Difference between revisions of "XENIX"
m (→Motorola: formatting) |
m (→History: Remove duplicate entries, add titles) |
||
| (53 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[Image:Xenix 386.jpg|thumb|right|200px|Xenix on a 386]] | [[Image:Xenix 386.jpg|thumb|right|200px|Xenix on a 386]] | ||
| − | ''' | + | '''XENIX''' (the all-upper-case version of the name is the formal one, e.g. in contemporary [[Microsoft]] material; '''Xenix''' is the form usually used now) was Microsoft's [[software port|port]] of AT&T [[UNIX]]; it was a [[portable]] [[operating system]] with ports to various platforms. It was based on [[UNIX Sixth Edition|v6]], [[Unix Seventh Edition|v7]], [[UNIX System III|SYSIII]], and later [[UNIX System V|SYSV]]. |
: ''XENIX was originally developed on a DEC Virtual Address Extension (VAX) running the Virtual Memory System (VMS) and a PDP-11 running UNIX V7, albeit now using Microsoft's own in-house minicomputers, and then converted into assembly language specific to the new 16-bit Motorola 68000 and Intel 8086 microprocessors. This put XENIX at the high end of the microcomputer market, which was still dominated by 8-bit machines, but well below the lowest end of the minicomputer market'' - "XENIX -- Microsoft Short-lived Love Affair with Unix " | : ''XENIX was originally developed on a DEC Virtual Address Extension (VAX) running the Virtual Memory System (VMS) and a PDP-11 running UNIX V7, albeit now using Microsoft's own in-house minicomputers, and then converted into assembly language specific to the new 16-bit Motorola 68000 and Intel 8086 microprocessors. This put XENIX at the high end of the microcomputer market, which was still dominated by 8-bit machines, but well below the lowest end of the minicomputer market'' - "XENIX -- Microsoft Short-lived Love Affair with Unix " | ||
| − | + | Unfortunately, "Xenix even incorporated the elements of BSD and became the most widely installed base of any Unix variant. Talking about the different modifications of Xenix, it was ported to Zilog Z8001, Intel 8086, Tandy Corporation’s 68000 based computers, and even a variant for Apple Lisa." | |
<blockquote>Modifications to Western Electric v7 included those necessary to transport the UNIX system from the larger PDP-11 mini computer to the 16-bit microprocessors. Currently scheduled machines included the DEC LSI-11/23, Zilogs Z8001 and Z8002, Intel's 8086 and 286, and Motorola's MC68000. - Robert Greenburg, uSloth. </blockquote> | <blockquote>Modifications to Western Electric v7 included those necessary to transport the UNIX system from the larger PDP-11 mini computer to the 16-bit microprocessors. Currently scheduled machines included the DEC LSI-11/23, Zilogs Z8001 and Z8002, Intel's 8086 and 286, and Motorola's MC68000. - Robert Greenburg, uSloth. </blockquote> | ||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
Because of the price of the OS, about $500USD for the OS, and $500USD for the developer tools, combined with cheap [[IBM PC|PC]] and [[IBM-compatible PC|compatibles]], Xenix was the most widespread UNIX until the rise of [[Linux]]. Xenix due to its inherent [[multi-user]] capabilities became widespread in sales environments with POS (Point of Sales) terminals, and for scheduling systems commonly found in hotels and restaurants. Occasionally you can still find this setup still running on aging [[hardware]]. | Because of the price of the OS, about $500USD for the OS, and $500USD for the developer tools, combined with cheap [[IBM PC|PC]] and [[IBM-compatible PC|compatibles]], Xenix was the most widespread UNIX until the rise of [[Linux]]. Xenix due to its inherent [[multi-user]] capabilities became widespread in sales environments with POS (Point of Sales) terminals, and for scheduling systems commonly found in hotels and restaurants. Occasionally you can still find this setup still running on aging [[hardware]]. | ||
| − | + | With the rise of the [[IBM PC]], it primarily became an [[Intel x86|x86]] based OS. Xenix eventually became [[SCO Unix]], then later SCO [[OpenServer]], where it still languishes today. | |
| − | = Platforms = | + | == Platforms == |
=== Intel === | === Intel === | ||
| − | As mentioned in the | + | <!-- As mentioned in the [http://www.tenox.tc/docs/microsoft_xenix_oem_directory.pdf OEM guide], URL dead -->Xenix supported the following platforms: |
| − | *[[IBM 386]] [386] The 32bit ones will run on Qemu/Virtual PC | + | *[[IBM 386]] [386 GT] The 32bit ones will run on Qemu/Virtual PC ( Sometimes called 386AT ) |
| − | *IBM [[PS/2]] [ | + | *IBM [[PS/2]] [386 MC] This version was specifically for [[MCA]] computers with a 386 or higher CPU. ( Sometimes called 386PS ) |
| − | *[[IBM AT|IBM 286]] [286] | + | *SCO Announced Xenix for the Model 50(286), 60(286) and 80[Ran 386 MC], but its unknown if there are archives of it. |
| − | *IBM PC [8088 or x86] This is 'easy' to find. | + | *[[IBM AT|IBM 286]] [286] - This version is now easy to find, but hard to run... It does not work on a 386. |
| + | *IBM PC [8088 or x86] - This is 'easy' to find. | ||
This is a list of version numbers for the various Architectures: | This is a list of version numbers for the various Architectures: | ||
| − | * | + | *SysV 386 – 3.2, 4.2 |
| − | * | + | *386 – 2.2.3b, 2.3.1, 2.3.2f, 2.3.4a, 2.3.4h ( SCO v2.2.3b, v2.3.2f, v2.3.4h) |
| − | *386 – 2.2. | + | <nowiki>*</nowiki>(You Plan to Install TCP/IP (XENIX.386 v2.3.4 only) |
| − | * | + | *286 – 2.1.3*, 2.2.1e, 2.2.3b, 2.3.2b, 2.3.2d ( SC0 v2.1.3, v2.2.1e, v2.2.3b, v2.3.2d) |
| + | <nowiki>*</nowiki>(Honey DanBer UUCP package v2.3.2 onward) | ||
| + | *8086 – 2.1.3* (SCO v2.1.3) | ||
| + | |||
| + | *These are currently the only two that boot on pcjs's website. | ||
=== Motorola === | === Motorola === | ||
| − | + | *IBM System 9000 [[Motorola MC68000]] [c 1984] | |
| − | + | *[[Apple Lisa]] [[Motorola MC68000]] [c 1984] The emulator [[idle]] can run this. | |
| − | *IBM System 9000 [ | + | *[[TRS-80 Model II Family|TRS-80 Model 16B and Tandy 6000]] [[Motorola MC68000]] [c 1984] |
| − | |||
| − | *[[Apple Lisa]] [ | ||
=== Others === | === Others === | ||
| − | *[[ | + | * [[LSI-11]] - No versions of this exists online. There is a note (link below) that Xenix with Programmers console ran on a LSI-11/34. |
| − | *[[ | + | * [[PDP-11]] - link below |
| − | *[[Zilog Z8001]] [ | + | * [[VAX-11/780]] |
| + | * [[Zilog Z8001]] [c 1979] - I have only found sales literature that mentions this.* | ||
| − | *Note: This sounds like vaporware since neither the Onyx 1 nor the Commodore 900 ran Xenix | + | <nowiki>*</nowiki> Note: This sounds like vaporware since neither the Onyx 1 nor the Commodore 900 ran Xenix |
| − | |||
| − | |||
== Software == | == Software == | ||
| Line 61: | Line 63: | ||
*[[C programming language|C]] | *[[C programming language|C]] | ||
| − | *[[Basic]] [[ | + | *[[Basic]] - Basic [[Compiler]], Basic [[Interpreter]] |
*[[Cobol]] | *[[Cobol]] | ||
*[[FORTRAN|Fortran]] | *[[FORTRAN|Fortran]] | ||
| Line 67: | Line 69: | ||
*[[Assembler]] | *[[Assembler]] | ||
| − | "the base operating system does not include development tools such as a C compiler, but it does include the linker and, importantly, an assembler (which is needed to rebuild the configuration files). The assembler is, however, disguised to make it less obvious what it is by giving it a different name and that is what I have been trying to remember ever since I saw this post. Finally, this morning, it came to me. You | + | "the base operating system does not include development tools such as a C compiler, but it does include the linker and, importantly, an assembler (which is needed to rebuild the configuration files). The assembler is, however, disguised to make it less obvious what it is by giving it a different name and that is what I have been trying to remember ever since I saw this post. Finally, this morning, it came to me. You ''should'' find that you have something called 'storel' (read it as 's-to-rel' as in 'something that transforms .s files into relocatable (ie .o) files' and the name becomes a little less obscure) on the system - I ''think'' that it lives in /bin. but it ''might'' be somewhere else such as /etc." (Source: [http://www.vcfed.org/forum/archive/index.php/t-49002.html here]) |
=== Applications === | === Applications === | ||
| Line 74: | Line 76: | ||
*Microsoft Multiplan (available on the Apple Lisa) | *Microsoft Multiplan (available on the Apple Lisa) | ||
*Microsoft Word v5.0 | *Microsoft Word v5.0 | ||
| − | *vi ( | + | *vi (Not really an application, but more of a torture device. May not be present on the x86 version, so ed will have to be used.) |
=== Databases === | === Databases === | ||
| Line 91: | Line 93: | ||
*SCO Manager | *SCO Manager | ||
*SCO Multiview | *SCO Multiview | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
<nowiki>*</nowiki> - ''SCO in this case refers to the original Santa Cruz Operation, and not the later SCO Group who bought the name and started the SCO/Linux lawsuits.'' | <nowiki>*</nowiki> - ''SCO in this case refers to the original Santa Cruz Operation, and not the later SCO Group who bought the name and started the SCO/Linux lawsuits.'' | ||
| − | + | == Getting this to run == | |
| − | + | The 8086 version of XENIX runs fine in an emulator. | |
| − | + | Note: The 286 version of XENIX will only run on a 286 processor or a 286 processor emulator that handles the upper byte of the Global Descriptor byte 7, documented as reserved for use on a iAPX 386, by essentially ignoring it, and letting XENIX use it. A poor programming choice at best. (Now, that we know the publication dates of Intel's documentation (1982), we know they ignored the Intel documentation about the use of the upper byte of the descriptor words.. Details [http://www.os2museum.com/wp/ibm-xenix-two-steps-forward/comment-page-1/#comment-363304 here]) | |
| − | + | [[User:Neozeed]] wrote about [[Installing Xenix 2.x on Qemu|how to get it to run under QEMU 0.14]]. | |
| − | + | A repository has a file, that when run, unpacks Qemu 0.14, and has a disk, that boots straight into Xenix 2.3.4/386; the uname -a does confirm both the platform and the version. | |
| − | + | Also, there is: [ftp://major.butt.care/mirrors/Unix/Xenix/Xenix-2.3.4.exe Xenix 2.3.4/386][https://archive.org/details/xenix-234-installer Backup] | |
| − | + | Another directory has the same file from a SCO Mega pack called: | |
| + | SCO Xenix 2.3.4 - preinstalled, run in Windows. | ||
| − | + | ==External links== | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | == | ||
| − | + | ===Announcements=== | |
| − | |||
| − | + | * [https://www-01.ibm.com/common/ssi/cgi-bin/ssialias?htmlfid=897/ENUS284-159&infotype=AN&subtype=CA&appname=skmwww XENIX Operating System for the IBM System 9000] | |
| + | * [https://www.cbronline.com/news/santa_cruz_ships_xenix_v_for_ps2_developed_in_london/ Santa Cruz ships XENIX V for PS2 - Developed in London] | ||
| − | + | ===History=== | |
| − | https://archive.org/details/ | + | * [http://seefigure1.com/images/xenix/xenix-timeline.jpg The XENIX timeline] - The most comprehensive time vs port list |
| + | * [http://www.softpanorama.org/People/Torvalds/Finland_period/xenix_microsoft_shortlived_love_affair_with_unix.shtml Microsoft Short-lived Love Affair with Unix] - A detailed history | ||
| + | * [https://fossbytes.com/xenix-history-microsoft-unix-operating-system/ History Of Xenix - Microsoft's Forgotten Unix-based Operating System] | ||
| + | * [http://seefigure1.com/2014/04/15/xenixtime.html A bit of XENIX history] - XENIX history | ||
| + | * [http://www.edm2.com/index.php/XENIX XENIX] - Brief wiki page on XENIX; includes a bibliography | ||
| + | <!-- * [http://www.tenox.net/docs/ Cache of old UNIX docs] - Includes lots of Xenix documentation in PDF format.--> | ||
| + | * [https://archive.org/details/byte-magazine-1981-06/page/n249 The UNIX Operating System and the XENIX Standard Operating Environment] - Byte Magazine Article on Xenix, BYTE June 1980, pg 249 | ||
| + | <!-- *[https://virtuallyfun.com/wordpress/2009/02/10/apple-lisa-xenix/Apple Lisa (c1983) Xenix 3.0] --> | ||
| + | * [https://www.krsaborio.net/unix/xenix.htm Some Xenix information - Intel Ad Aug 1984] | ||
| + | * [http://www.catb.org/~esr/faqs/clone-unix-guide.txt A buyer's guide to UNIX versions for PC-clone hardware] - an extensive comparison of Xenix in the open market unix wars] | ||
| + | * [https://web.archive.org/web/20141202093953/http://wiretap.area.com/Gopher/Library/Techdoc/Bench/dhryst.txt Dhrystone 1.1 Benchmark Summary] - computer bench marks featuring Xenix systems, which correspond to actual Xenix releases | ||
| − | + | ===Emulators=== | |
| − | http://www. | + | * [http://www.hampa.ch/pce/download.html PCE - PC Emulator] - [x86] Architecture |
| + | * [https://download.qemu.org/qemu-0.14.0.tar.gz QEMU v0.14runs SCO Xenix for i386 and i286] | ||
| + | * [https://www.pcjs.org/software/pcx86/sys/unix/sco/xenix/386/2.3.4h/ SCO Xenix 386 v2.3.4h] - 80386 version of Xenix | ||
| + | <!-- * [https://www.pcjs.org/software/pcx86/sys/unix/sco/xenix/286/2.3.2b/ SCO Xenix 286 v2.3.2b] - Does not boot. <!-- --> | ||
| + | * [https://www.pcjs.org/disks/pcx86/unix/sco/xenix/286/2.1.3/ SCO Xenix 286 v2.1.3] - Runs Xenix 286 2.1.3 in a browser window. | ||
| + | * [https://www.pcjs.org/disks/pcx86/unix/sco/xenix/086/2.1.3/ SCO Xenix System V Release 2.1.3 for i8086] - Runs Xenix 8086 2.1.3 in a browser window. | ||
| + | <!-- * [https://www.pcjs.org/disks/pcx86/unix/sco/xenix/386/ ] <!-- --> | ||
| + | * [https://github.com/retrohun/blog/tree/master/dt/xenix286ondemand Tenon Xenix 286 2.3.2d on Linux w/ Qemu. ] | ||
| + | * [http://48k.ca/trs80gp.html trs80gp - A multi-system TRS-80 emulator] - For instructions check out [[Installing XENIX on a Tandy 6000]] | ||
| − | + | ===Repositories=== | |
| − | https:// | + | * [ftp://major.butt.care/mirrors/Unix/Xenix/ 386, 286, x86, 386MC, Tandy, Lisa, Text, and Docs] Comprehensive Mirror |
| + | * [https://github.com/retrohun/blog/tree/master/dt/xenix286ondemand Xenix286 on demand] | ||
| + | <!-- * [https://archive.org/details/msxenix/history/files/pics/progman5.jpg.~1~ xx] --> | ||
| + | * [https://winworldpc.com/product/xenix/286 Xenix 286] | ||
| + | * [http://www.vcfed.org/forum/showthread.php?30490-Xenix-Development-Systems Xenix Development Systems] | ||
| + | <!-- * [https://fsck.technology/software/SCO/SCO%20Unix%20Installers/ xx] --> | ||
| + | * [https://macintoshgarden.org/apps/xenix-30-apple-lisa Xenix 3.0 for Apple Lisa] | ||
| + | * [http://tenox.pdp-11.ru/xenix/ Tenox Operating Systems Archive] - Includes Xenix documentation in PDF format] | ||
| + | * [https://archive.org/details/Xenix386Ports SCO Xenix and a set of ported software] | ||
| + | * [https://github.com/pski/model2archive The Model 2 Archive - a huge git repository including XENIX for the TRS-80 Model 16B and Tandy 6000] | ||
| − | + | * [http://www.hampa.ch/pub/software/XENIX/ SCO Xenix 2.1.3 for 8086 and 80286] | |
| + | * [http://www.hampa.ch/pce/download.html The PCE Emulator that runs Xenix 86 (open source)] | ||
| − | + | ====Support Level Supplements for Xenix==== | |
| − | http:// | + | * [http://ftp.sunet.se/mirror/archive/ftp.sunet.se/pub/vendor/sco/SLS/ SCO Xenix Update PTF/ltr/SLS files.] |
| + | * [http://ps-2.kev009.com/ohland/XENIX/XENIX_for_MCA.html SCO Xenix for MCA] | ||
| + | * [https://wdb1.sco.com/kb/showta?taid=102045&qid=1163837384&sid=1299958135&pgnum=1 Actual SCO/Xinous Updates] | ||
| − | + | ===Archaeology=== | |
| − | http://www. | + | * [https://museo.freaknet.org/gallery/software/xenix/versions.txt A list of version numbers pulled from disks] |
| + | * [https://www.krsaborio.net/unix/research/1981/06.htm The UNIX Operating System and the XENIX Standard Operating Environment] - the story by the XENIX Product Manager at Microsoft | ||
| + | * [http://seefigure1.com/2014/04/15/xenixtime.html A bit of XENIX History] (from a MS Developer '86 ~ '89) | ||
| + | * [https://www.abortretry.fail/p/the-history-of-xenix The History of XENIX: A Failed Future and a Long Life] The history of Xenix with the least amount of errors - mostly at the beginning. | ||
| + | * [https://comp.os.vms.narkive.com/Qoy6kBJU/xenix-vax-pdp XENIX VAX/PDP] | ||
| + | * [http://www.os2museum.com/wp/category/xenix/ Category Archives: Xenix] - precursor to the next group | ||
| + | ** [https://www.os2museum.com/wp/the-xenix-386-2-2-3-mystery/ The XENIX 386 2.2.3 Mystery] | ||
| + | ** [http://www.os2museum.com/wp/the-xenix-2-2-3-mystery-continued/ The XENIX 2.2.3 Mystery, Continued] | ||
| + | ** [http://www.os2museum.com/wp/oldest-surviving-386-pc-os/ Oldest Surviving 386 PC OS?] | ||
| + | ** [https://www.os2museum.com/wp/missing-xenix-disks/ Xenix 2.1.0 Oldest PC Xenix ] | ||
| + | * [https://soylentnews.org/search.pl?query=Xenix Searching For: Xenix] - Xenix at SoylentNews | ||
| + | ** [https://soylentnews.org/article.pl?sid=17/03/03/1620222 Restoring Xenix 386 2.2.3c, Part 1] | ||
| + | ** [https://soylentnews.org/article.pl?sid=17/03/07/1632251 Xenix 2.2.3c Restoration: No Tools, No Problem (Part 2)] | ||
| + | ** [https://soylentnews.org/article.pl?sid=17/03/11/2014253 Xenix 2.2.3c Restoration: Damage Mapping (Part 3)] | ||
| + | ** [https://soylentnews.org/article.pl?sid=17/03/13/086250 Xenix 2.2.3c Restoration: Xrossing The X (Part 4)] - Includes some extraordinary efforts to get some utilities to run | ||
| + | * [https://www.bell-labs.com/usr/dmr/www/xenix.gif XENIX ad from Dennis Ritchie's home page at Bell Labs] | ||
| + | * [https://www.linux-magazine.com/index.php/Online/Features/Remembering-XENIX Remembering XENIX] | ||
| + | * [https://www.snellman.net/blog/archive/2015-09-01-the-most-obsolete-infrastructure-money-could-buy/ The most obsolete infrastructure money could buy - my worst job ever] - XENIX 286 problem from hell | ||
{{semi-stub}} | {{semi-stub}} | ||
Latest revision as of 23:46, 7 August 2024
XENIX (the all-upper-case version of the name is the formal one, e.g. in contemporary Microsoft material; Xenix is the form usually used now) was Microsoft's port of AT&T UNIX; it was a portable operating system with ports to various platforms. It was based on v6, v7, SYSIII, and later SYSV.
- XENIX was originally developed on a DEC Virtual Address Extension (VAX) running the Virtual Memory System (VMS) and a PDP-11 running UNIX V7, albeit now using Microsoft's own in-house minicomputers, and then converted into assembly language specific to the new 16-bit Motorola 68000 and Intel 8086 microprocessors. This put XENIX at the high end of the microcomputer market, which was still dominated by 8-bit machines, but well below the lowest end of the minicomputer market - "XENIX -- Microsoft Short-lived Love Affair with Unix "
Unfortunately, "Xenix even incorporated the elements of BSD and became the most widely installed base of any Unix variant. Talking about the different modifications of Xenix, it was ported to Zilog Z8001, Intel 8086, Tandy Corporation’s 68000 based computers, and even a variant for Apple Lisa."
Modifications to Western Electric v7 included those necessary to transport the UNIX system from the larger PDP-11 mini computer to the 16-bit microprocessors. Currently scheduled machines included the DEC LSI-11/23, Zilogs Z8001 and Z8002, Intel's 8086 and 286, and Motorola's MC68000. - Robert Greenburg, uSloth.
Because of the price of the OS, about $500USD for the OS, and $500USD for the developer tools, combined with cheap PC and compatibles, Xenix was the most widespread UNIX until the rise of Linux. Xenix due to its inherent multi-user capabilities became widespread in sales environments with POS (Point of Sales) terminals, and for scheduling systems commonly found in hotels and restaurants. Occasionally you can still find this setup still running on aging hardware.
With the rise of the IBM PC, it primarily became an x86 based OS. Xenix eventually became SCO Unix, then later SCO OpenServer, where it still languishes today.
Contents
Platforms
Intel
Xenix supported the following platforms:
- IBM 386 [386 GT] The 32bit ones will run on Qemu/Virtual PC ( Sometimes called 386AT )
- IBM PS/2 [386 MC] This version was specifically for MCA computers with a 386 or higher CPU. ( Sometimes called 386PS )
- SCO Announced Xenix for the Model 50(286), 60(286) and 80[Ran 386 MC], but its unknown if there are archives of it.
- IBM 286 [286] - This version is now easy to find, but hard to run... It does not work on a 386.
- IBM PC [8088 or x86] - This is 'easy' to find.
This is a list of version numbers for the various Architectures:
- SysV 386 – 3.2, 4.2
- 386 – 2.2.3b, 2.3.1, 2.3.2f, 2.3.4a, 2.3.4h ( SCO v2.2.3b, v2.3.2f, v2.3.4h)
*(You Plan to Install TCP/IP (XENIX.386 v2.3.4 only)
- 286 – 2.1.3*, 2.2.1e, 2.2.3b, 2.3.2b, 2.3.2d ( SC0 v2.1.3, v2.2.1e, v2.2.3b, v2.3.2d)
*(Honey DanBer UUCP package v2.3.2 onward)
- 8086 – 2.1.3* (SCO v2.1.3)
- These are currently the only two that boot on pcjs's website.
Motorola
- IBM System 9000 Motorola MC68000 [c 1984]
- Apple Lisa Motorola MC68000 [c 1984] The emulator idle can run this.
- TRS-80 Model 16B and Tandy 6000 Motorola MC68000 [c 1984]
Others
- LSI-11 - No versions of this exists online. There is a note (link below) that Xenix with Programmers console ran on a LSI-11/34.
- PDP-11 - link below
- VAX-11/780
- Zilog Z8001 [c 1979] - I have only found sales literature that mentions this.*
* Note: This sounds like vaporware since neither the Onyx 1 nor the Commodore 900 ran Xenix
Software
A quick list of a few software programs that were available on Xenix. I know the x86 platform was the most supported, I now know that some of these made it to the less popular 68000 platform.
Microsoft
Microsoft made several of their programs in the 1980's available on the Xenix platform. Microsoft Multiplan, and the BASIC Compiler.
Languages
"the base operating system does not include development tools such as a C compiler, but it does include the linker and, importantly, an assembler (which is needed to rebuild the configuration files). The assembler is, however, disguised to make it less obvious what it is by giving it a different name and that is what I have been trying to remember ever since I saw this post. Finally, this morning, it came to me. You should find that you have something called 'storel' (read it as 's-to-rel' as in 'something that transforms .s files into relocatable (ie .o) files' and the name becomes a little less obscure) on the system - I think that it lives in /bin. but it might be somewhere else such as /etc." (Source: here)
Applications
- Autodesk AutoCAD 10i
- Microsoft Multiplan (available on the Apple Lisa)
- Microsoft Word v5.0
- vi (Not really an application, but more of a torture device. May not be present on the x86 version, so ed will have to be used.)
Databases
- Foxpro
Games
SCO*
- SCO Professional
- SCO Lyrix (available on the Apple Lisa)
- SCO Integra
- SCO Manager
- SCO Multiview
* - SCO in this case refers to the original Santa Cruz Operation, and not the later SCO Group who bought the name and started the SCO/Linux lawsuits.
Getting this to run
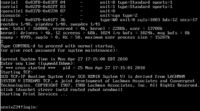
The 8086 version of XENIX runs fine in an emulator.
Note: The 286 version of XENIX will only run on a 286 processor or a 286 processor emulator that handles the upper byte of the Global Descriptor byte 7, documented as reserved for use on a iAPX 386, by essentially ignoring it, and letting XENIX use it. A poor programming choice at best. (Now, that we know the publication dates of Intel's documentation (1982), we know they ignored the Intel documentation about the use of the upper byte of the descriptor words.. Details here)
User:Neozeed wrote about how to get it to run under QEMU 0.14.
A repository has a file, that when run, unpacks Qemu 0.14, and has a disk, that boots straight into Xenix 2.3.4/386; the uname -a does confirm both the platform and the version.
Also, there is: Xenix 2.3.4/386Backup
Another directory has the same file from a SCO Mega pack called: SCO Xenix 2.3.4 - preinstalled, run in Windows.
External links
Announcements
- XENIX Operating System for the IBM System 9000
- Santa Cruz ships XENIX V for PS2 - Developed in London
History
- The XENIX timeline - The most comprehensive time vs port list
- Microsoft Short-lived Love Affair with Unix - A detailed history
- History Of Xenix - Microsoft's Forgotten Unix-based Operating System
- A bit of XENIX history - XENIX history
- XENIX - Brief wiki page on XENIX; includes a bibliography
- The UNIX Operating System and the XENIX Standard Operating Environment - Byte Magazine Article on Xenix, BYTE June 1980, pg 249
- Some Xenix information - Intel Ad Aug 1984
- A buyer's guide to UNIX versions for PC-clone hardware - an extensive comparison of Xenix in the open market unix wars]
- Dhrystone 1.1 Benchmark Summary - computer bench marks featuring Xenix systems, which correspond to actual Xenix releases
Emulators
- PCE - PC Emulator - [x86] Architecture
- QEMU v0.14runs SCO Xenix for i386 and i286
- SCO Xenix 386 v2.3.4h - 80386 version of Xenix
- SCO Xenix 286 v2.1.3 - Runs Xenix 286 2.1.3 in a browser window.
- SCO Xenix System V Release 2.1.3 for i8086 - Runs Xenix 8086 2.1.3 in a browser window.
- Tenon Xenix 286 2.3.2d on Linux w/ Qemu.
- trs80gp - A multi-system TRS-80 emulator - For instructions check out Installing XENIX on a Tandy 6000
Repositories
- 386, 286, x86, 386MC, Tandy, Lisa, Text, and Docs Comprehensive Mirror
- Xenix286 on demand
- Xenix 286
- Xenix Development Systems
- Xenix 3.0 for Apple Lisa
- Tenox Operating Systems Archive - Includes Xenix documentation in PDF format]
- SCO Xenix and a set of ported software
- The Model 2 Archive - a huge git repository including XENIX for the TRS-80 Model 16B and Tandy 6000
Support Level Supplements for Xenix
Archaeology
- A list of version numbers pulled from disks
- The UNIX Operating System and the XENIX Standard Operating Environment - the story by the XENIX Product Manager at Microsoft
- A bit of XENIX History (from a MS Developer '86 ~ '89)
- The History of XENIX: A Failed Future and a Long Life The history of Xenix with the least amount of errors - mostly at the beginning.
- XENIX VAX/PDP
- Category Archives: Xenix - precursor to the next group
- Searching For: Xenix - Xenix at SoylentNews
- Restoring Xenix 386 2.2.3c, Part 1
- Xenix 2.2.3c Restoration: No Tools, No Problem (Part 2)
- Xenix 2.2.3c Restoration: Damage Mapping (Part 3)
- Xenix 2.2.3c Restoration: Xrossing The X (Part 4) - Includes some extraordinary efforts to get some utilities to run
- XENIX ad from Dennis Ritchie's home page at Bell Labs
- Remembering XENIX
- The most obsolete infrastructure money could buy - my worst job ever - XENIX 286 problem from hell
| v • d • e UNIX Versions, Vendors and Related |
|---|
| Research Unix PDP-7 UNIX • V1 • V2 • V3 • V4 • V5 • V6 • V7 • V8 • V9 • V10 • LSX • MINI-UNIX • Unix/32V
AT&T - CB-UNIX • PWB/UNIX • USG UNIX • System III • System IV • System V BSD - 2.9 BSD • 2.10 BSD • 2.11 BSD • 3BSD • 4BSD • 4.1 BSD • 4.2 BSD • 4.3 BSD • 4.4 BSD BSD Descendants 386BSD • NetBSD • FreeBSD • OpenBSD • NeXTSTEP • Darwin |
| Other - xv6 • AMIX • SunOS • Solaris • ULTRIX • A/UX • XENIX • AIX • Dell UNIX |