| − | Apesar de os monitores modernos possuírem circuitos de proteção
| |
| − | contra o uso com freqüências horizontal e/ou vertical indevidas,
| |
| − | sempre existe teoricamente a possibilidade de danificar o seu
| |
| − | monitor.
| |
| − | | |
| − | NÓS NÃO NOS RESPONSABILIZAMOS POR ESTES POSSÍVEIS DANOS AO SEU
| |
| − | MONITOR. VOCÊ ESTÁ INSTALANDO/UTILIZANDO A INTERFACE GRÁFICA DO
| |
| − | TROPIX SOB SUA PRÓPRIA RESPONSABILIDADE E RISCO!
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | Version 4.9.0 Updated 10:12:08
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | INSTALL (ref) TROPIX: Installation Guide Pag. 42
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | ************************************************** *******
| |
| − | * *
| |
| − | * Capítulo 20 *
| |
| − | * *
| |
| − | * CRIAÇÃO E INSTALAÇÃO DOS DISQUETES/ARQUIVOS *
| |
| − | * DA INTERFACE GRÁFICA *
| |
| − | * *
| |
| − | ************************************************** *******
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | Este capítulo contém informações apenas para a instalação através
| |
| − | de disquetes. Se você está instalando através de um CDROM, pode
| |
| − | pulá-lo.
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | A distribuição da Interface Gráfica X-Window é feita através da
| |
| − | coleção "xwin.tgz": obtenha-a na página do TROPIX
| |
| − | ("http://tropix.nce.ufrj.br").
| |
| − | | |
| − | Uma vez tendo obtida esta coleção, é necessário preparar os 2
| |
| − | arquivos ou criar os 2 disquetes de 3½". Ela contém os seguintes
| |
| − | arquivos:
| |
| − | | |
| − | fdimage.exe
| |
| − | xwin1.dsk
| |
| − | xwin2.dsk
| |
| − | | |
| − | O arquivo "fdimage.exe" é um utilitário de cópia para os Windows
| |
| − | (você provavelmente já o tem, obtido durante a instalação do TROPIX
| |
| − | básico), e os arquivos restantes são os conteúdos dos 2 disquetes.
| |
| − | | |
| − | Assim como no caso do TROPIX básico, se você possui uma partição
| |
| − | DOS/Windows FAT16/32 ou NTFS em seu computador, a criação dos
| |
| − | disquetes XWIN1 e XWIN2 pode ser dispensada. Siga o roteiro do
| |
| − | capítulo 9 (substituindo "gar1" por "xwin1" e "xwin2").
| |
| − | | |
| − | Uma vez com os disquetes ou arquivos preparados, entre no sistema
| |
| − | TROPIX (como superusuário), vá para o diretório "/usr/etc/install",
| |
| − | e execute o comando
| |
| − | | |
| − | install.xwin
| |
| − | | |
| − | e siga as suas instruções. O sistema necessita de cerca de 10 MB no
| |
| − | disco.
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | Version 4.9.0 Updated 10:12:08
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | INSTALL (ref) TROPIX: Installation Guide Pag. 43
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | ************************************************** *******
| |
| − | * *
| |
| − | * Capítulo 21 *
| |
| − | * *
| |
| − | * CONFIGURAÇÃO DA INTERFACE GRÁFICA *
| |
| − | * *
| |
| − | ************************************************** *******
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | Uma vez instalados todos os arquivos da Interface Gráfica X-Window
| |
| − | (se você está instalando através do CDROM isto é automático, para o
| |
| − | caso de disquetes veja o capítulo anterior), vamos dar a seguir o
| |
| − | método passo a passo para a configuração do sistema. Isto deve ser
| |
| − | feito como superusuário.
| |
| − | | |
| − | 1. Configuração da "internet": Ela deverá está ativa, pelo menos
| |
| − | para acessos internos ("loopback"); isto normalmente, a
| |
| − | instalação do TROPIX já realiza. Para maiores detalhes, veja
| |
| − | o manual "internet" (através do comando "man").
| |
| − | | |
| − | 2. Especificação do "mouse": O sistema vem configurado para o
| |
| − | "mouse" PS/2.
| |
| − | | |
| − | Para outros tipos de "mouse, o arquivo
| |
| − | "/usr/xwin/conf/xconfig" deverá ser editado. Se o seu "mouse"
| |
| − | for serial (COM1, COM2) ou USB, mova os dois caracteres "#"
| |
| − | das linhas do seu tipo de "mouse" para as duas linhas do
| |
| − | "mouse" PS/2.
| |
| − | | |
| − | Use o utilitário "dmesg" para verificar se, durante a carga
| |
| − | do sistema, o seu "mouse" está sendo reconhecido.
| |
| − | | |
| − | 3. Execução do servidor no modo de 16 cores (4 bits).
| |
| − | Inicialmente o arquivo de configuração
| |
| − | "/usr/xwin/conf/xconfig" está preparado para executar o
| |
| − | servidor no modo gráfico do padrão VGA, de 16 cores e
| |
| − | resolução de 640x480 e 800x600. Este modo deve funcionar com
| |
| − | qualquer placa gráfica, e será sua (única) opção caso a sua
| |
| − | placa não tenha sucesso nas tentativas abaixo.
| |
| − | | |
| − | Para tanto, basta teclar o comando "startx" (sem ter alterado
| |
| − | o arquivo de configuração). O sistema iniciará com o fundo
| |
| − | padrão do TROPIX, duas janelas "xterm", um relógio e um
| |
| − | selecionador de "desktops". Em cada janela "xterm" é
| |
| − | executado o interpretador de comandos padrão "sh".
| |
| − | | |
| − | Para voltar ao modo texto, a maneira mais simples é teclar
| |
| − | simultaneamente <ctl-alt-bs>.
| |
| − | | |
| − | Este é o modo mais básico de funcionamento do sistema
| |
| − | X-Window; se ele não funcionar envie-nos os arquivos
| |
| − | "/var/log/xwin/xserver.log" e "/var/log/xwin/xclients.log"
| |
| − | para o endereço eletrônico do capítulo 1.
| |
| − | | |
| − | 4. Determinação da placa gráfica: Uma vez funcionando no modo de
| |
| − | 16 cores, podemos verificar se existe a possibilidade de
| |
| − | utilizar um servidor específico para a sua placa gráfica.
| |
| − | Isto proporcionará a possibilidade de usar uma gama maior de
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | Version 4.9.0 Updated 10:12:08
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | INSTALL (ref) TROPIX: Installation Guide Pag. 44
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | cores, e outras resoluções (800x600, 1024x768, 1280x1024,
| |
| − | ...).
| |
| − | | |
| − | Dependendo da sua placa gráfica, podemos editar o arquivo de
| |
| − | configuração "/usr/xwin/conf/xconfig". Se for uma placa ATI,
| |
| − | coloque em comentário as linhas:
| |
| − | | |
| − | Driver "svga"
| |
| − | Device "Generic VGA"
| |
| − | | |
| − | colocando um "#" no início da linha, e tire o comentário das
| |
| − | linhas:
| |
| − | | |
| − | Driver "accel"
| |
| − | Device "ati"
| |
| − | | |
| − | Além disto, altere o número de bits por cor comentando a
| |
| − | linha:
| |
| − | | |
| − | DefaultColorDepth 4
| |
| − | | |
| − | e tirando o "#" de uma das linhas (experimente):
| |
| − | | |
| − | DefaultColorDepth 8
| |
| − | DefaultColorDepth 16
| |
| − | DefaultColorDepth 24
| |
| − | | |
| − | Para cada tentativa, entre no modo gráfico teclando "startx",
| |
| − | e para voltar ao modo de texto, tecle simultaneamente
| |
| − | <ctl-alt-bs>. Obtenha infomações de sucesso/insucesso no
| |
| − | arquivo "/var/log/xwin/xserver.log".
| |
| − | | |
| − | As instruções são semelhantes, se a sua placa for uma NVIDIA
| |
| − | ou TRIDENT, usando-se
| |
| − | | |
| − | Device "nv"
| |
| − | ou
| |
| − | Device "trident"
| |
| − | | |
| − | 5. Se a sua placa gráfica não for uma das acima, ou as
| |
| − | tentativas acima não tiveram sucesso, você poderá apenas (na
| |
| − | presente versão) usar o modo de 16 cores (4 bits).
| |
| − | | |
| − | 6. Para alterar de resolução, tecle <ctl-alt-+> ou <ctl-alt-->
| |
| − | ("+" e "-" do teclado numérico).
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | Uma vez funcionando, você poderá tentar alterar o número de cores e
| |
| − | o tamanho do seu "desktop". Em caso de não conseguir, envie-nos os
| |
| − | dois arquivos do diretório "/var/log/xwin", conforme acima.
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | Version 4.9.0 Updated 10:12:08
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | INSTALL (ref) TROPIX: Installation Guide Pag. 45
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | ************************************************** *******
| |
| − | * *
| |
| − | * Capítulo 22 *
| |
| − | * *
| |
| − | * UTILIZAÇÃO BÁSICA DA INTERFACE GRÁFICA *
| |
| − | * *
| |
| − | ************************************************** *******
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | Uma vez com o sistema em funcionamento, teremos (com já foi citado
| |
| − | acima), duas janelas "xterm", um relógio e um selecionador de
| |
| − | "desktops".
| |
| − | | |
| − | A pequena janela "xterm" superior é a da "console", e não deve ser
| |
| − | usada normalmente, pois nela serão escritas as mensagens de erro do
| |
| − | sistema operacional.
| |
| − | | |
| − | Para movimentar uma janela, clique e arraste o botão da esquerda do
| |
| − | "mouse" na moldura da janela.
| |
| − | | |
| − | Para alterar o tamanho de uma janela, clique e arraste o botão da
| |
| − | esquerda do "mouse" em um dos 4 cantos da janela (nem todas as
| |
| − | janelas admitem isto).
| |
| − | | |
| − | Para promover uma janela (isto é, colocá-la na frente das demais),
| |
| − | clique o botão da esquerda na moldura da janela. Para rebaixá-la
| |
| − | (isto é, colocá-la atrás das demais), clique o botão da direita na
| |
| − | moldura da janela. Se você tiver um "mouse" de 3 botões, pode
| |
| − | também promover uma janela com o botão do meio.
| |
| − | | |
| − | O botão da esquerda, clicado fora de qualquer janela, apresenta um
| |
| − | "menu" de utilitários, além da opção para sair do modo gráfico
| |
| − | (retornando ao modo de texto). O botão da direita, clicado fora de
| |
| − | qualquer janela, apresenta uma lista das janelas ativas.
| |
| − | | |
| − | Tudo o que foi descrito até agora refere-se ao "desktop" 0.
| |
| − | Clicando em um outro selecionador de "desktop" (no canto inferior
| |
| − | direito), você terá um novo espaço independente para a criação de
| |
| − | janelas. Você dispõe (na presente configuração), de 6 "desktops".
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | Version 4.9.0 Updated 10:12:08
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | INSTALL (ref) TROPIX: Installation Guide Pag. 46
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | ************************************************** *******
| |
| − | * *
| |
| − | * Capítulo 23 *
| |
| − | * *
| |
| − | * OBTENÇÃO E INSTALAÇÃO DO CÓDIGO FONTE DO TROPIX *
| |
| − | * *
| |
| − | ************************************************** *******
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | O código fonte do TROPIX é distribuído através dos 3 arquivos
| |
| − | "kernel.tgz" (o núcleo do sistema), "lib.tgz" (as bibliotecas) e
| |
| − | "cmd.tgz" (os utilitários). Tratam-se de coleções TAR comprimidas
| |
| − | através do utilitário "gzip".
| |
| − | | |
| − | Uma vez obtida uma coleção "*.tgz" através de um navegador, devemos
| |
| − | descomprimi-la. Isto pode ser feito de diversos modos:
| |
| − | | |
| − | 1. Se você armazenou a coleção "*.tgz" em um sistema de arquivos
| |
| − | DOS/Windows FAT16/32, e está com o TROPIX instalado, pode
| |
| − | acessá-la diretamente através do TROPIX, montando a partição
| |
| − | com um comando da forma
| |
| − | | |
| − | mount /dev/hda1 /mnt
| |
| − | | |
| − | Em seguida, descomprima-a com:
| |
| − | | |
| − | cd /mnt/... (Diretório do TROPIX)
| |
| − | gunzip *.tgz (Nome da coleção)
| |
| − | gar -ixv <*.tar (Nome da coleção TAR obtida)
| |
| − | rm *.tar (Remove a coleção TAR)
| |
| − | | |
| − | 2. Se a sua partição DOS/Windows for NTFS (como ela é somente de
| |
| − | leitura), o procedimento acima deverá ser efetuado após a
| |
| − | cópia do arquivo "*.tgz" para uma partição TROPIX.
| |
| − | | |
| − | 3. Se você está usando um sistema UNIX, deverá usar os
| |
| − | utilitários "gunzip" e "tar". Verifique os detalhes no seu
| |
| − | sistema UNIX.
| |
| − | | |
| − | 4. Se você está apenas com Windows, pode descomprimir a coleção
| |
| − | com o utilitário "Winzip" e ler cada um dos programas através
| |
| − | dos utilitários "Notepad", "Wordpad" ou "Word", entre outros.
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | Version 4.9.0 Updated 10:12:08
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | INSTALL (ref) TROPIX: Installation Guide Pag. 47
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | ************************************************** *******
| |
| − | * *
| |
| − | * Capítulo 24 *
| |
| − | * *
| |
| − | * COMPILAÇÃO DO NÚCLEO, BIBLIOTECAS *
| |
| − | * E UTILITÁRIOS DO TROPIX *
| |
| − | * *
| |
| − | ************************************************** *******
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | Abaixo damos orientações para compilar os diversos componentes da
| |
| − | distribuição do código fonte do TROPIX:
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | 1. NÚCLEO DO SISTEMA: Uma vez com a árvore do núcleo instalada
| |
| − | no TROPIX, você poderá compilar os diversos módulos que a
| |
| − | integram: "boot/boot0", "boot/boot1", "boot/boot2" e
| |
| − | "kernel".
| |
| − | | |
| − | Em cada um dos diretórios há o "Makefile" para controlar a
| |
| − | respectiva compilação.
| |
| − | | |
| − | Repare que no diretório "kernel" há o arquivo "scbfile.v" que
| |
| − | contém parâmetros para configurar o seu núcleo em particular
| |
| − | (veja "edscb" (cmd)).
| |
| − | | |
| − | 2. BIBLIOTECAS: Na raiz da árvore há um "Makefile" para a
| |
| − | compilação de todas as 4 bibliotecas. Se for desejado, pode
| |
| − | ser compilada cada uma delas separadamente (indo para o
| |
| − | diretório correspondente).
| |
| − | | |
| − | 3. UTILITÁRIOS: Na raiz da árvore há um "Makefile" para a
| |
| − | compilação de todos os utilitários. Se for desejado, pode ser
| |
| − | compilado cada um deles separadamente (indo para o diretório
| |
| − | correspondente).
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | Version 4.9.0 Updated 10:12:08
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | INSTALL (ref) TROPIX: Installation Guide Pag. 48
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | ************************************************** *******
| |
| − | * *
| |
| − | * Capítulo 25 *
| |
| − | * *
| |
| − | * O USO DO EDITOR DE TEXTOS "VI" *
| |
| − | * *
| |
| − | ************************************************** *******
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | O utilitário "vi" é o editor de textos "padrão" dos sistemas
| |
| − | operacionais de filosofia UNIX. Neste capítulo será dada uma
| |
| − | pequena introdução ao seu uso, suficiente para realizar alterações
| |
| − | nos arquivos de configuração (que eventualmente sejam necessárias),
| |
| − | durante a instalação do TROPIX.
| |
| − | | |
| − | Maiores detalhes poderão ser vistos (posteriormente com o sistema
| |
| − | em funcionamento regular), atráves de "man vi" ou ainda "man -g
| |
| − | vi".
| |
| − | | |
| − | Para editar um arquivo (por exemplo, de nome "abc"), teclamos "vi
| |
| − | abc", e o "vi" inicia o seu funcionamento mostrando a primeira
| |
| − | página do arquivo "abc", com o cursor no primeiro caractere da
| |
| − | primeira linha.
| |
| − | | |
| − | Podemos então utilizar os seguintes comandos (repare que o cursor
| |
| − | indica onde o comando será executado):
| |
| − | | |
| − | <sp> Avança (o cursor de) um caractere na linha.
| |
| − | <bs> Retrocede um caractere na linha.
| |
| − | "-" Retrocede uma linha no arquivo.
| |
| − | <enter> Avança uma linha no arquivo.
| |
| − | <^D> Avança meia página no arquivo.
| |
| − | <^U> Retrocede meia página no arquivo.
| |
| − | "1g" Retrocede para o início do arquivo.
| |
| − | "g" Avança para o final do arquivo.
| |
| − | | |
| − | "i" Insere texto antes do cursor (até um <esc>).
| |
| − | "a" Insere texto após o cursor (até um <esc>).
| |
| − | "o" Cria novas linhas e insere texto (até um <esc>).
| |
| − | "x" Remove o caractere indicado pelo cursor.
| |
| − | "dd" Remove uma linha.
| |
| − | "yyp" Copia uma linha.
| |
| − | | |
| − | "/..." Procura a cadeia "..."
| |
| − | "n" Procura a ocorrência seguinte da cadeia.
| |
| − | "N" Procura a ocorrência anterior da cadeia.
| |
| − | | |
| − | "." Repete o último comando de edição.
| |
| − | "u" Desfaz o último comando de edição.
| |
| − | | |
| − | ":w" Atualiza o arquivo.
| |
| − | ":q" Sai do "vi" (somente se o arquivo está atualizado).
| |
| − | ":q!" Sai do "vi", sem atualizar o arquivo.
| |
| − | | |
| − | Repare que o arquivo sendo editado ("abc" no caso) só será
| |
| − | atualizado quando for dado o comando ":w". Se foi feita
| |
| − | acidentalmente alguma modificação indesejada, podemos sair do "vi"
| |
| − | com o comando ":q!", conservando o arquivo em sua forma original.
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | Version 4.9.0 Updated 10:12:08
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | INSTALL (ref) TROPIX: Installation Guide Pag. 49
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | ************************************************** *******
| |
| − | * *
| |
| − | * Capítulo 26 *
| |
| − | * *
| |
| − | * UMA LISTA DOS PRINCIPAIS COMANDOS DOS TROPIX *
| |
| − | * *
| |
| − | ************************************************** *******
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | Para a sua comodidade, damos abaixo uma lista alfabética dos
| |
| − | principais comandos do TROPIX, juntamente com uma breve descrição
| |
| − | de cada um. Para obter mais informações sobre um comando "x" (por
| |
| − | exemplo), use "man x".
| |
| − | | |
| − | a2ps - conversor de arquivos texto em PostScript
| |
| − | as - montador para INTEL-80386/486/PENTIUM
| |
| − | bison - gerador de analisadores sintáticos do GNU
| |
| − | c - escreve as linhas de um arquivo em várias colunas
| |
| − | cat - concatena e copia arquivos
| |
| − | cc - compilador para a linguagem "C"
| |
| − | cdplay - reproduz faixas de CDs
| |
| − | cdtowave - extrai faixas de CDs
| |
| − | chgrp - troca a identificação do grupo de arquivos
| |
| − | chmod - modifica a permissão de acesso de arquivos
| |
| − | chown - troca a identificação do dono (UID) de arquivos
| |
| − | clear - limpa a tela do terminal
| |
| − | clr - limpa a tela do terminal
| |
| − | cls - limpa a tela do terminal
| |
| − | cmp - compara pares de arquivos
| |
| − | cmpobj - compara pares de módulos objeto
| |
| − | cmptree - compara árvores
| |
| − | comm - seleciona ou rejeita linhas comuns a dois arquivos
| |
| − | ordenados
| |
| − | coremap - imprime um mapa de alocação da memória
| |
| − | cp - copia arquivos
| |
| − | cpfs - copia sistemas de arquivos
| |
| − | cptree - copia uma árvore
| |
| − | crypt - codifica/decodifica arquivos
| |
| − | data - mostra/atualiza a data/hora corrente do sistema
| |
| − | dc - calculador de mesa com aritmética inteira
| |
| − | dd - copia e converte arquivos
| |
| − | df - informa sobre o espaço disponível de sistemas de
| |
| − | arquivos
| |
| − | diff - comparador diferencial de arquivos
| |
| − | dmesg - imprime as mensagens iniciais de carga do núcleo
| |
| − | dosmp - monta/processa um sistema de arquivos no formato
| |
| − | MS-DOS/Windows
| |
| − | du - informa sobre o uso de disco
| |
| − | echo - ecoa os arqumentos
| |
| − | ed - editor de textos orientado por linhas
| |
| − | edboot - gerencia "boot0" e "boot2"
| |
| − | editscb - edita/imprime o bloco de controle da INTERNET
| |
| − | edobj - editor de módulos objeto
| |
| − | edscb - imprime/edita o bloco de controle do núcleo do
| |
| − | TROPIX
| |
| − | edusr - gerencia as contas/senhas
| |
| − | eject - ejeta o meio removível de um dispositivo
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | Version 4.9.0 Updated 10:12:08
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | INSTALL (ref) TROPIX: Installation Guide Pag. 50
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | ex - editor visual de textos
| |
| − | exportfs - lista/atualiza a tabela "exports" do NFS
| |
| − | fdc - calculador de mesa com aritmética flutuante
| |
| − | fdisk - imprime e/ou modifica a tabela de partições
| |
| − | de um disco
| |
| − | fdformat - formata disquetes
| |
| − | file - tenta identificar o conteúdo de um arquivo
| |
| − | finger - obtém informações sobre usuários remotos
| |
| − | fsck - verifica a consistência de sistemas de arquivos
| |
| − | fsdefrag - melhora a alocação dos blocos de um sistema de
| |
| − | arquivos
| |
| − | fsname - consulta/atualiza nomes/volumes de sistemas de
| |
| − | arquivos
| |
| − | ftp - programa de cópia remota de arquivos da INTERNET
| |
| − | gar - utilitário para a criação/atualização de coleções
| |
| − | de arquivos
| |
| − | grep - busca de padrões em arquivos
| |
| − | gunzip - comprime ou expande arquivos
| |
| − | gzip - comprime ou expande arquivos
| |
| − | help - imprime resumos de utilização de comandos
| |
| − | hpprint - impressor para HP DeskJet (PCL)
| |
| − | ifdef - realiza préprocessamentos parciais
| |
| − | includes - descobre arquivos incluídos
| |
| − | kill - envia sinais a processos
| |
| − | lasttime - lista os nomes de arquivos modificados recentemente
| |
| − | lc - lista o conteúdo de diretórios
| |
| − | ld - link-editor de módulos objeto
| |
| − | ldshlib - carrega/descarrega uma biblioteca compartilhada
| |
| − | linkoptim - substitui arquivos duplicados por elos físicos
| |
| − | ln - cria elos físicos ou simbólicos para arquivos
| |
| − | ls - lista características de arquivos e conteúdos de
| |
| − | diretórios
| |
| − | mail - recebe ou envia cartas do correio eletrônico
| |
| − | make - gerenciador de manutenção de programas
| |
| − | man - mostra um manual na tela do terminal/vídeo/janela
| |
| − | mkdev - cria/atualiza os dispositivos de "/dev"
| |
| − | mkdir - cria diretórios
| |
| − | mkfifo - cria FIFOs
| |
| − | mkfs - gera um sistema de arquivos
| |
| − | mklib - cria/atualiza bibliotecas de módulos objeto
| |
| − | mknod - cria um arquivo especial
| |
| − | mount - monta um sistema de arquivos
| |
| − | mv - move (troca o nome de) arquivos
| |
| − | mvtree - move (troca o nome) de uma árvore/diretório
| |
| − | nettime - obtém a data/hora corrente de um nó remoto
| |
| − | nice - executa um comando com prioridade modificada
| |
| − | nm - imprime a tabela de símbolos de módulos objeto
| |
| − | nohup - executa um comando imune ao sinal SIGHUP
| |
| − | pallwd - imprime todos os diretórios correntes
| |
| − | passwd - altera a senha do usuário
| |
| − | paste - une linhas de vários arquivos
| |
| − | ping - teste de acesso a um nó remoto
| |
| − | pop3 - acessa uma caixa postal remota através do
| |
| − | protocolo POP3
| |
| − | pr - imprime arquivos
| |
| − | prdisktb - Imprime a tabela de discos/partições
| |
| − | prsync - imprime o estado da sincronização dos processos
| |
| − | ps - imprime informações sobre processos
| |
| − | pwd - imprime o diretório corrente
| |
| − | reboot - Encerra o uso do TROPIX, e recarrega o computador
| |
| − | rlogin - entra em sessão em um nó remoto
| |
| − | rm - Remove arquivos
| |
| − | rmdir - remove diretórios
| |
| − | rmtree - remove árvores
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | Version 4.9.0 Updated 10:12:08
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | INSTALL (ref) TROPIX: Installation Guide Pag. 51
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | sbvol - controla o volume da placa de som SB-16
| |
| − | sbwave - Toca música PCM através da placa de som SB-16
| |
| − | semafree - libera o semáforo pelo qual o processo está
| |
| − | esperando
| |
| − | setmode - atribui as proteções corretas aos arquivos do
| |
| − | sistema
| |
| − | sh - interpretador de comandos
| |
| − | show - mostra um arquivo na tela do terminal
| |
| − | shutdown - reinicializa o computador após um certo tempo
| |
| − | size - imprime tamanhos e características de módulos
| |
| − | objeto
| |
| − | sleep - suspende a execução por um intervalo de tempo
| |
| − | sort - ordena e/ou intercala arquivos
| |
| − | sroff - formatador de textos
| |
| − | strip - remove as tabelas de símbolos de módulos-objeto
| |
| − | stty - consulta/altera parâmetros de terminais/vídeos
| |
| − | su - muda de conta temporariamente
| |
| − | subst - busca/substitui cadeias em vários arquivos
| |
| − | sync - Atualiza os blocos do cache nos discos
| |
| − | sysmap - desenha um mapa de uso de alguns recursos do
| |
| − | sistema (programa gráfico)
| |
| − | tac - descompila a descrição instalada de um terminal/
| |
| − | vídeo
| |
| − | tail - obtém a parte final de um arquivo
| |
| − | tcmpfrom - comparação/atualização remota de árvores
| |
| − | (caminhando árvores remotas)
| |
| − | tcmpto - comparação/atualização remota de árvores
| |
| − | (caminhando árvores locais)
| |
| − | tcpfrom - cópia remota de árvores (caminhando árvores
| |
| − | remotas)
| |
| − | tcpto - cópia remota de árvores (caminhando árvores
| |
| − | locais)
| |
| − | tee - copia a entrada padrão para diversos arquivos e a
| |
| − | saida padrão
| |
| − | telnet - comunica com um nó remoto utilizando o protocolo
| |
| − | TELNET
| |
| − | test - testa propriedades de arquivos
| |
| − | textmap - imprime uma tabela de programas reentrantes em uso
| |
| − | tic - compila e instala a descrição de um terminal/vídeo
| |
| − | touch - Modifica os tempos de arquivos
| |
| − | tpipe - escreve arquivos remotos na saída padrão
| |
| − | tr - traduz caracteres
| |
| − | tty - imprime o nome do terminal/vídeo
| |
| − | umount - desmonta sistemas de arquivos
| |
| − | uname - imprime a identificação do sistema
| |
| − | uniq - indica linhas repetidas de um arquivo
| |
| − | untext - libera os recursos de programas reentrantes
| |
| − | uptime - fornece o tempo decorrido desde o último "boot"
| |
| − | vi - editor visual de textos
| |
| − | walk - caminha em árvores do sistema de arquivos
| |
| − | wc - contador de páginas, linhas, palavras e caracteres
| |
| − | who - informa quem está no sistema
| |
| − | write - escreve mensagens para um outro usuário
| |
| − | xcoremap - desenha um mapa de alocação da memória
| |
| − | (programa gráfico)
| |
| − | xclock - relógio analógico (programa gráfico)
| |
| − | xcpu - desenha o gráfico de uso da CPU
| |
| − | xd - "dump" em hexadecimal e ISO
| |
| − | xdefrag - Melhora a alocação dos blocos de um sistema
| |
| − | de arquivos T1
| |
| − | xedit - editor de textos simples para o sistema X-Window
| |
| − | xfm - gerenciador gráfico de arquivos
| |
| − | xmandel - desenha as imagens fractais de Mandelbrot
| |
| − | xpop3 - acessa uma caixa postal remota através do
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | Version 4.9.0 Updated 10:12:08
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | INSTALL (ref) TROPIX: Installation Guide Pag. 52
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | protocolo POP3
| |
| − | xpaint - mostra uma imagem (gif, jpeg, bmp ou xpm) em uma
| |
| − | janela (programa gráfico)
| |
| − | xterm - Emulador de terminal ANSI para X-Window
| |
| − | ziptool - ferramenta para dispositivos Iomega ZIP
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | Version 4.9.0 Updated 10:12:08
| |
| | </pre> | | </pre> |
| | | | |
| − | I am downloading it, I don't know yet... Qemu? Bochs? Virtual PC? Some kind of 486+ emulator
| + | == What Runs? == |
| | | | |
| − | == What Runs? ==
| + | fortune seems to be the coolest program so far. coremap is pretty neat too. The C compiler seems to be based on GCC, they did write their own assembler, linker.. It's a very strange system. |
| | | | |
| − | [[lynx]] I think.
| + | ==External links== |
| | | | |
| | + | * [http://allegro.nce.ufrj.br/tropix/index.html O Sistema Operacional TROPIX] (in Spanish) |
| | | | |
| | {{Nav Unix}} | | {{Nav Unix}} |
| | + | |
| | {{stub}} | | {{stub}} |
| | + | |
| | + | [[Category: UNIX Clones]] |