Difference between revisions of "LSI-11"
(First ship date) |
|||
| (22 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
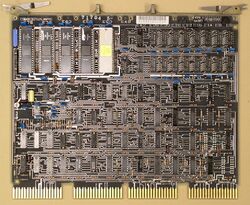
| − | + | [[Image:LSI-11.jpg|250px|thumb|right|M7264 KD11-F board (etch revision F), with KEV11-A]] | |
| − | + | The '''LSI-11''', first shipped in the Fall of 1975, was DEC's first cost-reduced [[PDP-11]] [[Central Processing Unit|CPU]], introducing the [[QBUS]], and using the [[LSI-11 chip set]]. It was the first of the [[LSI-11 CPUs]]; it had the same QBUS limitations, and use of [[QBUS CPU ODT|ODT]] for control, as the others. | |
| − | + | The LSI-11 is a [[DEC card form factor|quad]] board (M7264) with additional functionality on-board. They were popular in [[Original Equipment Manufacturer|OEM]] usage. | |
| − | + | The usual CPU options were available for the LSI-11: the [[KEV11-A floating point|KEV11-A]], for the [[PDP-11 Extended Instruction Set|EIS]]/[[FIS floating point|FIS]] instructions; the [[KEV11-B Extended Instruction Set|KEV11-B]] provides EIS without FIS; the [[KEV11-C Commercial Instruction Set|KEV11-C]] provides a subset of the PDP-11 [[PDP-11 Commercial Instruction Set|CIS]] (it also apparently includes the EIS, but not the FIS). It also supported the optional [[KUV11 Writeable Control Store]]. | |
| − | The | + | The [[integrated circuit|chip]] order (from the left, with the contact finger edge down, and the component side facing the viewer) is [[KEV11]], μROM 1, μROM 0, Control, Data Path. |
| − | + | ==Variant models== | |
| − | The | + | Many different LSI-11 models exist, including the '''KD11-F''' and '''KD11-H''' base versions, and numerous other variants. The KD11-F version includes 4KW of [[Metal Oxide Semiconductor|MOS]] [[Random Access Memory|RAM]] on-board; the KD11-H version has the RAM deleted. |
| − | + | Others included various KEV11 chips pre-installed: | |
| − | + | * the KD11-L is a KD11-F with a KEV11-A | |
| + | * the KD11-N is a KD11-H with a KEV11-A | ||
| + | * the KD11-P is a KD11-F with a KEV11-C | ||
| + | * the KD11-Q is a KD11-H with a KEV11-C | ||
| − | + | Some models include additional cards: | |
| − | + | * the KD11-J is a KD11-H sold with an [[MMV11-A QBUS core memory]] card | |
| + | * the KD11-R is a KD11-H sold with an [[MSV11-C QBUS MOS memory]] card | ||
| − | + | ==See also== | |
| − | + | * [[LSI-11/2]] | |
| − | == | + | ==External links== |
| − | + | * [http://www.bitsavers.org/pdf/dec/pdp11/1103/ -11/03] - documentation at [[Bitsavers]] | |
| − | + | ** [http://www.bitsavers.org/pdf/dec/pdp11/1103/EK-LSI11-TM-002.pdf LSI-11, PDP-11/03 user's manual] (EK-LSI11-TM-002) | |
| − | + | ** [http://www.bitsavers.org/pdf/dec/pdp11/1103/1103_Schematics.pdf PDP-11/03 engineering drawings] - includes all KD11 versions | |
| − | + | ** [http://www.bitsavers.org/pdf/dec/pdp11/1103/Titelbaum_LSI-11_1975.pdf The LSI-11 - A System Microcomputer] | |
| − | + | * [http://web.frainresearch.org:8080/projects/pdp-11/lsi-11.php LSI-11 Processors] | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | * | ||
| − | * | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | The | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | * [ | ||
{{PDP-11}} | {{PDP-11}} | ||
| − | [[Category:QBUS | + | [[Category: PDP-11 QBUS Processors]] |
Latest revision as of 22:06, 20 December 2023
The LSI-11, first shipped in the Fall of 1975, was DEC's first cost-reduced PDP-11 CPU, introducing the QBUS, and using the LSI-11 chip set. It was the first of the LSI-11 CPUs; it had the same QBUS limitations, and use of ODT for control, as the others.
The LSI-11 is a quad board (M7264) with additional functionality on-board. They were popular in OEM usage.
The usual CPU options were available for the LSI-11: the KEV11-A, for the EIS/FIS instructions; the KEV11-B provides EIS without FIS; the KEV11-C provides a subset of the PDP-11 CIS (it also apparently includes the EIS, but not the FIS). It also supported the optional KUV11 Writeable Control Store.
The chip order (from the left, with the contact finger edge down, and the component side facing the viewer) is KEV11, μROM 1, μROM 0, Control, Data Path.
Variant models
Many different LSI-11 models exist, including the KD11-F and KD11-H base versions, and numerous other variants. The KD11-F version includes 4KW of MOS RAM on-board; the KD11-H version has the RAM deleted.
Others included various KEV11 chips pre-installed:
- the KD11-L is a KD11-F with a KEV11-A
- the KD11-N is a KD11-H with a KEV11-A
- the KD11-P is a KD11-F with a KEV11-C
- the KD11-Q is a KD11-H with a KEV11-C
Some models include additional cards:
- the KD11-J is a KD11-H sold with an MMV11-A QBUS core memory card
- the KD11-R is a KD11-H sold with an MSV11-C QBUS MOS memory card
See also
External links
- -11/03 - documentation at Bitsavers
- LSI-11, PDP-11/03 user's manual (EK-LSI11-TM-002)
- PDP-11/03 engineering drawings - includes all KD11 versions
- The LSI-11 - A System Microcomputer
- LSI-11 Processors
| v • d • e PDP-11 Computers and Peripherals |
|---|
| UNIBUS PDP-11s - PDP-11/20 • PDP-11/15 • PDP-11/35 • PDP-11/40 • PDP-11/45 • PDP-11/50 • PDP-11/55 • PDP-11/70 PDP-11/05 • PDP-11/10 • PDP-11/04 • PDP-11/34 • PDP-11/60 • PDP-11/44 • PDP-11/24 • PDP-11/84 • PDP-11/94 QBUS PDP-11s - PDP-11/03 • PDP-11/23 • PDP-11/23+ • MicroPDP-11/73 • MicroPDP-11/53 • MicroPDP-11/83 • MicroPDP-11/93 QBUS CPUs: LSI-11 • LSI-11/2 • KDF11-A • KDF11-B • KDJ11-A • KDJ11-B • KDJ11-D • KDJ11-E Buses: UNIBUS • UNIBUS map • SPC • MUD • EUB • QBUS • CD interconnect • PMI Also: PDP-11 architecture • PDP-11 Extended Instruction Set • FP11 floating point • PDP-11 Memory Management |
| [Expand] |
|---|